瑞吉外卖项目 基于spring Boot+mybatis-plus开发 超详细笔记,有源码链接
| 阿里云国内75折 回扣 微信号:monov8 |
| 阿里云国际,腾讯云国际,低至75折。AWS 93折 免费开户实名账号 代冲值 优惠多多 微信号:monov8 飞机:@monov6 |
本项目是基于自学b站中 黑马程序员 的瑞吉外卖项目:视频链接
黑马程序员Java项目实战《瑞吉外卖》轻松掌握springboot + mybatis plus开发核心技术的真java实战项目_哔哩哔哩_bilibili![]() https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV13a411q753?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click这篇博客是记录自己学习该项目的markdown笔记并且自己把视频中一些没实现的功能给实现了本人技术可能不到位笔记仅供参考学习使用
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV13a411q753?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click这篇博客是记录自己学习该项目的markdown笔记并且自己把视频中一些没实现的功能给实现了本人技术可能不到位笔记仅供参考学习使用
本人自己把视频中老师没讲的一些功能给实现了比如后台按条件查询客户订单用户个人查询自己的订单菜品套餐的启售停售购物车中菜品或者是套餐数量减少后台套餐的修改。代码不一定规范但是功能是没问题的
项目中的资料下载链接从黑马公众号获取到的最初状态的源码后面自己补充了一些课程没讲的功能功能的实现代码在我博客的笔记中有
链接https://pan.baidu.com/s/1cdHI5cDjyHKZ4_0GmIevnQ
提取码668a
目录
菜品信息分页查询(功能完善里面的代码要熟悉,有集合泛型的转换对象copy)
一、项目背景介绍



技术选型
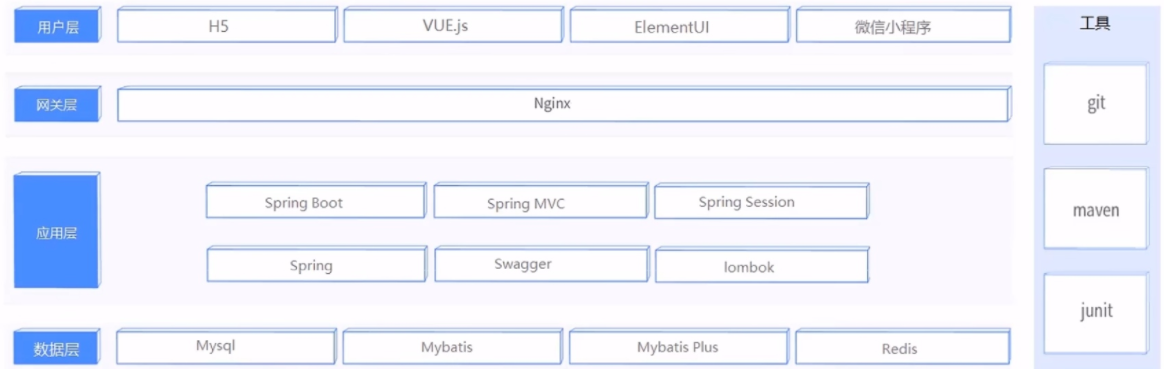


二、软件开发整体介绍
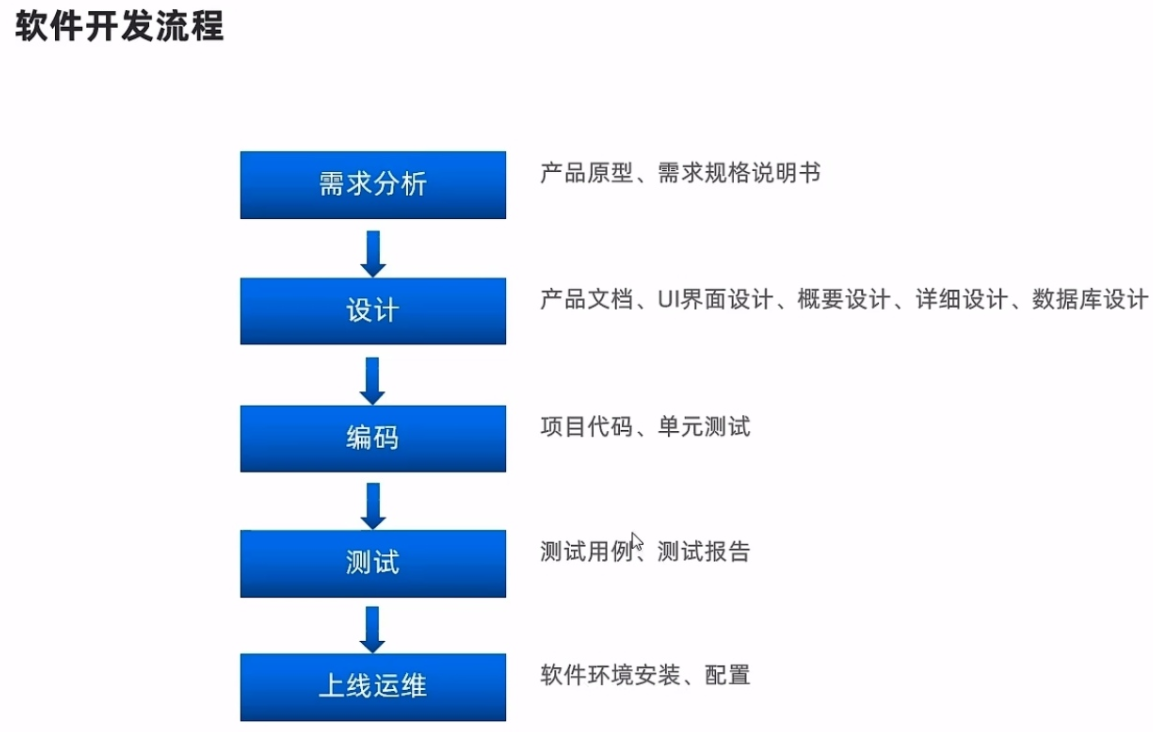

三、开发环境的搭建
①数据库环境的搭建
1.创建数据库

2.导入表结构直接运行外部SQL文件

数据表的说明
| 序号 | 表名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | employee | 员工表 |
| 2 | category | 菜品和套餐分类表 |
| 3 | dish | 菜品表 |
| 4 | setmeal | 套餐表 |
| 5 | setmeal_dish | 套餐菜品关系表 |
| 6 | dish_flavor | 菜品口味关系表 |
| 7 | user | 用表(c端) |
| 8 | address_book | 地址薄表 |
| 9 | shopping_cart | 购物车表 |
| 10 | orders | 订单表 |
| 11 | orders_detail | 订单明细表 |
②maven项目搭建
1.创建一个maven项目
注意:创建maven项目后一定要检查项目的编码maven仓库的配置jdk的配置等
2.导入pom文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.6</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>reggie_take_out</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.20</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.76</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.23</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.6.6</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>3.创建application.yml文件
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
# 应用的名称选择性配置
name: reggie_take_out
datasource:
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/reggie?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
username: root
password: root
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
#在映射实体或者属性时将数据库中表名和字段名中的下划线去掉按照驼峰命名法映射
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 把SQL的查询的过程输出到控制台
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: ASSIGN_ID3.创建Boot程序入口
package com.itheima.reggie;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/14
*/
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
@ServletComponentScan
public class ReggieApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ReggieApplication.class,args);
log.info("项目启动成功...");
}
}4.运行Boot程序看是否成功
③导入前端文件
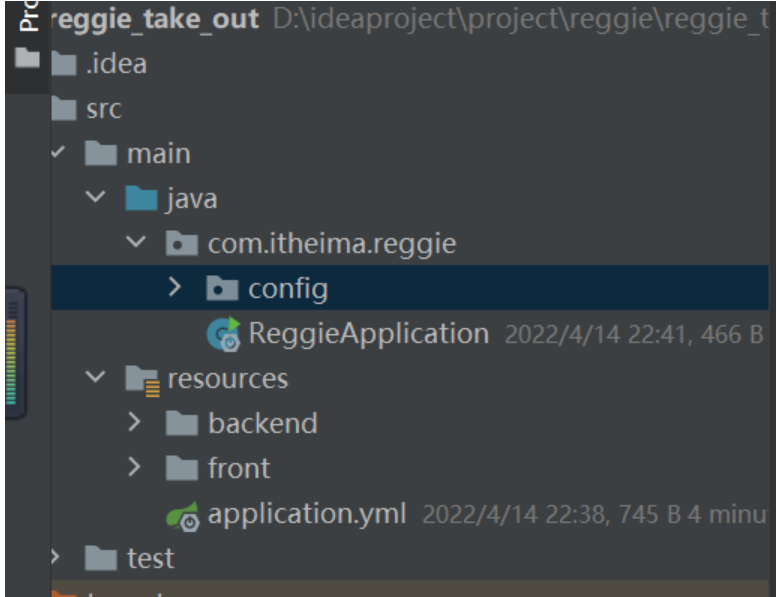
注意前端文件的位置在Boot项目中前台默认就只能访问 resource目录下的static和template文件夹下的文件所以如果要使用这种方式直接创建一个static目录就行然后把这些前端资源放在这个static目录下就行
如果你不想把前端文件放在这两个默认的文件夹下那么就可以自己定义mvc的支持这里我们使用的就是这方式多学习一种定义的方法以后自定义映射的时候可以使用
package com.itheima.reggie.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/14
*/
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
/**
* 设置资源映射
* @param registry
* 前面表示的是浏览器访问的请求
* 后面表示的是要把请求映射到哪里去
*/
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
log.info("开始进行静态资源映射");
registry.addResourceHandler("/backend/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/backend/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/front/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/front/");
}
}
记得在启动程序加上@ServletComponentScan这个注解否则这个配置类不会生效
四、后台登陆功能开发
①需求分析
需求分析是通过产品原型来进行的这个是项目经理负责的
②代码开发
前端页面访问地址http://localhost:8080/backend/page/login/login.html
查看登陆请求信息点击登录会发送登录请求http://localhost:8080/employee/login
我们去后端进行代码开发相关的接口就行
创建相关的包
实体类和mapper的开发
在entity导入实体类employee类
使用mybatis-plus提供的自动生成mapper:
package com.itheima.reggie.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Employee;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface EmployeeMapper extends BaseMapper<Employee> {
}使用快捷键 Ctrl + f3 就可以看见mybatis-plus 帮我们定义的mapper接口
service
package com.itheima.reggie.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Employee;
public interface EmployeeService extends IService<Employee> {
}package com.itheima.reggie.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Employee;
import com.itheima.reggie.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/15
*/
@Service //这两个泛型一个是实体类对应的mapper,一个是实体类
public class EmployeeServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<EmployeeMapper,Employee> implements EmployeeService {
}查看帮我们实现的方法
封装返回的结果类
创建一个新的包common用来存放共同使用的类把这个返回结果类放入这个公共包
package com.itheima.reggie.common;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 通用返回结果类服务端响应的数据最终都会封装成此对象
* @param <T>
*/
@Data
public class R<T> {
private Integer code; //编码1成功0和其它数字为失败
private String msg; //错误信息
private T data; //数据
private Map map = new HashMap(); //动态数据
public static <T> R<T> success(T object) {
R<T> r = new R<T>();
r.data = object;
r.code = 1;
return r;
}
public static <T> R<T> error(String msg) {
R r = new R();
r.msg = msg;
r.code = 0;
return r;
}
public R<T> add(String key, Object value) {
this.map.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}controller
登陆的具体流程图在平板上记得传过来。
先处理业务逻辑然后再编码
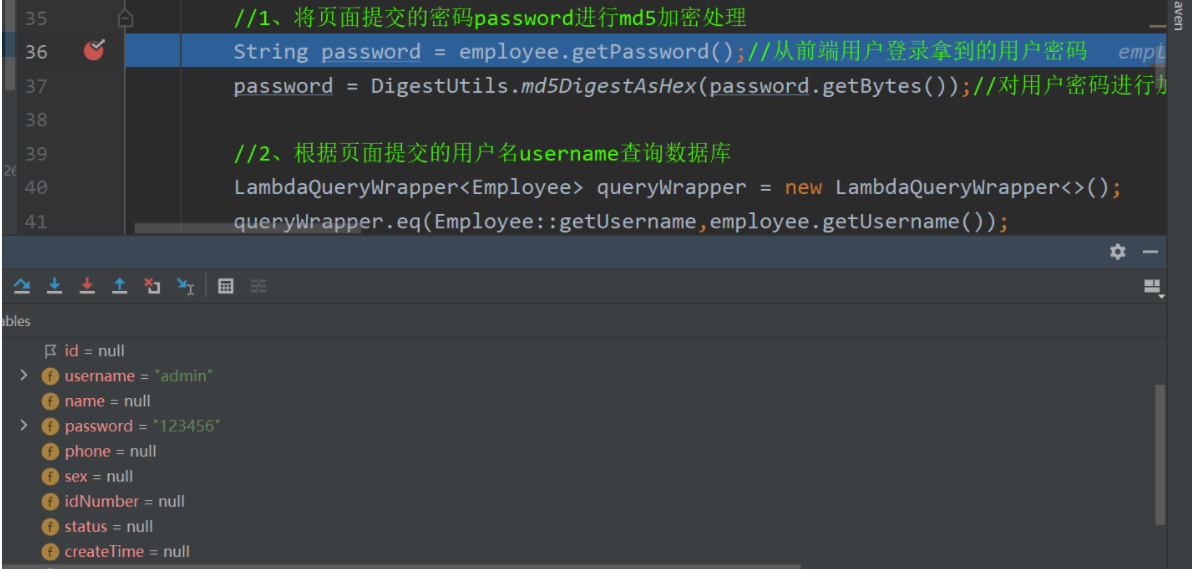
1、将页面提交的密码password进行md5加密处理
2、根据页面提交的用户名username查询数据库
3、如果没有查询到则返回登录失败结果
4、密码比对如果不一致则返回登录失败结果
5、查看员工状态如果为已禁用状态则返回员工已禁用结果
6、登录成功将员工id存入Session并返回登录成功结果package com.itheima.reggie.controller;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.common.R;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Employee;
import com.itheima.reggie.service.EmployeeService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.util.DigestUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/15
*/
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/employee")
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@PostMapping("/login") //使用restful风格开发
public R<Employee> login(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody Employee employee){//接收前端的json数据,这个json数据是在请求体中的
//这里为什么还有接收一个request对象的数据?
//登陆成功后我们需要从请求中获取员工的id并且把这个id存到session中这样我们想要获取登陆对象的时候就可以随时获取
//1、将页面提交的密码password进行md5加密处理
String password = employee.getPassword();//从前端用户登录拿到的用户密码
password = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(password.getBytes());//对用户密码进行加密
//2、根据页面提交的用户名username查询数据库
LambdaQueryWrapper<Employee> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(Employee::getUsername,employee.getUsername());
//在设计数据库的时候我们对username使用了唯一索引,所以这里可以使用getOne方法
Employee emp = employeeService.getOne(queryWrapper);//这里的切入Wrapper是什么
//3、如果没有查询到则返回登录失败结果
if (emp == null ){
return R.error("用户不存在");
}
//4、密码比对如果不一致则返回登录失败结果
if (!emp.getPassword().equals(password)){
//emp.getPassword()用户存在后从数据库查询到的密码(加密状态的) password是前端用户自己输入的密码(已经加密处理)
return R.error("密码不正确");
}
//5、查看员工状态如果为已禁用状态则返回员工已禁用结果
if (emp.getStatus() == 0){
return R.error("账号已禁用");
}
//6、登录成功将员工id存入Session并返回登录成功结果
request.getSession().setAttribute("employee",emp.getId());
//把从数据库中查询到的用户返回出去
return R.success(emp);
}
}③功能测试
使用debug的形式启动项目然后在浏览器访问:http://localhost:8080/backend/page/login/login.html
然后打开浏览器的f12,查看具体的请求情况
在后台查看debug的状态
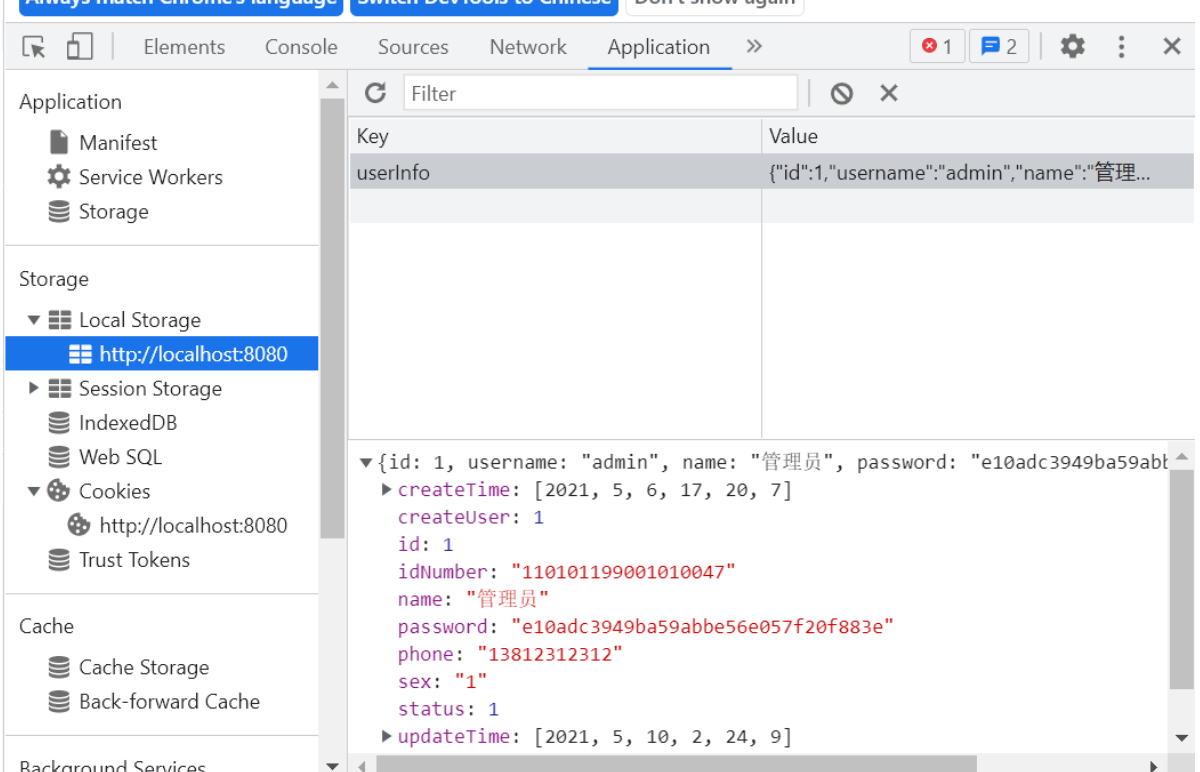
 运行成功后这个密码是123456数据存在了浏览器中这个代码是吧返回的数据保持在浏览器中
运行成功后这个密码是123456数据存在了浏览器中这个代码是吧返回的数据保持在浏览器中
localStorage.setItem('userInfo',JSON.stringify(res.data))在浏览器我们可以看见key为userInfovalue为我们返回的数据
五、后台系统退出功能
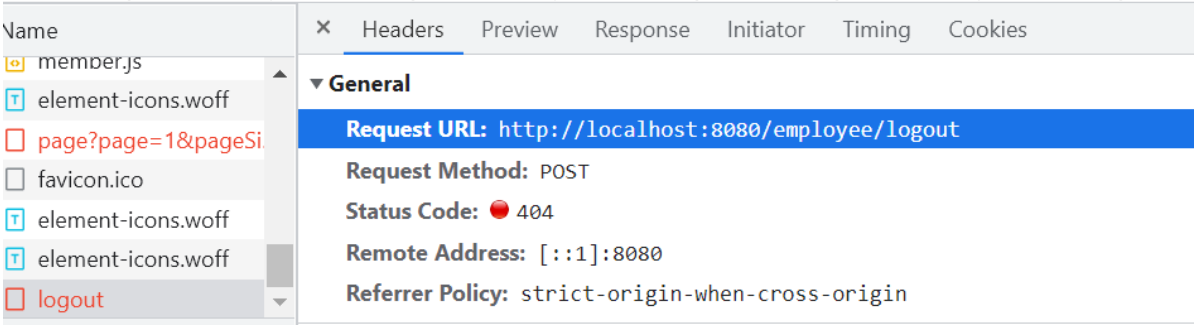
点击退出按钮发送退出的请求http://localhost:8080/employee/logout
后端代码处理
①在controller中创建对应的处理方法来接受前端的请求请求方式为post
②清理session中的用户id
③返回结果前端页面会进行跳转到登录页面
前端代码也要把浏览器中的数据给清除
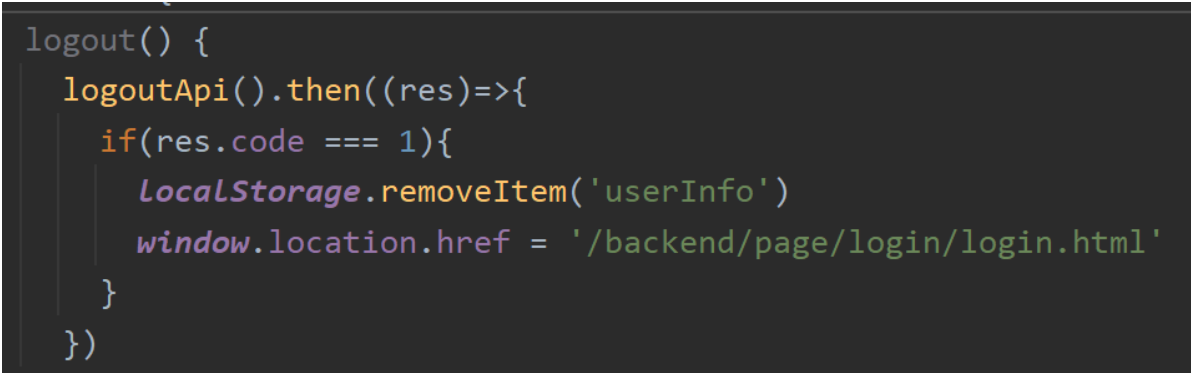
/**
* 退出功能
* ①在controller中创建对应的处理方法来接受前端的请求请求方式为post
* ②清理session中的用户id
* ③返回结果前端页面会进行跳转到登录页面
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/logout")
public R<String> logout(HttpServletRequest request){
//清理session中的用户id
request.getSession().removeAttribute("employee");
return R.success("退出成功");
}功能测试先登陆然后退出即可看浏览器中的数据是否会被清除
六、员工管理模块
完善登陆功能
问题分析前面的登陆存在一个问题如果用户不进行登陆直接访问系统的首页照样可以正常访问这种设计是不合理的我们希望看到的效果是只有完成了登陆后才可以访问系统中的页面如果没有登陆则跳转到登陆页面
那么如何实现
答案就是使用过滤器或者是拦截器在拦截器或者是过滤器中判断用户是否已经完成了登陆如果没有登陆则跳转到登陆页面
代码实现这里使用的是过滤器
①创建自定义过滤器LongCheckFilter
package com.itheima.reggie.filter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/15
* 检查用户是否已经完成登陆
* filterName过滤器名字
* urlPatterns拦截的请求这里是拦截所有的请求
*
*/
@WebFilter(filterName = "LongCheckFilter",urlPatterns = "/*")
@Slf4j
public class LongCheckFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
log.info("拦截到的请求:{}",request.getRequestURL());
//对请求进行放行
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
}
}②在启动类加上注解@ServletComponentScan
然后先测试一下过滤器能不能生效具体的逻辑等下再书写发送请求看后台能不能打印拦截的信息
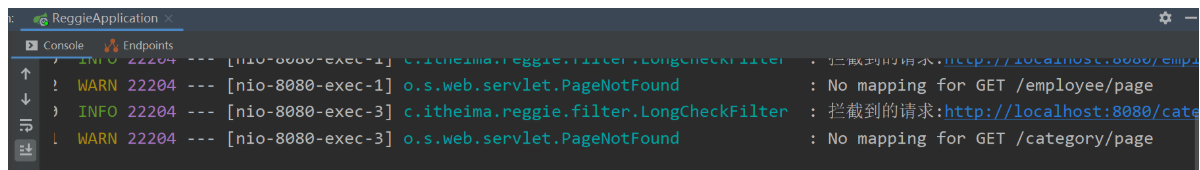
③完善过滤器的处理逻辑

具体逻辑的代码实现
package com.itheima.reggie.filter;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.itheima.reggie.common.R;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.util.AntPathMatcher;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/15
* 检查用户是否已经完成登陆
* filterName过滤器名字
* urlPatterns拦截的请求这里是拦截所有的请求
*
*/
@WebFilter(filterName = "LongCheckFilter",urlPatterns = "/*")
@Slf4j
public class LongCheckFilter implements Filter {
//路径匹配器支持通配符
public static final AntPathMatcher PATH_MATCHER = new AntPathMatcher();
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
//对请求和响应进行强转,我们需要的是带http的
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
//1、获取本次请求的URI
String requestURL = request.getRequestURI();
//定义不需要处理的请求路径 比如静态资源(静态页面我们不需要拦截,因为此时的静态页面是没有数据的)
String[] urls = new String[]{
"/employee/login",
"/employee/logout",
"/backend/**",
"/front/**"
};
//做调试用的
//log.info("拦截到请求{}",requestURL);
//2、判断本次请求是否需要处理
boolean check = check(urls, requestURL);
//3、如果不需要处理则直接放行
if(check){
//log.info("本次请求{}不需要处理",requestURL);
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
return;
}
//4、判断登录状态如果已登录则直接放行
if(request.getSession().getAttribute("employee") != null){
//log.info("用户已登录用户id为{}",request.getSession().getAttribute("employee"));
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
return;
}
//log.info("用户未登录");
//5、如果未登录则返回未登录结果通过输出流方式向客户端页面响应数据,具体响应什么数据看前端的需求然后前端会根据登陆状态做页面跳转
response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(R.error("NOTLOGIN")));
return;
}
/**
* 路径匹配检查本次请求是否需要放行
* @param urls
* @param requestURI
* @return
*/
public boolean check(String[] urls,String requestURI){
for (String url : urls) {
//把浏览器发过来的请求和我们定义的不拦截的url做比较匹配则放行
boolean match = PATH_MATCHER.match(url, requestURI);
if(match){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}功能测试: 发起几个请求看看后台的输出和能不能访问到资源里面的数据和能不能跳转注意上面的后台日志代码已经被注释需要在后台看到日志的话需要把注释去掉
新增员工
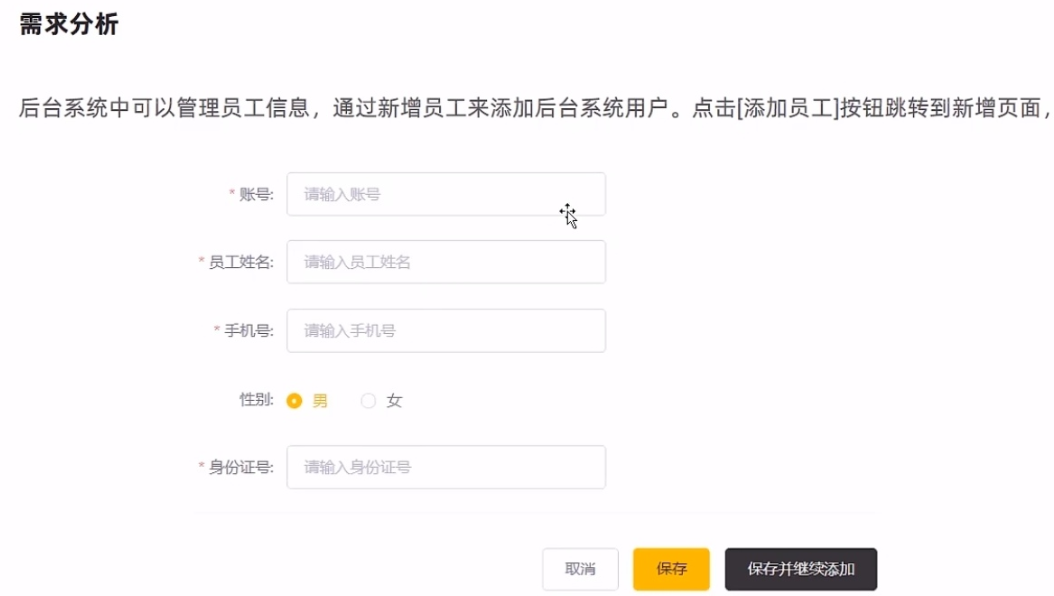
数据模型
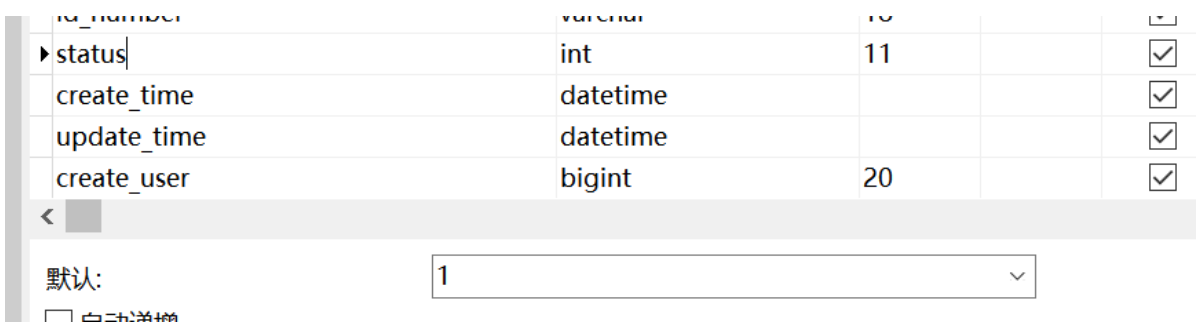
新增员工其实就是将我们的新增页面录入的员工数据插入到employee表注意employee表中对username字段加入了唯一的约束因为username是员工的登陆账号必须是唯一的
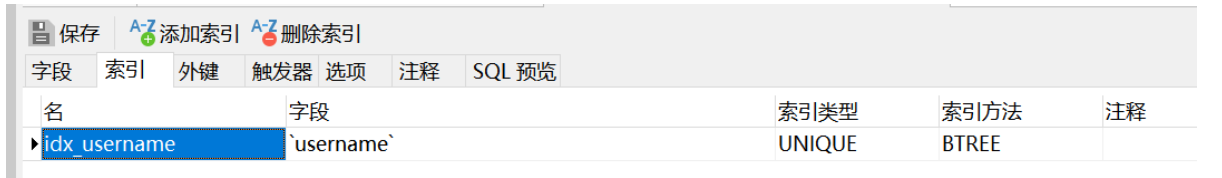
employee表中的status字段默认设置为1表示员工状态可以正常登陆
代码开发
梳理一下代码执行的流程

/**
* 新增员工
* @param employee
* @return
*/
@PostMapping()//因为请求就是 /employee 在类上已经写了所以咱俩不用再写了
public R<String> save(HttpServletRequest request,@RequestBody Employee employee){
//对新增的员工设置初始化密码123456,需要进行md5加密处理后续员工可以直接修改密码
employee.setPassword(DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex("123456".getBytes()));
employee.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
employee.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
//获得当前登录用户的id
Long empId = (Long) request.getSession().getAttribute("employee");
employee.setCreateUser(empId); //创建人的id,就是当前用户的id在进行添加操作的id
employee.setUpdateUser(empId);//最后的更新人是谁
//mybatis提供的新增方法
employeeService.save(employee);
return R.success("新增员工成功");
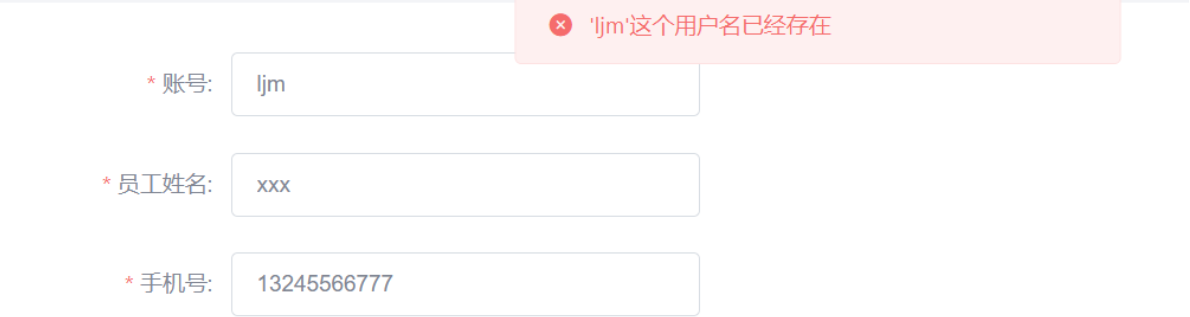
}功能测试登陆之后点击添加然后确认然后去数据库看一下新增数据成功没新增成功那就表示代码可以执行 注意但是因为我们把username设置为唯一索引所以下次再新增用户的时候就会出现异常这个异常是MySQL数据库抛出来的
解决bug:

全局异常捕获
这个全局异常捕获写在common包下
package com.itheima.reggie.common;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.sql.SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/15
* 全局异常处理
*/
@ControllerAdvice(annotations = {RestController.class, Controller.class}) //表示拦截哪些类型的controller注解
@ResponseBody
@Slf4j
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 处理SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException异常的方法
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException.class)
public R<String> exceptionHandle(SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException exception){
log.error(exception.getMessage()); //报错记得打日志
if (exception.getMessage().contains("Duplicate entry")){
//获取已经存在的用户名这里是从报错的异常信息中获取的
String[] split = exception.getMessage().split(" ");
String msg = split[2] + "这个用户名已经存在";
return R.error(msg);
}
return R.error("未知错误");
}
}功能测试登陆后添加一个一个已经存在账号名看前端页面提示的是什么信息以及看后台是否输出了报错日志

员工信息分页查询
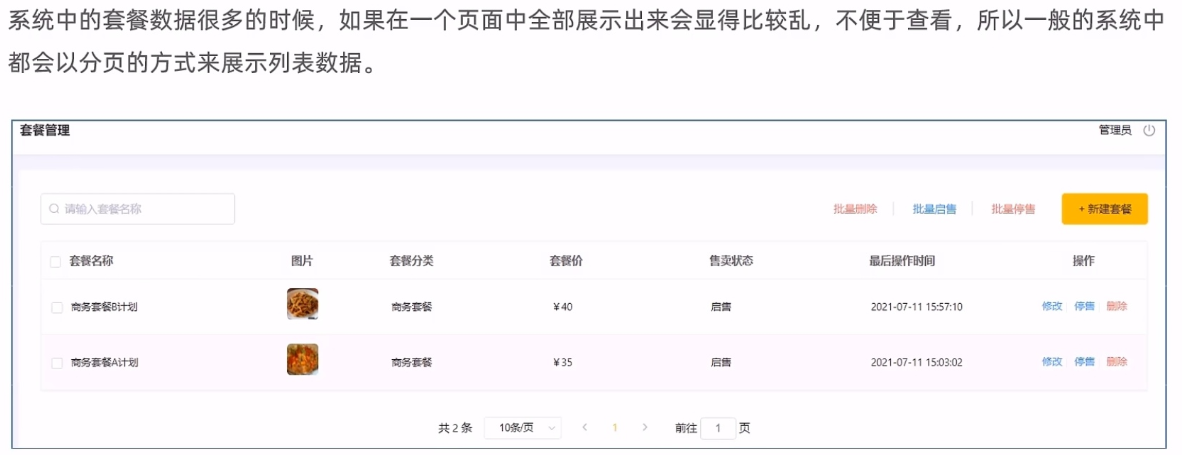
需求分析系统中的员工比较多的时候如果在一个页面中全部展示出来会显得比较乱不便于查看所以一般都系统中都会以分页的方式来展示列表数据。
流程分析

Java代码
//配置mybatis-plus的分页插件
package com.itheima.reggie.config;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.MybatisPlusInterceptor;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.PaginationInnerInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/15
* 配置mybatis-plus提供的分页插件拦截器
*/
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor(){
MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
mybatisPlusInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor());
return mybatisPlusInterceptor;
}
} /**
* 员工信息分页
* @param page 当前页数
* @param pageSize 当前页最多存放数据条数,就是这一页查几条数据
* @param name 根据name查询员工的信息
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/page")
public R<Page> page(int page,int pageSize,String name){
//这里之所以是返回page对象(mybatis-plus的page对象)是因为前端需要这些分页的数据(比如当前页总页数)
//在编写前先测试一下前端传过来的分页数据有没有被我们接受到
//log.info("page = {},pageSize = {},name = {}" ,page,pageSize,name);
//构造分页构造器 就是page对象
Page pageInfo = new Page(page,pageSize);
//构造条件构造器 就是动态的封装前端传过来的过滤条件 记得加泛型
LambdaQueryWrapper<Employee> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper();
//根据条件查询 注意这里的条件是不为空
queryWrapper.like(StringUtils.isNotEmpty(name),Employee::getName,name);
//添加一个排序条件
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Employee::getUpdateTime);
//执行查询 这里不用封装了mybatis-plus帮我们做好了
employeeService.page(pageInfo,queryWrapper);
return R.success(pageInfo);
}功能测试分页的三个时机①用户登录成功时分页查询一次 ②用户使用条件查询的时候分页一次 ③跳转页面的时候分页查询一次
启用/禁用员工账号
需求分析
在员工管理列表页面中可以对某个员工账号进行启用或者是禁用操作。账号禁用的员工不能登陆系统启用后的员工可以正常登陆
需要注意的是只有管理员(admin用户)才可以对其他普通用户进行启用操作禁用操作所以普通用户登录系统后启用禁用按钮不显示
并且如果某个员工账号的状态为正常则按钮显示为’‘禁用’如果员工账号状态为已禁用则按钮显示为“启用”。
普通员工登录系统后启用禁用按钮不显示
代码开发

注意:这里修改状态码要反着来因为正常的用户你只能把它设置为禁用已经禁用的账号你只能把它设置为正常

流程分析
注意启用禁用的员工账号本质上就是一个更新操作也就是对status状态字段进行修改操作
在controller中创建update方法此方法是一个通用的修改员工信息的方法,因为status也是employee中的一个属性而已这里使用了动态SQL的功能根据具体的数据修改对应的字段信息
/**
* 根据id修改员工信息
* @param employee
* @return
*/
@PutMapping
public R<String> update(HttpServletRequest request,@RequestBody Employee employee){
log.info(employee.toString());
Long empId = (Long)request.getSession().getAttribute("employee");
employee.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
employee.setUpdateUser(empId);
employeeService.updateById(employee);
return R.success("员工信息修改成功");
}功能测试测试的时候我们发现出现了问题就是我们修改员工的状态提示信息显示修改成功但是我们去数据库查验证的时候发现员工的状态码压根就没有变化这是为什么呢

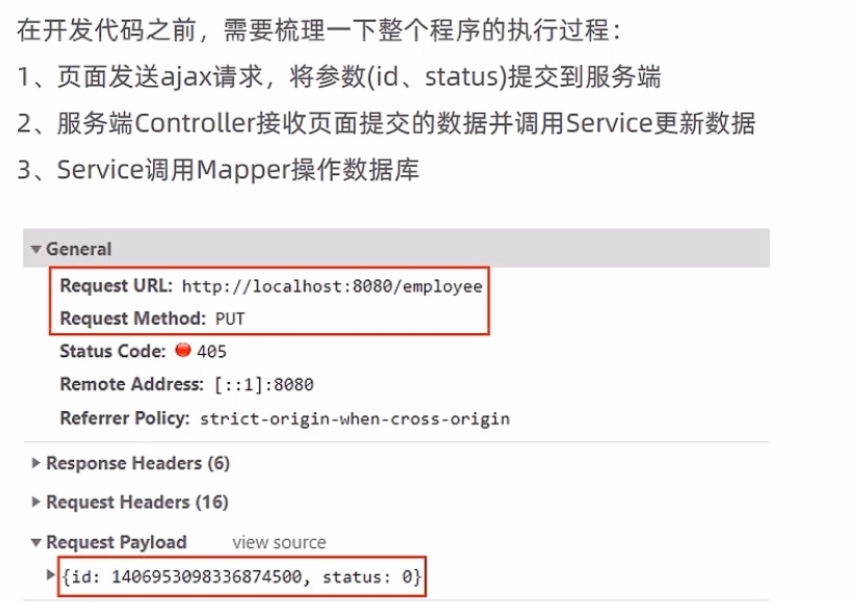
仔细观察id后我们会发现后台的SQL语句使用的id和数据库中的id是不一样的
原因是mybatis-plus对id使用了雪花算法所以存入数据库中的id是19为长度但是前端的js只能保证数据的前16位的数据的精度对我们id后面三位数据进行了四舍五入所以就出现了精度丢失就会出现前度传过来的id和数据里面的id不匹配就没办法正确的修改到我们想要的数据
当然另一种解决bug的方法是:关闭mybatis-plus的雪花算法来处理ID我们使用自增ID的策略来往数据库添加id就行
使用自定义消息转换器
代码bug修复
思路既然js对long型的数据会进行精度丢失那么我们就对数据进行转型我们可以在服务端Java端给页面响应json格式的数据时进行处理将long型的数据统一转换为string字符串
代码实现步骤
步骤一自定义消息转换类
package com.itheima.reggie.common;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.module.SimpleModule;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.std.ToStringSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalDateDeserializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalDateTimeDeserializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalTimeDeserializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalDateSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalDateTimeSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalTimeSerializer;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import static com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES;
/**
* 对象映射器:基于jackson将Java对象转为json或者将json转为Java对象
* 将JSON解析为Java对象的过程称为 [从JSON反序列化Java对象]
* 从Java对象生成JSON的过程称为 [序列化Java对象到JSON]
*/
public class JacksonObjectMapper extends ObjectMapper {
public static final String DEFAULT_DATE_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd";
public static final String DEFAULT_DATE_TIME_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";
public static final String DEFAULT_TIME_FORMAT = "HH:mm:ss";
public JacksonObjectMapper() {
super();
//收到未知属性时不报异常
this.configure(FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
//反序列化时属性不存在的兼容处理
this.getDeserializationConfig().withoutFeatures(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES);
SimpleModule simpleModule = new SimpleModule()
.addDeserializer(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_DATE_TIME_FORMAT)))
.addDeserializer(LocalDate.class, new LocalDateDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_DATE_FORMAT)))
.addDeserializer(LocalTime.class, new LocalTimeDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_TIME_FORMAT)))
.addSerializer(BigInteger.class, ToStringSerializer.instance)
.addSerializer(Long.class, ToStringSerializer.instance)
.addSerializer(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_DATE_TIME_FORMAT)))
.addSerializer(LocalDate.class, new LocalDateSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_DATE_FORMAT)))
.addSerializer(LocalTime.class, new LocalTimeSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_TIME_FORMAT)));
//注册功能模块 例如可以添加自定义序列化器和反序列化器
this.registerModule(simpleModule);
}
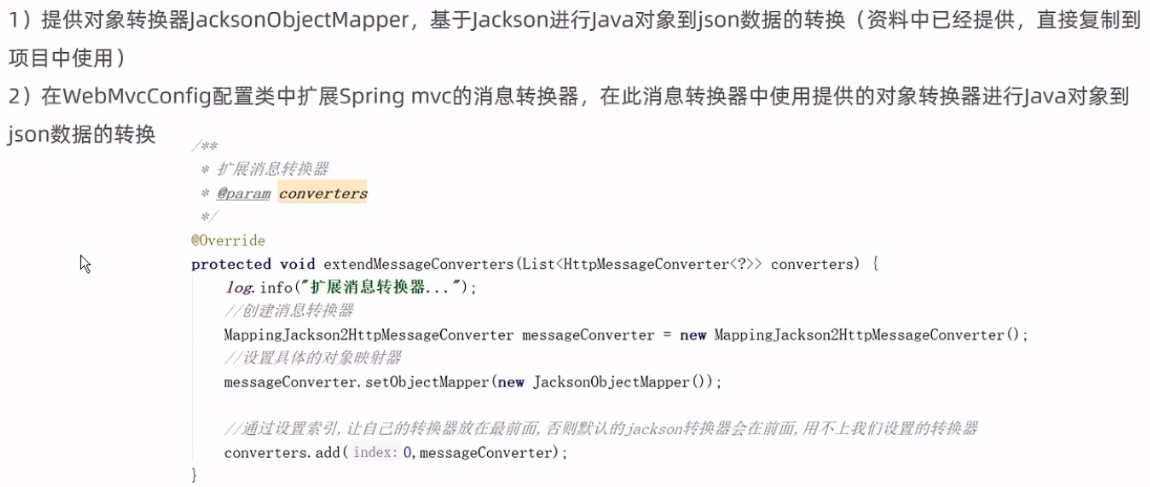
}步骤二在前面的webMvcConfig 配置类中扩展spring mvc 的消息转换器在此消息转换器中使用spring提供的对象转换器进行Java对象到json数据的转换
/**
* 扩展mvc框架的消息转换器
* @param converters
*/
@Override
protected void extendMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
//log.info("扩展消息转换器...");
//创建消息转换器对象
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter messageConverter = new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter();
//设置对象转换器底层使用Jackson将Java对象转为json
messageConverter.setObjectMapper(new JacksonObjectMapper());
//将上面的消息转换器对象追加到mvc框架的转换器集合中
//转换器是有优先级顺序的这里我们把自己定义的消息转换器设置为第一优先级所以会优先使用我们的转换器来进行相关数据进行转换如果我们的转换器没有匹配到相应的数据来转换那么就会去寻找第二个优先级的转换器以此类推
converters.add(0,messageConverter);
}然后启动程序使用f12查看服务器响应到浏览器的用户id是不是变成了字符串和数据库中是否相对应
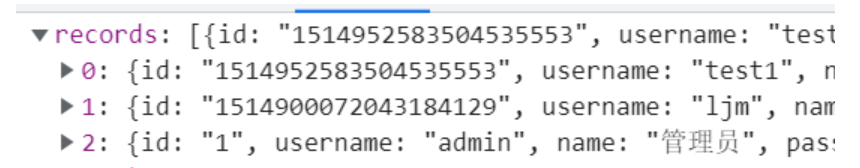
发现对应即消息转换器配置成功
然后再去测试 启用与禁用 员工账号这个功能发现操作更新成功并且数据库修改成功
编辑员工信息
需求分析

 数据回显后端代码其实主要逻辑在前端。。。。。
数据回显后端代码其实主要逻辑在前端。。。。。
/**
* 根据前端传过来的员工id查询数据库进行数据会显给前端
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public R<Employee> getById(@PathVariable Long id){
Employee employee = employeeService.getById(id);
if (employee != null){
return R.success(employee) ;
}
return R.error("没有查询到该员工信息");
}修改回显数据后点击保存会发送一个update的请求给后端前面我们已经写了这个update的controller所以只需要在前端跳转发请求就行这样就实现了方法的复用减少了代码两
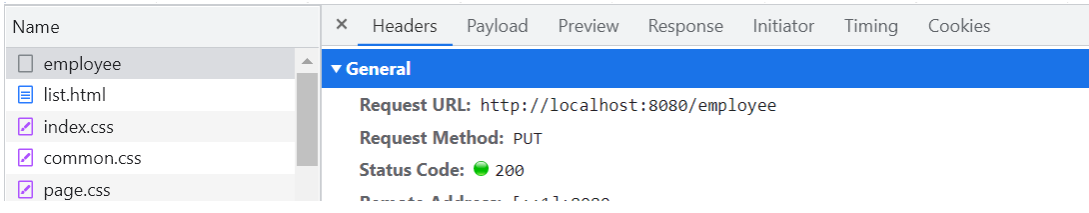
功能测试自己测试编辑看能不能数据回显可不可以修改成功修改后数据库的数据有没有跟着变化
七、菜品分类管理
公共字段填充(这里有重点)
问题分析


把相关的注解加在需要mybatis-plus自动帮我们填充的字段上面
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) //插入时填充字段
private LocalDateTime createTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE) //插入和更新时填充字段
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) //插入时填充字段
private Long createUser;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE) //插入和更新时填充字段
private Long updateUser;然后设置一个处理类在此类中为公共字段赋值需要实现 接口
package com.itheima.reggie.common;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.handlers.MetaObjectHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
* 自定义元数据对象处理器
*/
@Slf4j
@Component //注意:这个要记得交给spring容器管理不然这个功能就没发用。。。。
//那么怎么确定你要添加的功能是不是要交给容器管理呢就是你直接写了一个工具类或者是功能类需要对数据库的数据或者是数据库数据的结果产生影响的时候你明明写了这样一个类但是功能却没有生效那么这个时候就要首先考虑是不是容器没有托管这个类
public class MyMetaObjecthandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
/**
* 插入操作自动填充
* @param metaObject
*/
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
metaObject.setValue("createTime", LocalDateTime.now());
metaObject.setValue("updateTime",LocalDateTime.now());
metaObject.setValue("createUser", new Long(1)); //这里的id是不能直接获取的所以这里先写死后面教你怎么动态获取员工id
metaObject.setValue("updateUser",new Long(1));
}
/**
* 更新操作自动填充
* @param metaObject
*/
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
metaObject.setValue("updateTime",LocalDateTime.now());
metaObject.setValue("updateUser",new Long(1));
}
}
功能完善




然后为了动态的获取员工的id,这里我们使用了threadLocal这个局部变量来获取和存储员工id;
创建一个工具类来设置和获取threadLocal中的员工id, 注意要先把数据设置进threadLocal中才能获取到
package com.itheima.reggie.common;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
* 基于ThreadLocal封装工具类用户保存和获取当前登录用户id
*/
public class BaseContext {
//用来存储用户id
private static ThreadLocal<Long> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
/**
* 设置值
* @param id
*/
public static void setCurrentId(Long id){
threadLocal.set(id);
}
/**
* 获取值
* @return
*/
public static Long getCurrentId(){
return threadLocal.get();
}
}
在前面我们写的LongCheckFilter这个过滤器中把这个地方的代码加上添加和保存id的代码
//4、判断登录状态如果已登录则直接放行
if(request.getSession().getAttribute("employee") != null){
//log.info("用户已登录用户id为{}",request.getSession().getAttribute("employee"));
//把用户id存储到本地的threadLocal
Long emId = (Long) request.getSession().getAttribute("employee");
BaseContext.setCurrentId(emId);
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
return;
}把处理器中的静态id改为动态获取
metaObject.setValue("createUser", BaseContext.getCurrentId());
metaObject.setValue("updateUser",BaseContext.getCurrentId());

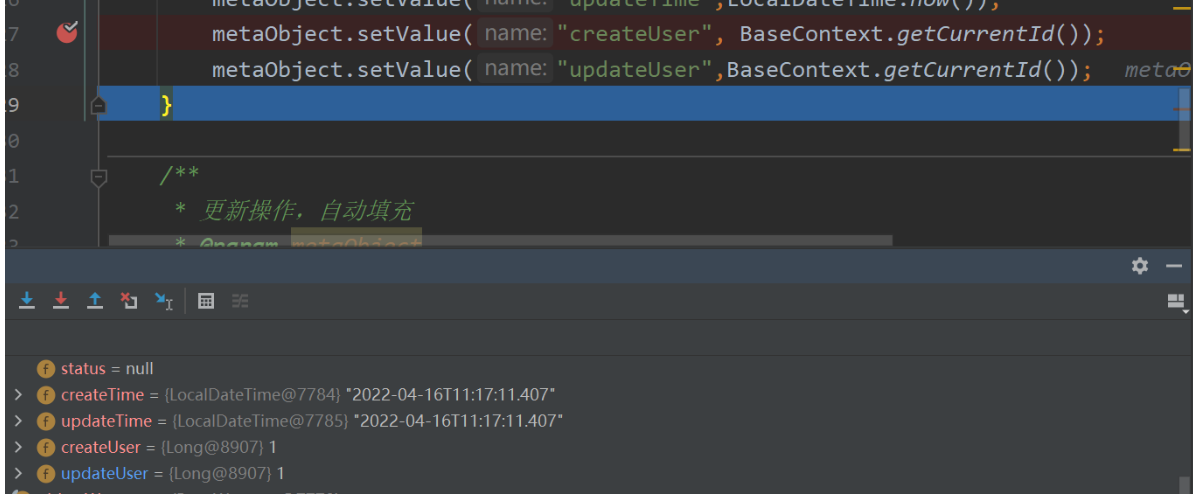
这里的ID之所以全为1是因为操作添加员工这个功能的管理员为admin它的id就是1
新增分类
需求分析
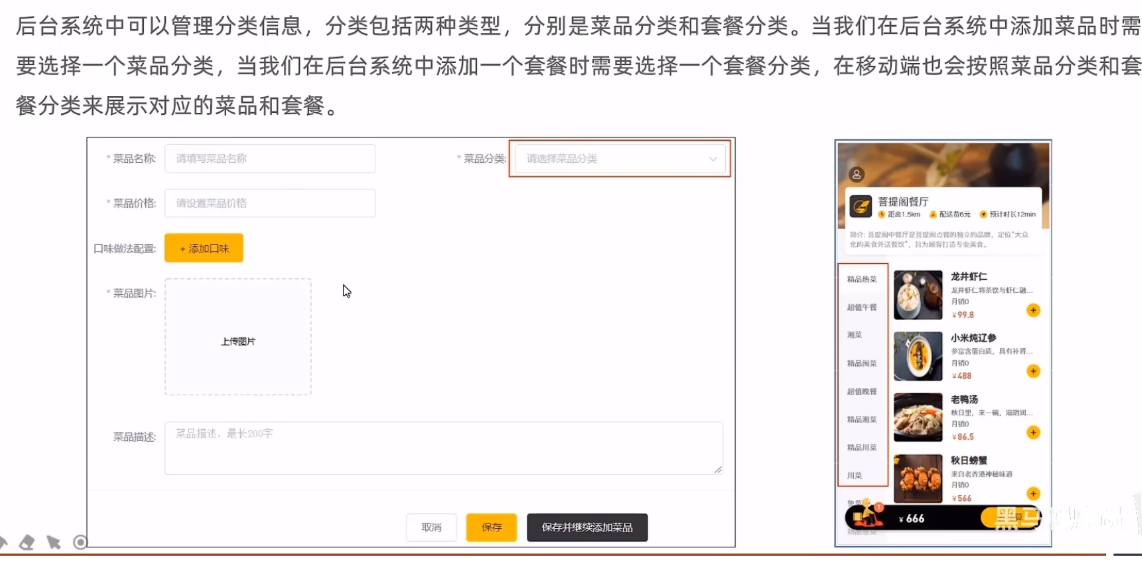
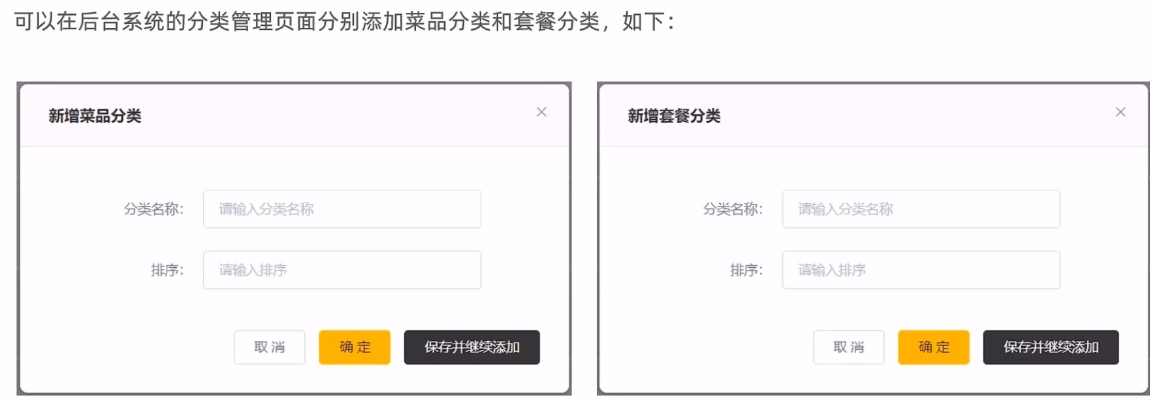
数据模型
从资料去复制实体Category类到entity包
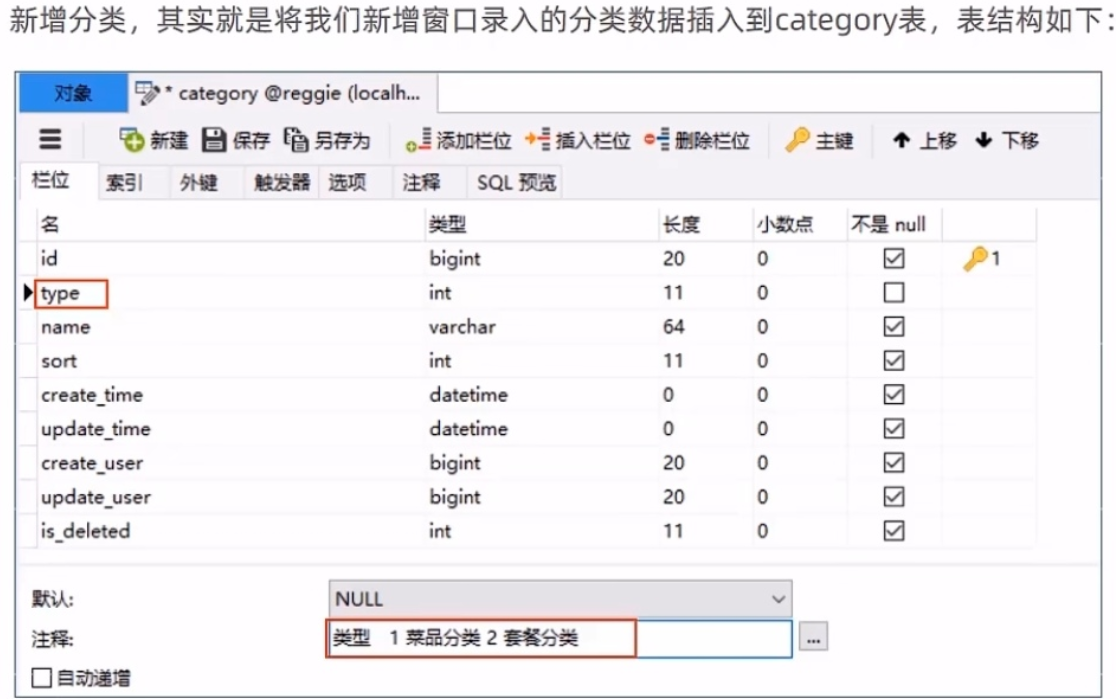
数据库中的表结构

创建mapper:
package com.itheima.reggie.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Category;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface CategoryMapper extends BaseMapper<Category> {
}
创建service
package com.itheima.reggie.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Category;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
*/
public interface CategoryService extends IService<Category> {
}package com.itheima.reggie.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Category;
import com.itheima.reggie.mapper.CategoryMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.service.CategoryService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
*/
@Service
public class CategoryServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<CategoryMapper, Category> implements CategoryService {
}编写controller
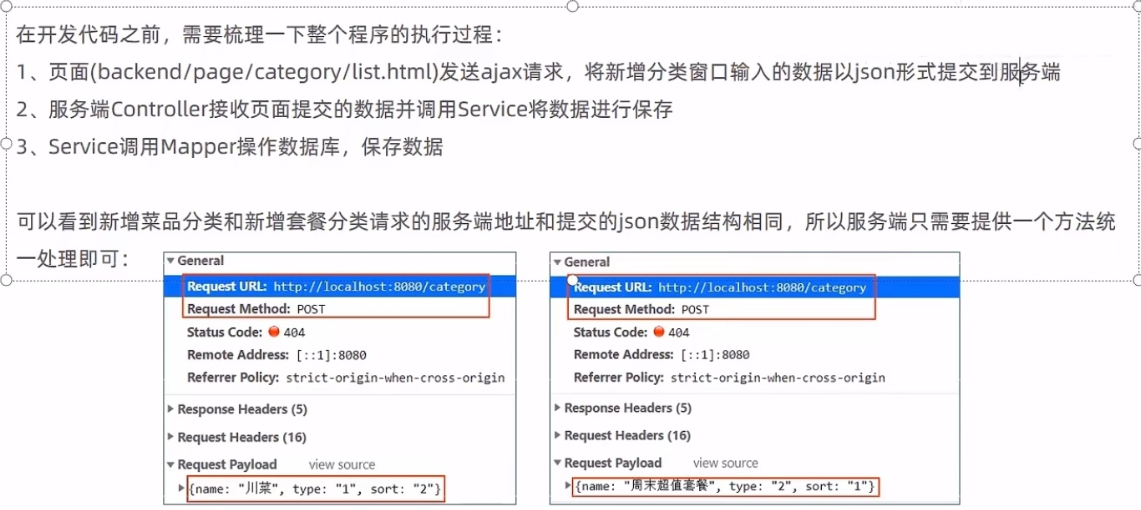
我们发现新增菜品分类的请求地址是:http://localhost:8080/category
提交的数据格式为
{name: "湘菜", type: "1", sort: "1"}/**
* 新增套餐分类
* @param category
* @return
*/
@PostMapping
public R<String> save(@RequestBody Category category){
log.info("{category}" ,category);
categoryService.save(category);
return R.success("新增分类成功");
}功能测试登录后点击添加新增菜品分类看是否成功数据库的数据是否变化
菜品类的分页
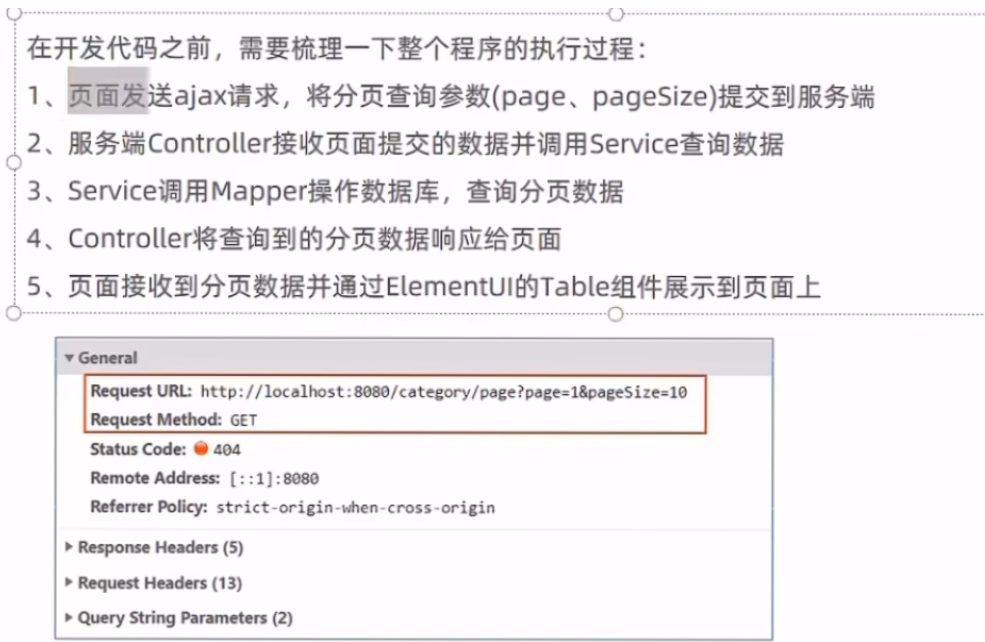
代码开发
/**
* 分页查询
* @param page
* @param pageSize
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/page")
public R<Page> page(int page,int pageSize){
//创建一个分页构造器
Page<Category> categoryPage = new Page<>(page,pageSize);
//创建一个条件构造器 用来排序用的 注意这个条件构造器一定要使用泛型否则使用条件查询这个方法的时候会报错
LambdaQueryWrapper<Category> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper();
//添加排序条件 根据sort字段进行排序
queryWrapper.orderByAsc(Category::getSort);
categoryService.page(categoryPage,queryWrapper);
return R.success(categoryPage);
}功能测试
删除分类这里有注意点
需求分析
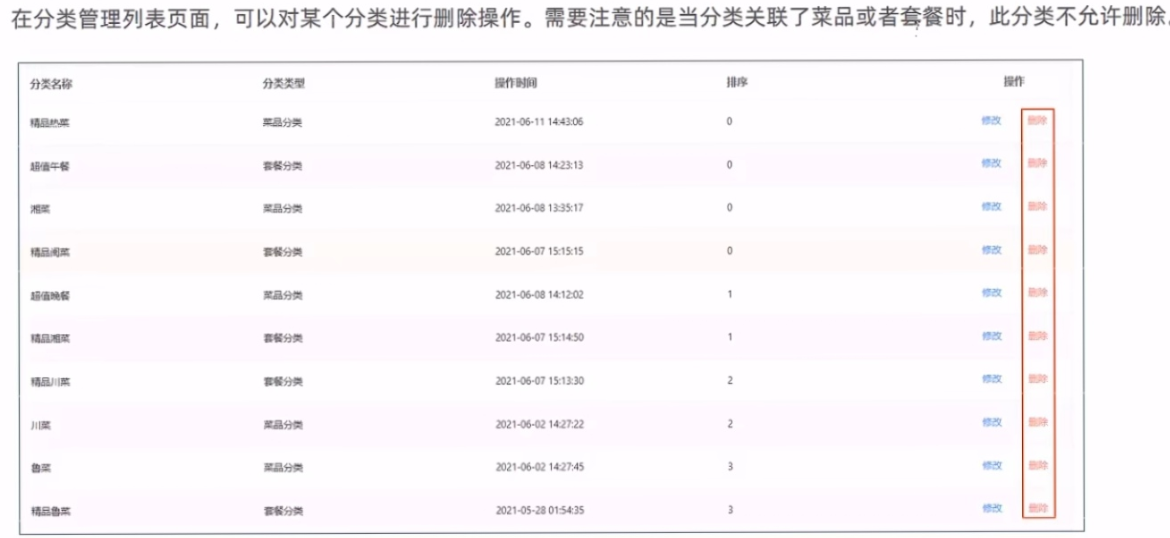
代码实现 注意这里的删除功能是不完整的因为可能需要删除的数据是与其他表关联的所以删除之前要先判断该条数据是否与其他表中的数据关联
/**
* 根据id来删除分类的数据
* @param id
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping()
public R<String> delete(@RequestParam("ids") Long ids){ //注意这里前端传过来的数据是ids
categoryService.removeById(ids);
return R.success("分类信息删除成功");
}功能完善

创建对应的mapper:
package com.itheima.reggie.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Dish;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
*/
@Mapper
public interface DishMapper extends BaseMapper<Dish> {
}package com.itheima.reggie.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Setmeal;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
*/
@Mapper
public interface SetmealMapper extends BaseMapper<Setmeal> {
}创建service
package com.itheima.reggie.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Dish;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
*/
public interface DishService extends IService<Dish> {
}package com.itheima.reggie.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Setmeal;
public interface SetmealService extends IService<Setmeal> {
}package com.itheima.reggie.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Dish;
import com.itheima.reggie.mapper.DishMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.service.DishService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class DishServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<DishMapper, Dish> implements DishService {
}
package com.itheima.reggie.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Setmeal;
import com.itheima.reggie.mapper.SetmealMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.service.SetmealService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class SetmealServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<SetmealMapper, Setmeal> implements SetmealService {
}添加自定义的service方法(就是我们需要的业务mybatis没有提供所以就需要自己另外在service创建新的方法并且在相关的业务中实现)
//在CategoryService中定义自己需要的方法直接写就行
void remove(Long id);在CategoryService实现类中重写该方法
自定义异常类因为这里需要抛异常了package com.itheima.reggie.common;
/**
* 自定义业务异常类
*/
public class CustomException extends RuntimeException {
public CustomException(String message){
super(message);
}
}
//然后在外面前面写的GlobalExceptionHandler全局异常捕获器中添加该异常这样就可以把相关的异常信息显示给前端操作的人员看见
/**
* 处理自定义的异常为了让前端展示我们的异常信息这里需要把异常进行全局捕获然后返回给前端
* @param exception
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(CustomException.class)
public R<String> exceptionHandle(CustomException exception){
log.error(exception.getMessage()); //报错记得打日志
//这里拿到的message是业务类抛出的异常信息我们把它显示到前端
return R.error(exception.getMessage());
}/**
* 根据id删除 分类删除之前需要进行判断是否有关联数据
* @param id
*/
@Override
public void remove(Long id) {
LambdaQueryWrapper<Dish> dishLambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加查询条件
dishLambdaQueryWrapper.eq(Dish::getCategoryId,id);
//注意:这里使用count方法的时候一定要传入条件查询的对象否则计数会出现问题计算出来的是全部的数据的条数
int count = dishService.count(dishLambdaQueryWrapper);
//查询当前分类是否关联了菜品如果已经管理直接抛出一个业务异常
if (count > 0){
//已经关联了菜品抛出一个业务异常
throw new CustomException("当前分类项关联了菜品,不能删除");
}
//查询当前分类是否关联了套餐如果已经管理直接抛出一个业务异常
LambdaQueryWrapper<Setmeal> setmealLambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
setmealLambdaQueryWrapper.eq(Setmeal::getCategoryId,id);
//注意:这里使用count方法的时候一定要传入条件查询的对象否则计数会出现问题计算出来的是全部的数据的条数
int setmealCount = setmealService.count(setmealLambdaQueryWrapper);
if (setmealCount > 0){
//已经关联了套餐抛出一个业务异常
throw new CustomException("当前分类项关联了套餐,不能删除");
}
//正常删除
super.removeById(id);
}然后在controller调用刚刚实现的方法就行把之前的remove方法给删除就行重新调用我们自己实现的方法
/**
* 根据id来删除分类的数据
* @param id
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping
public R<String> delete(@RequestParam("ids") Long id){ //注意这里前端传过来的数据是ids
categoryService.remove(id);
return R.success("分类信息删除成功");
}测试自己添加测试数据测试就行记得一定要测试一下删除有相关联的数据看会不会删除和在前端提示异常信息
修改分类
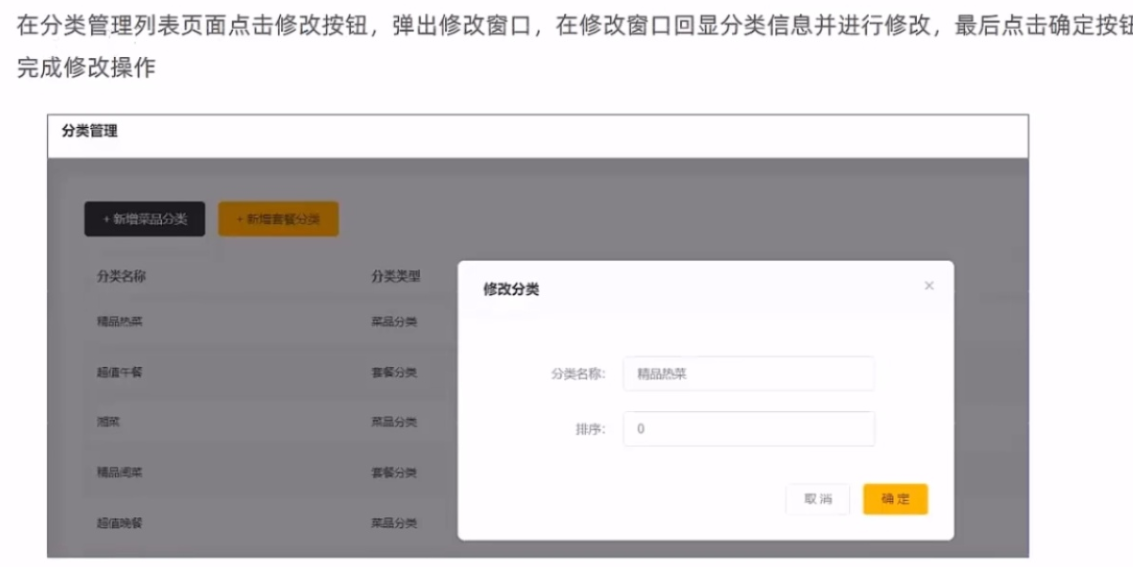
这里的编辑的数据回显前端已经帮我们做好了所以我们就不需要去数据库查询了这样可以减少对数据库的操作

/**
* 根据id修改分类
* @param category
* @return
*/
@PutMapping
public R<String> update(@RequestBody Category category){
categoryService.updateById(category);
return R.success("修改分类信息成功");
}记得在对应的实体类加上公共字段的值设置前面我们配置了这个所以这里只需要加注解就行
//创建时间
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private LocalDateTime createTime;
//更新时间
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
//创建人
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Long createUser;
//修改人
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Long updateUser;八、菜品管理的业务功能
文件的上传和下载重点
整体介绍

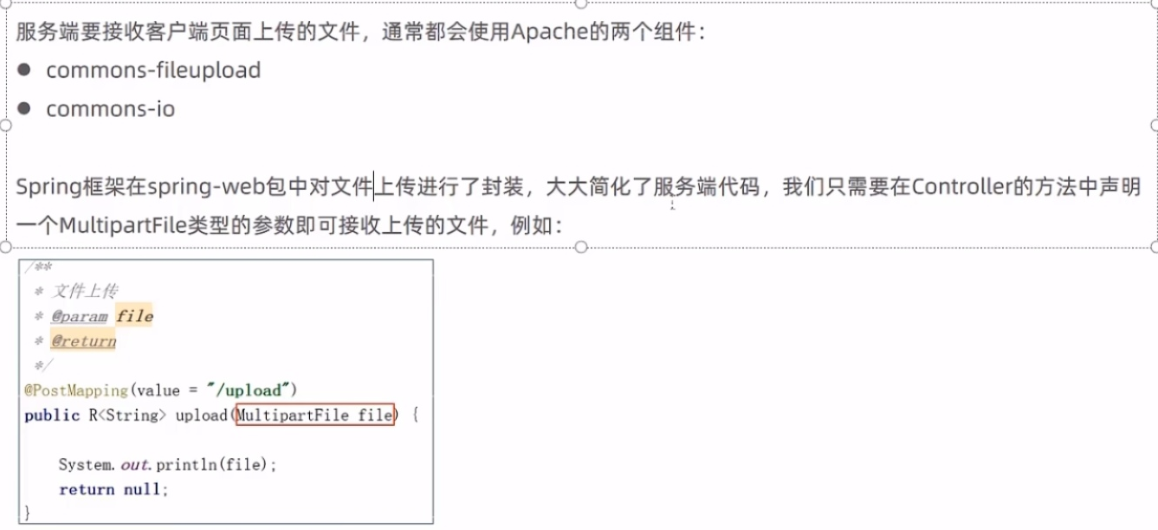
文件下载

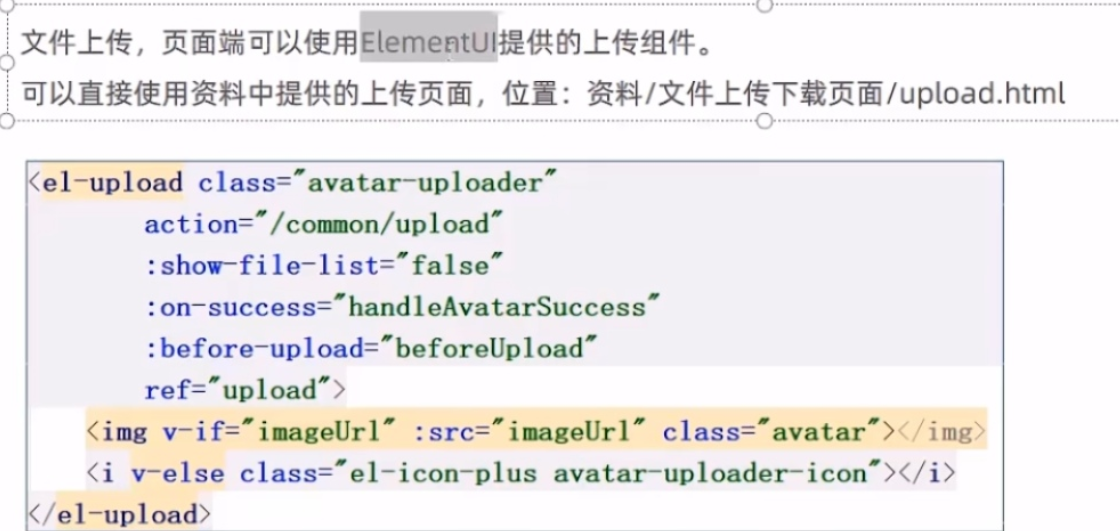
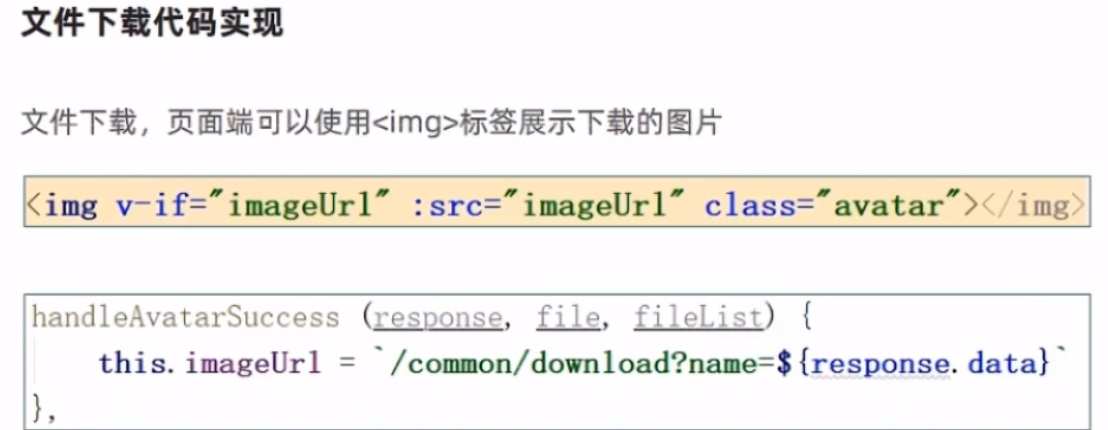
后端具体代码的实现
yml配置文件配置上传图片的存储位置
reggie:
path: E:\reggie\package com.itheima.reggie.controller;
import com.itheima.reggie.common.R;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
* 文件上传和下载
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/common")
public class CommonController {
@Value("${reggie.path}")
private String basePath;
/**
* 文件的上传
* @param file
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/upload")
public R<String> upload(MultipartFile file){
//这个file是一个临时文件需要转存到指定位置否则本次请求完成后临时文件会删除
//拿到文件的原始名
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
//拿到文件的后缀名 比如 .png .jpg
String suffix = originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf("."));
//使用uuid生成的作为文件名的一部分这样可以防止文件名相同造成的文件覆盖
String fileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + suffix;
//创建一个目录对象看传文件的时候接收文件的目录存不存在
File dir = new File(basePath);
if (!dir.exists()){
//文件目录不存在直接创建一个目录
dir.mkdirs();
}
try {
//把前端传过来的文件进行转存
file.transferTo(new File(basePath + fileName));
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return R.success(fileName);
}
@GetMapping("/download")
public void download(String name, HttpServletResponse response){
try {
//输入流通过输入流读取文件内容 这里的name是前台用户需要下载的文件的文件名
//new File(basePath + name) 是为了从存储图片的地方获取用户需要的图片对象
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File(basePath + name));
//输出流通过输出流将文件写回浏览器
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
//设置写回去的文件类型
response.setContentType("image/jpeg");
//定义缓存区准备读写文件
int len = 0 ;
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
while ((len = fileInputStream.read(buff)) != -1){
outputStream.write(buff,0,len);
outputStream.flush();
}
//关流
outputStream.close();
fileInputStream.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}注意这里上传的文件的文件名要和这个地方的一样接收文件的参数的名不能随便定义要和下面的name的值一致
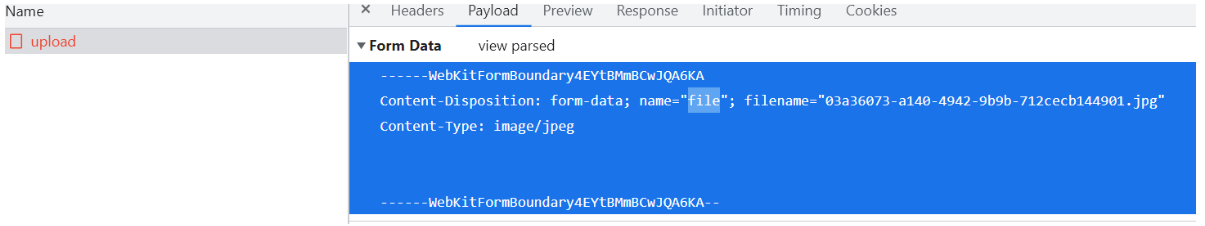
新增菜品业务的实现是重点
需求分析
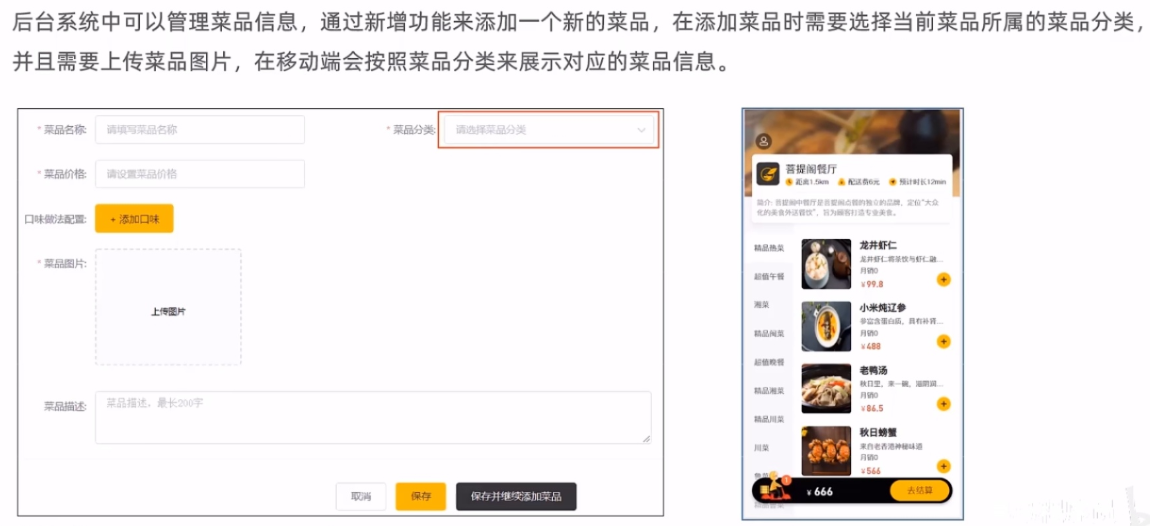
数据模型
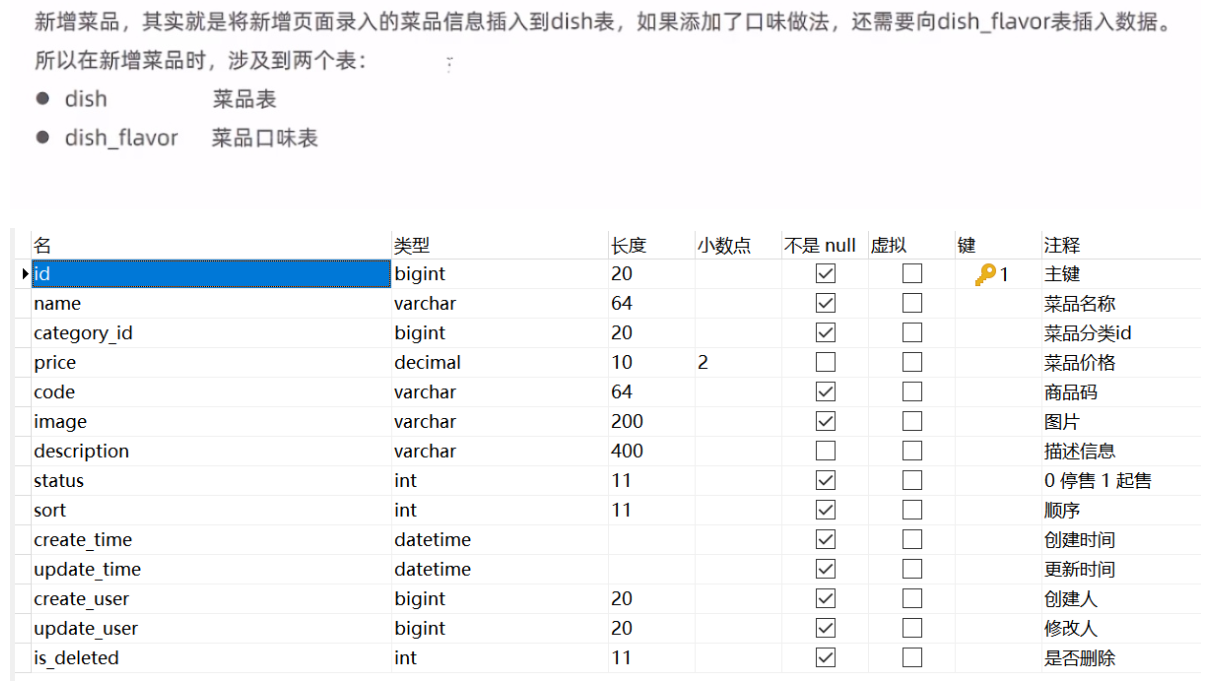

代码开发

创建相关的mapper和service层
package com.itheima.reggie.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.DishFlavor;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface DishFlavorMapper extends BaseMapper<DishFlavor> {
}package com.itheima.reggie.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.DishFlavor;
public interface DishFlavorService extends IService<DishFlavor> {
}package com.itheima.reggie.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.DishFlavor;
import com.itheima.reggie.mapper.DishFlavorMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.service.DishFlavorService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
*/
@Service
public class DishFlavorServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<DishFlavorMapper, DishFlavor> implements DishFlavorService {
}编写controller

先获取和返回菜品分类列表; 前端主要的代码;
// 获取菜品分类列表
const getCategoryList = (params) => {
return $axios({
url: '/category/list',
method: 'get',
params
})
}
if (res.code === 1) {
this.dishList = res.data //这里就相当于把所有的category对象的数据赋值给dishList
}
这是菜品分类和数据双向绑定的前端代码: 我们返回的是一个集合
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item
label="菜品分类:"
prop="categoryId"
>
<el-select
v-model="ruleForm.categoryId"
placeholder="请选择菜品分类"
>
<el-option v-for="(item,index) in dishList" :key="index" :label="item.name" :value="item.id" />
</el-select>
</el-form-item>在CategoryController书写查询代码不过这里的返回值和参数接收值可能和自己想的有点不一样。。。这个的返回值和参数值 值得多思考一下 这里之所以返回list集合是因为这个要展示的数据是引用类型的数据集集合可以存放任意类型的数据
/**
* 根据条件查询分类数据
* @param category
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/list")
//这个接口接收到参数其实就是一个前端传过来的type,这里之所以使用Category这个类来接受前端的数据是为了以后方便
//因为这个Category类里面包含了type这个数据,返回的数据多了你自己用啥取啥就行
private R<List<Category>> list(Category category){
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper<Category> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper();
//添加查询条件
queryWrapper.eq(category.getType() != null,Category::getType,category.getType());
//添加排序条件 使用两个排序条件,如果sort相同的情况下就使用更新时间进行排序
queryWrapper.orderByAsc(Category::getSort).orderByDesc(Category::getUpdateTime);
List<Category> list = categoryService.list(queryWrapper);
return R.success(list);
}测试的返回数据:
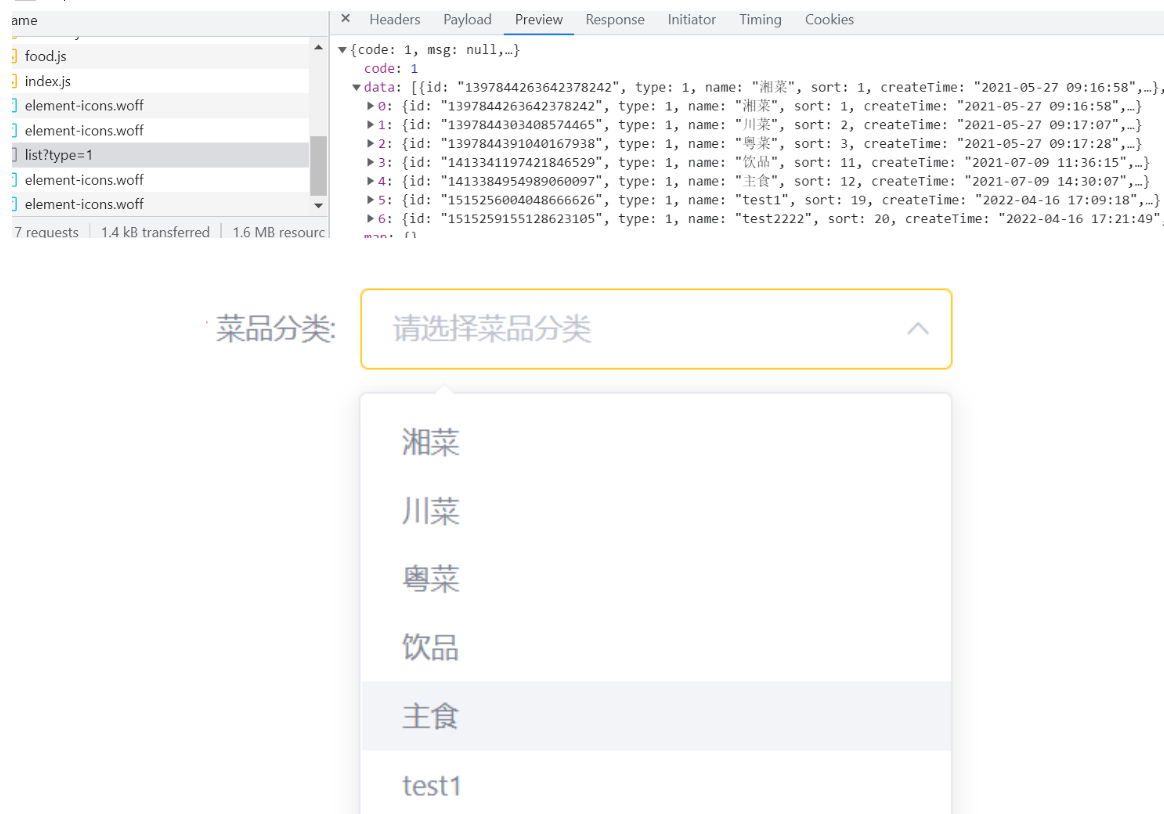
接收页面提交的数据涉及两张表
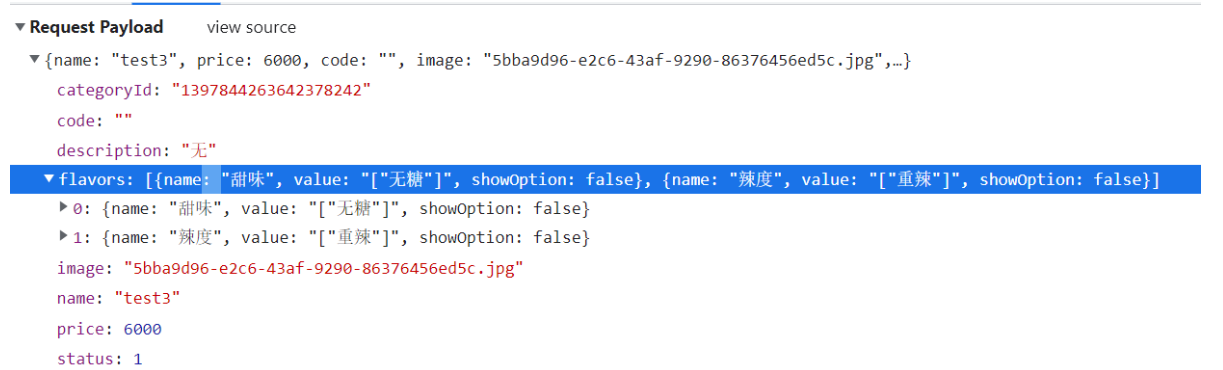
点击保存按钮的时候把前端的json数据提交到后台后台接收数据对数据进行处理要与两张表打交道一个是dish一个是dish_flavor表
先用前端页面向后端发一次请求看看前端具体的请求是什么我们好写controller然后再看前端提交携带的参数是什么我们好选择用什么类型的数据来接收
看下图这是前端传过来的具体参数我们需要什么参数类型来接收这些数据就大概知道了因为这里传过来的参数比较复杂所以这里有两种方式进行封装第一创建与这些数据对应的实体类dto 第二使用map来接收

这里我们选择使用第一种方式
package com.itheima.reggie.dto;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Dish;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.DishFlavor;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Data
public class DishDto extends Dish {
private List<DishFlavor> flavors = new ArrayList<>();
private String categoryName; //后面要用的
private Integer copies; //后面要用的
} 
前端关键代码
<el-button
type="primary"
@click="submitForm('ruleForm')"
>
保存
</el-button>
let params = {...this.ruleForm}
// params.flavors = this.dishFlavors
params.status = this.ruleForm ? 1 : 0
params.price *= 100 //存到数据库的时候是以分为单位所以这里x100
params.categoryId = this.ruleForm.categoryId
params.flavors = this.dishFlavors.map(obj => ({ ...obj, value: JSON.stringify(obj.value) }))
if (this.actionType == 'add') {
delete params.id
addDish(params).then(res => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('菜品添加成功')
if (!st) {
this.goBack()
} else { ....
// 新增接口
const addDish = (params) => {
return $axios({
url: '/dish',
method: 'post',
data: { ...params }
})
}后端代码
在DishService中新增一个方法
//新增菜品,同时插入菜品对应的口味数据,需要同时操作两张表:dish dish_flavor
void saveWithFlavor(DishDto dishDto);相关的实现
@Autowired
private DishFlavorService dishFlavorService;
/**
* 新增菜品同时保存对应的口味数据
* @param dishDto
*/
@Override
@Transactional //涉及到对多张表的数据进行操作,需要加事务需要事务生效,需要在启动类加上事务注解生效
public void saveWithFlavor(DishDto dishDto) {
//保存菜品的基本信息到菜品表dish中
this.save(dishDto);
Long dishId = dishDto.getId();
//为了把dishId set进flavors表中
//拿到菜品口味
List<DishFlavor> flavors = dishDto.getFlavors();
//这里对集合进行赋值 可以使用循环或者是stream流
flavors = flavors.stream().map((item) ->{
//拿到的这个item就是这个DishFlavor集合
item.setDishId(dishId);
return item; //记得把数据返回去
}).collect(Collectors.toList()); //把返回的集合搜集起来,用来被接收
//把菜品口味的数据到口味表 dish_flavor 注意dish_flavor只是封装了name value 并没有封装dishId(从前端传过来的数据发现的,然而数据库又需要这个数据)
dishFlavorService.saveBatch(dishDto.getFlavors()); //这个方法是批量保存
}在启动类开启事务 加上这个注解就行 @EnableTransactionManagement
controller 层的代码
package com.itheima.reggie.controller;
import com.itheima.reggie.common.R;
import com.itheima.reggie.dto.DishDto;
import com.itheima.reggie.service.DishService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/16
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/dish")
@Slf4j
public class DishController {
@Autowired
private DishService dishService;
/**
* 新增菜品
* @param dishDto
* @return
*/
@PostMapping
public R<String> save(@RequestBody DishDto dishDto){ //前端提交的是json数据的话我们在后端就要使用这个注解来接收参数否则接收到的数据全是null
dishService.saveWithFlavor(dishDto);
return R.success("新增菜品成功");
}
}功能测试记得功能测试
菜品信息分页查询(功能完善里面的代码要熟悉,有集合泛型的转换对象copy)
需求分析


图片下载的请求前面已经写好了前端也写好了相关的请求所以第二步的图片下载和展示就不需要我们管了
代码编写
controller层的代码:不过这里是有bug的后面会改善
/**
* 菜品信息分页查询
* @param page
* @param pageSize
* @param name
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/page")
public R<Page> page(int page,int pageSize,String name){
//构造一个分页构造器对象
Page<Dish> dishPage = new Page<>(page,pageSize);
//构造一个条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper<Dish> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加过滤条件 注意判断是否为空 使用对name的模糊查询
queryWrapper.like(name != null,Dish::getName,name);
//添加排序条件 根据更新时间降序排
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Dish::getUpdateTime);
//去数据库处理分页 和 查询
dishService.page(dishPage,queryWrapper);
//因为上面处理的数据没有分类的id,这样直接返回R.success(dishPage)虽然不会报错但是前端展示的时候这个菜品分类这一数据就为空
return R.success(dishPage);
}功能完善引入了DishDto
package com.itheima.reggie.dto;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.Dish;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.DishFlavor;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Data
public class DishDto extends Dish {
private List<DishFlavor> flavors = new ArrayList<>();
private String categoryName;
private Integer copies; //后面用的
}/**
* 菜品信息分页查询
* @param page
* @param pageSize
* @param name
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/page")
public R<Page> page(int page,int pageSize,String name){
//构造一个分页构造器对象
Page<Dish> dishPage = new Page<>(page,pageSize);
Page<DishDto> dishDtoPage = new Page<>(page,pageSize);
//上面对dish泛型的数据已经赋值了这里对DishDto我们可以把之前的数据拷贝过来进行赋值
//构造一个条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper<Dish> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加过滤条件 注意判断是否为空 使用对name的模糊查询
queryWrapper.like(name != null,Dish::getName,name);
//添加排序条件 根据更新时间降序排
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Dish::getUpdateTime);
//去数据库处理分页 和 查询
dishService.page(dishPage,queryWrapper);
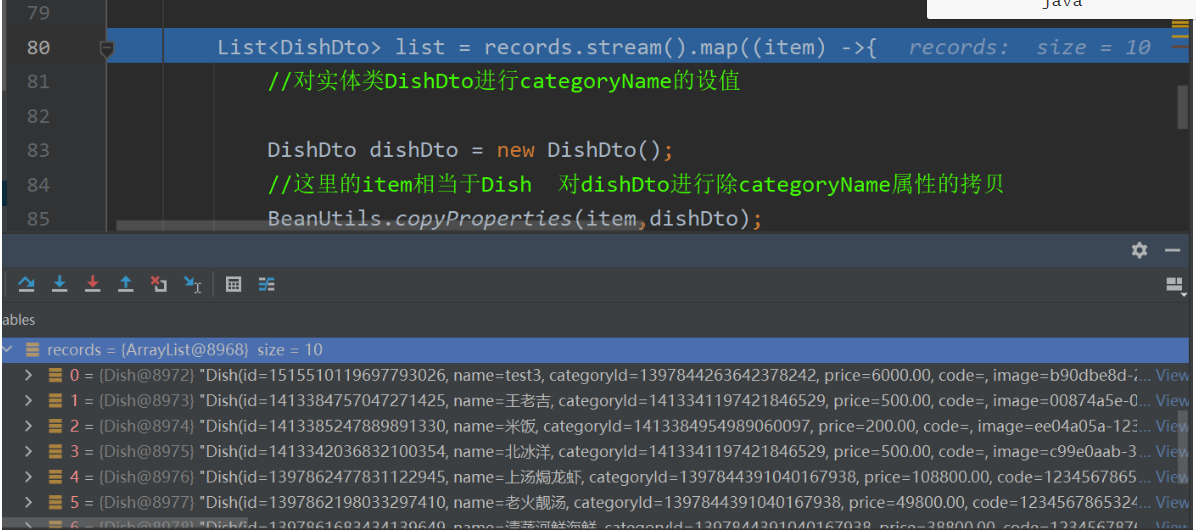
//获取到dish的所有数据 records属性是分页插件中表示分页中所有的数据的一个集合
List<Dish> records = dishPage.getRecords();
List<DishDto> list = records.stream().map((item) ->{
//对实体类DishDto进行categoryName的设值
DishDto dishDto = new DishDto();
//这里的item相当于Dish 对dishDto进行除categoryName属性的拷贝
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item,dishDto);
//获取分类的id
Long categoryId = item.getCategoryId();
//通过分类id获取分类对象
Category category = categoryService.getById(categoryId);
if ( category != null){
//设置实体类DishDto的categoryName属性值
String categoryName = category.getName();
dishDto.setCategoryName(categoryName);
}
return dishDto;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//对象拷贝 使用框架自带的工具类第三个参数是不拷贝到属性
BeanUtils.copyProperties(dishPage,dishDtoPage,"records");
dishDtoPage.setRecords(list);
//因为上面处理的数据没有分类的id,这样直接返回R.success(dishPage)虽然不会报错但是前端展示的时候这个菜品分类这一数据就为空
//所以进行了上面的一系列操作
return R.success(dishDtoPage);
}records的值 protected List<T> records;
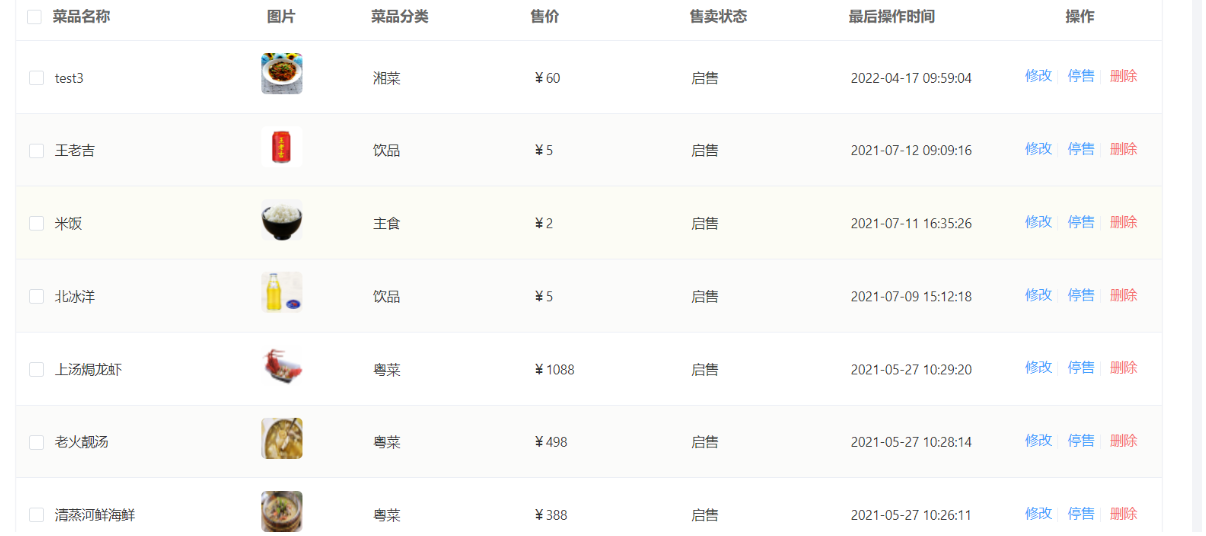
功能测试
修改菜品(回显和保存修改都是两张表)
需求分析
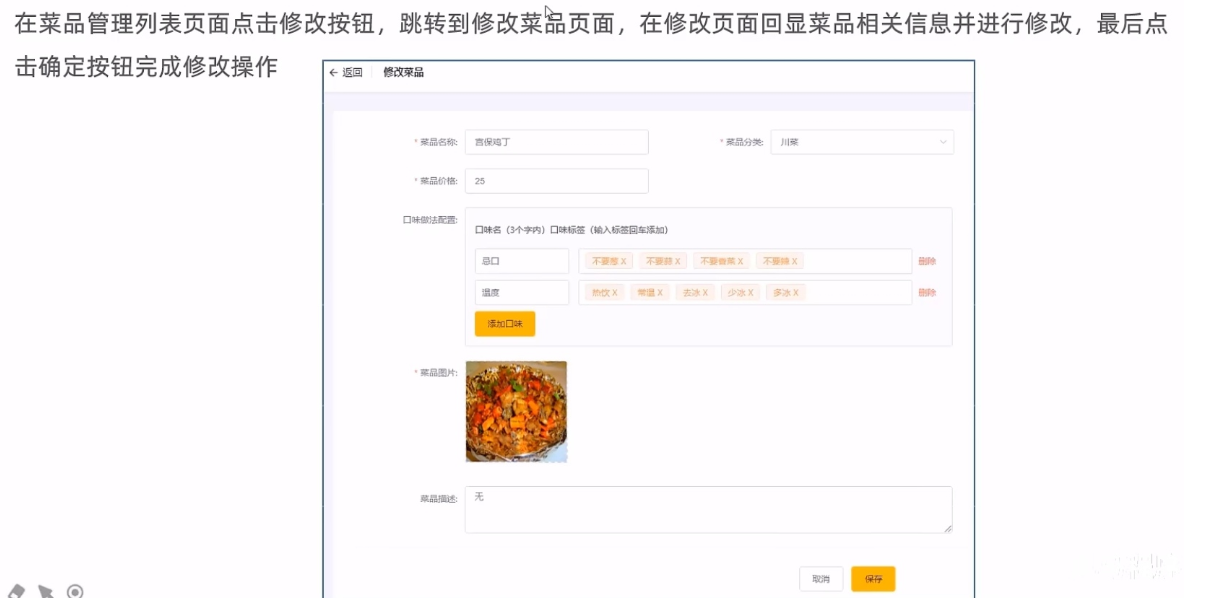
代码开发

第一次交互的后端代码已经完成了菜品分类的信息前面做新增菜品的时候就已经完成了这里前端发一个相关接口的请求就行
第三次交互图片的下载前面也已经写了所以前端直接发生请求就行
菜品信息的回显
在service添加自己要实现的方法
//根据id来查询菜品信息和对应的口味信息
DishDto getByIdWithFlavor(Long id);方法的 实现
@Autowired
private DishFlavorService dishFlavorService;
/**
* 根据id来查询菜品信息和对应的口味信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Override
public DishDto getByIdWithFlavor(Long id) {
//查询菜品的基本信息 从dish表查询
Dish dish = this.getById(id);
//查询当前菜品对应的口味信息,从dish_flavor查询 条件查询
LambdaQueryWrapper<DishFlavor> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(DishFlavor::getDishId,dish.getId());
List<DishFlavor> flavors = dishFlavorService.list(queryWrapper);
//然后把查询出来的flavors数据set进行 DishDto对象
DishDto dishDto = new DishDto();
//把dish表中的基本信息copy到dishDto对象因为才创建的dishDto里面的属性全是空
BeanUtils.copyProperties(dish,dishDto);
dishDto.setFlavors(flavors);
return dishDto;
}controller 层的编写
/**
* 根据id来查询菜品信息和对应的口味信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public R<DishDto> get(@PathVariable Long id){ //这里返回什么数据是要看前端需要什么数据,不能直接想当然的就返回Dish对象
DishDto dishDto = dishService.getByIdWithFlavor(id);
return R.success(dishDto);
}保存修改(重点)
保存修改设计两张表的数据的修改
DishService中添加自己实现的方法
//更新菜品信息同时还更新对应的口味信息
void updateWithFlavor(DishDto dishDto);相关的实现
@Override
@Transactional
public void updateWithFlavor(DishDto dishDto) {
//更新dish表的基本信息 因为这里的dishDto是dish的子类
this.updateById(dishDto);
//更新口味信息---》先清理再重新插入口味信息
//清理当前菜品对应口味数据---dish_flavor表的delete操作
LambdaQueryWrapper<DishFlavor> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper();
queryWrapper.eq(DishFlavor::getDishId,dishDto.getId());
dishFlavorService.remove(queryWrapper);
//添加当前提交过来的口味数据---dish_flavor表的insert操作
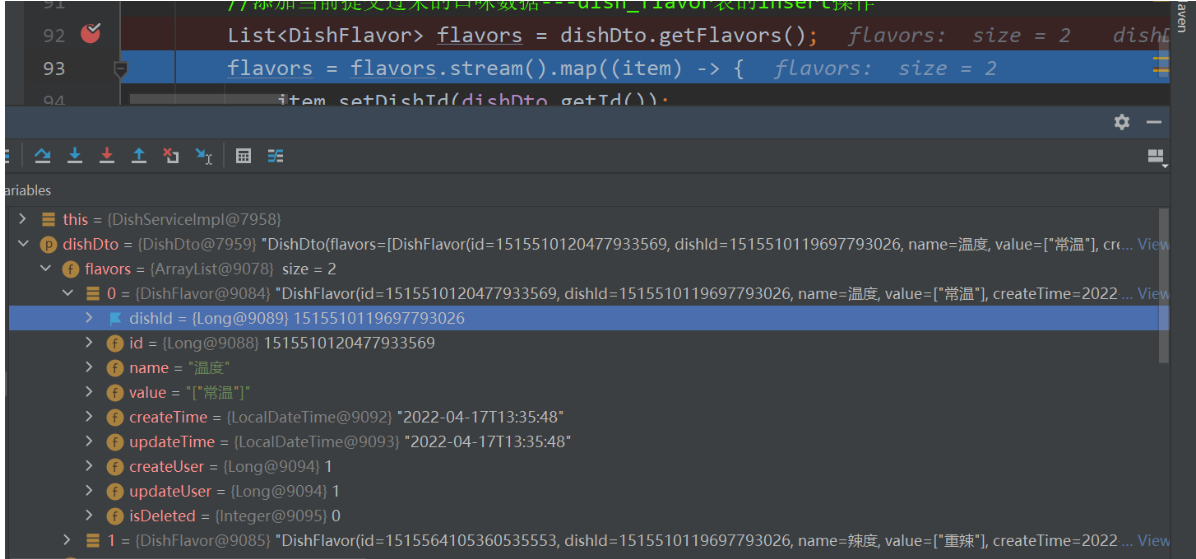
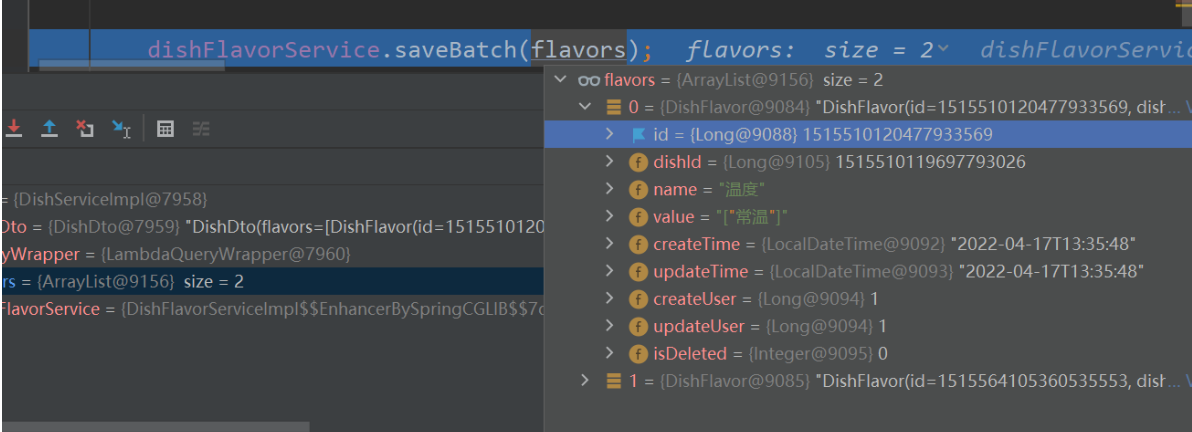
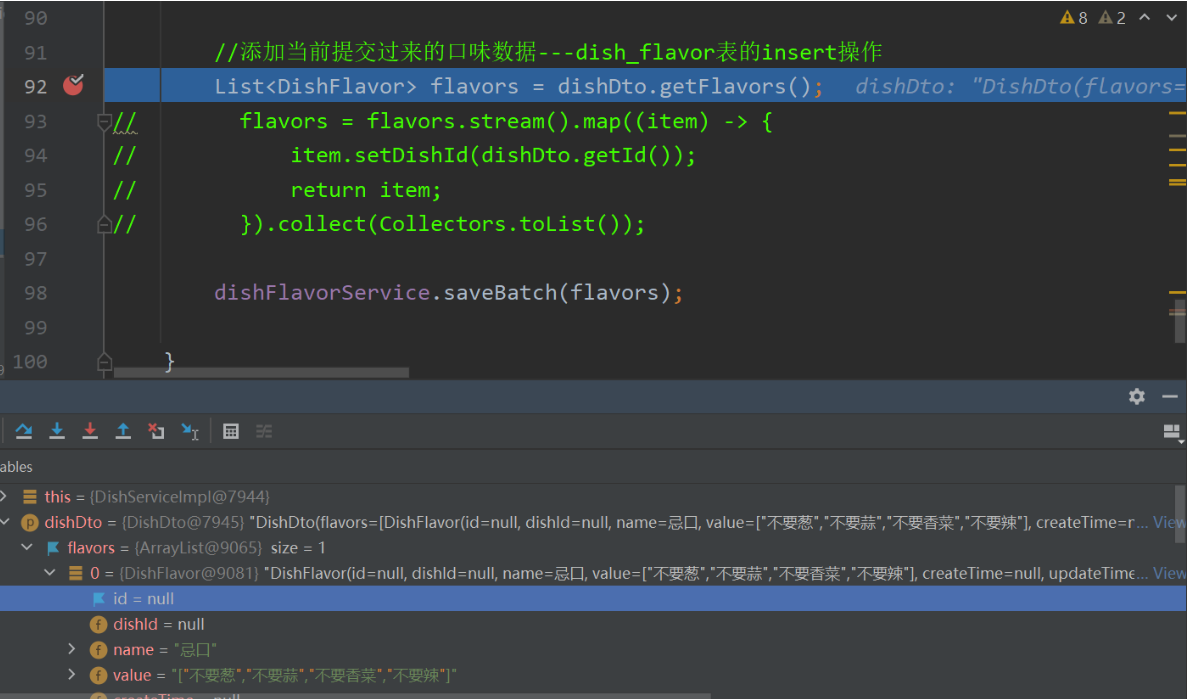
List<DishFlavor> flavors = dishDto.getFlavors();
//下面这段流的代码我注释,然后测试发现一次是报dishId没有默认值(先测)两次可以得到结果(后测重新编译过清除缓存过),相隔半个小时
//因为这里拿到的flavorsz只有name和value(这是在设计数据封装的问题),不过debug测试的时候发现有时候可以拿到全部数据,有时候又不可以... 所以还是加上吧。。。。。
flavors = flavors.stream().map((item) -> {
item.setDishId(dishDto.getId());
return item;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
dishFlavorService.saveBatch(flavors);
}小插曲
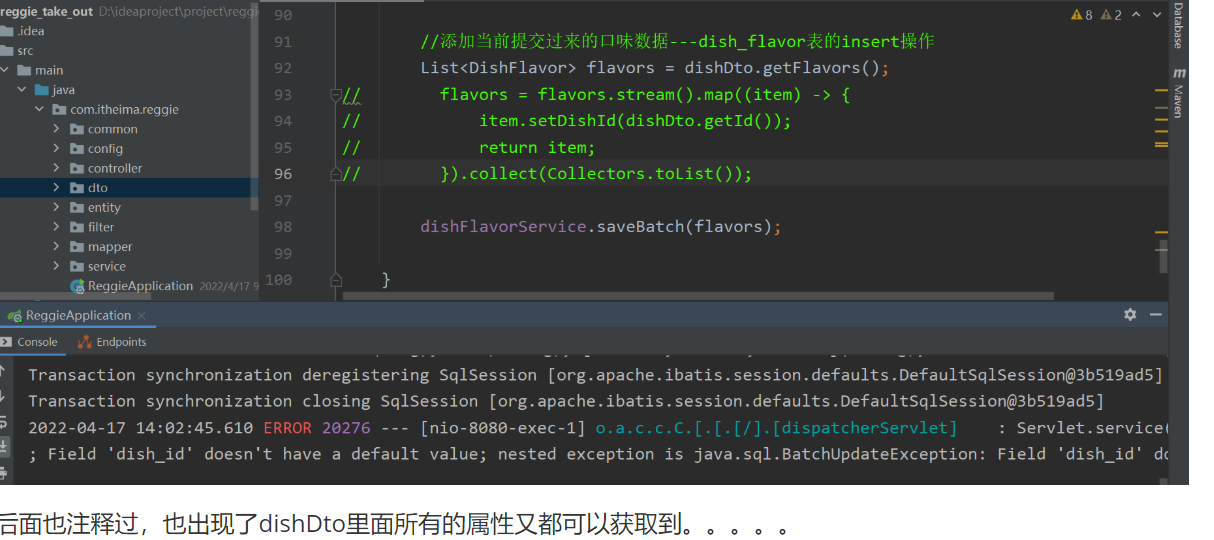
stream流没有被注释的时候dishDto里面所有的属性都可以获取的
注释掉的话debug发现传进来的dishDto中的dishId为null以及id全为null那么是不是意味着前面的使用id查询的语句也执行失败
需要自己单独实现的功能
见我的另一篇博客(8条消息) 瑞吉外卖项目剩余功能补充_未来很长别只看眼前的博客-CSDN博客
九、套餐管理
需求分析:
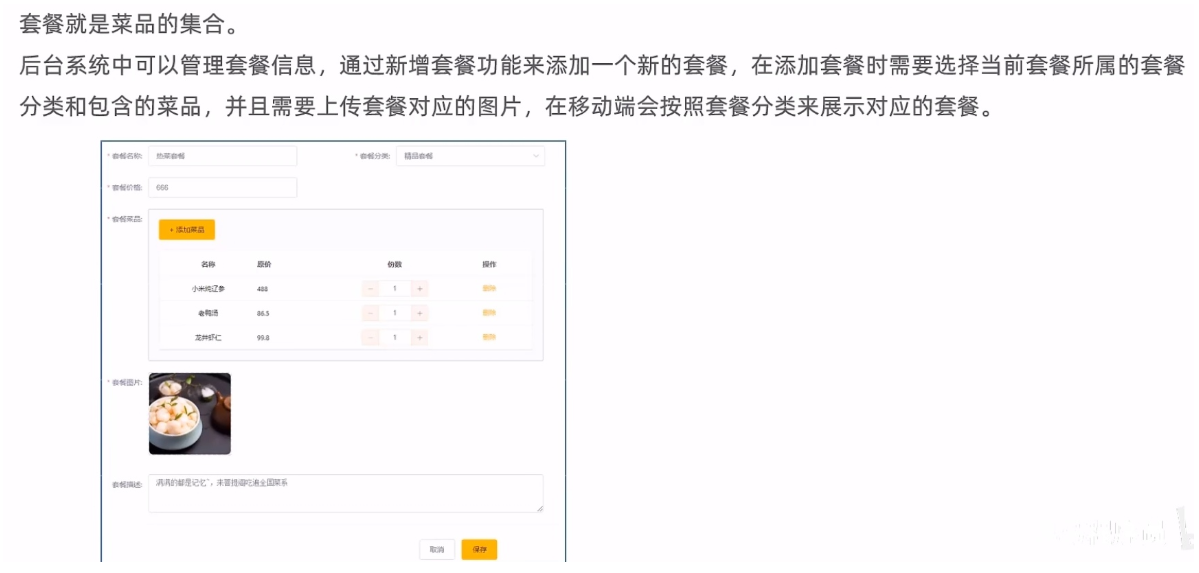
数据模型

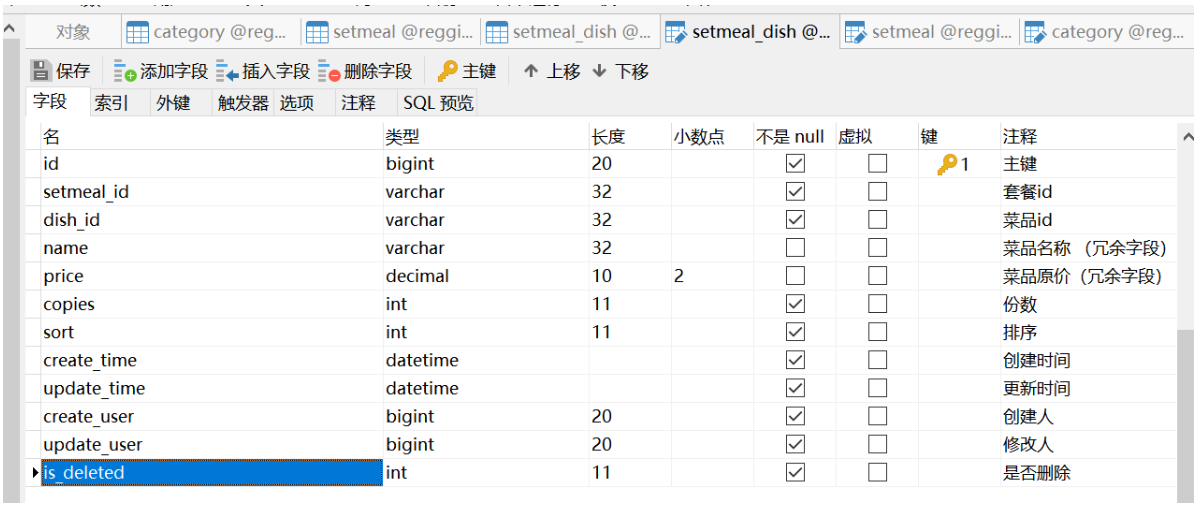
代码开发
准备工作

创建mapper
package com.itheima.reggie.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.SetmealDish;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface SetmealDishMapper extends BaseMapper<SetmealDish> {
}创建service
package com.itheima.reggie.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.SetmealDish;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/17
*/
public interface SetmealDishService extends IService<SetmealDish> {
}package com.itheima.reggie.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.itheima.reggie.entity.SetmealDish;
import com.itheima.reggie.mapper.SetmealDishMapper;
import com.itheima.reggie.service.SetmealDishService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author LJM
* @create 2022/4/17
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class SetmealDishServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<SetmealDishMapper, SetmealDish> implements SetmealDishService {
}添加菜品数据回显
controller层代码

第一个交互前面写了分类管理通过type的值来控制在前端展示的是 菜品分类(type=1) 或者是 套餐分类type=2
第二个交互前面也写了在categorycontroller里面的list方法
第四和第五前面也写了
第三个交互前端请求的地址
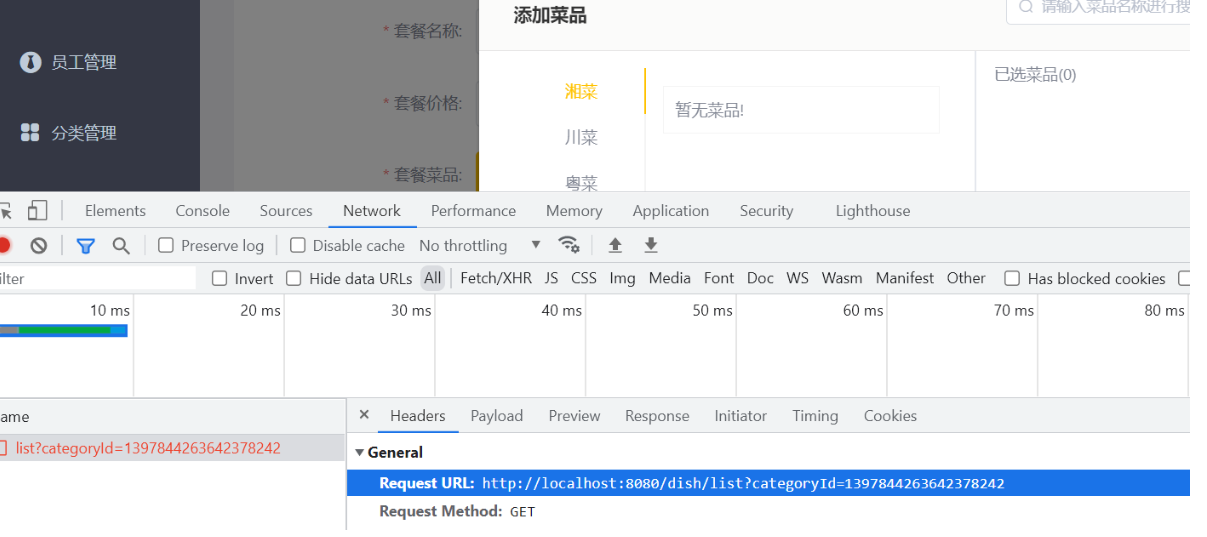
在DishController书写代码
/**
* 根据条件查询对应的菜品数据
* @param dish
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/list")
public R<List<Dish>> list(Dish dish){ //会自动映射的
//这里可以传categoryId,但是为了代码通用性更强,这里直接使用dish类来接受因为dish里面是有categoryId的,以后传dish的其他属性这里也可以使用
//构造查询条件
LambdaQueryWrapper<Dish> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(dish.getCategoryId() != null ,Dish::getCategoryId,dish.getCategoryId());
//添加条件查询状态为1起售状态的菜品
queryWrapper.eq(Dish::getStatus,1);
//添加排序条件
queryWrapper.orderByAsc(Dish::getSort).orderByDesc(Dish::getUpdateTime);
List<Dish> list = dishService.list(queryWrapper);
return R.success(list);
}控制台输出的sql语句
SELECT id,name,category_id,price,code,image,description,status,sort,create_time,update_time,create_user,update_user,is_deleted FROM dish WHERE (category_id = ? AND status = ?) ORDER BY sort ASC,update_time DESC保存添加套餐理解里面的关系有点困难
实现要求点击保存按钮发送ajax请求,将套餐相关的数据以json形式提交到服务端
前端提交请求
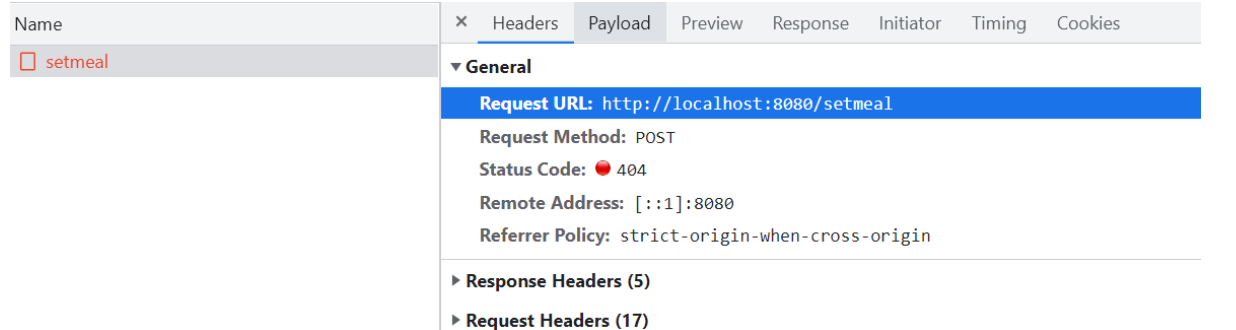
前端携带的参数重要
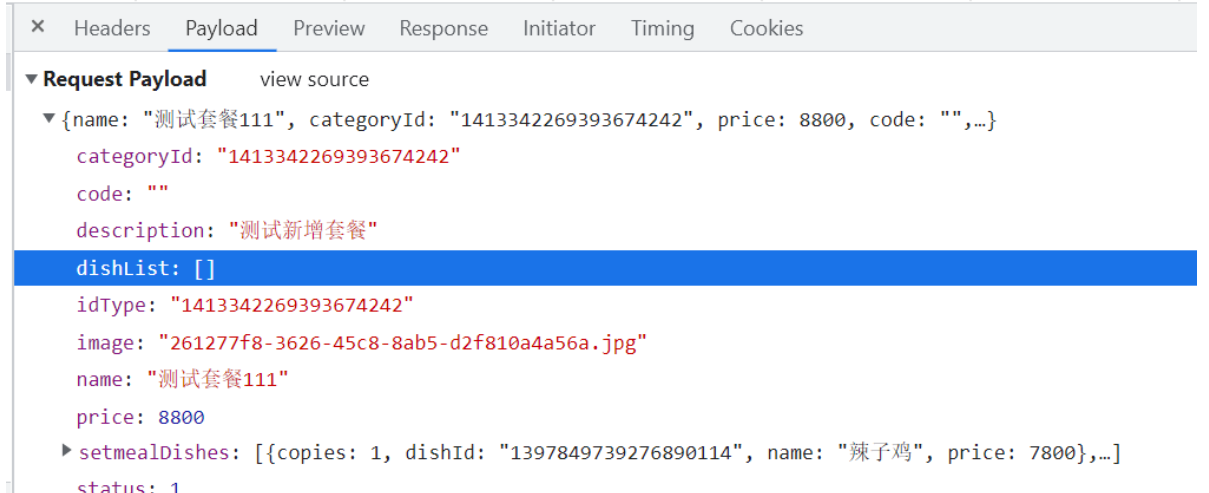
根据前端传过来的数据我们可以在后端确定我们需要在后端使用什么来接受前端的参数
编写controller上面的dishList我们数据库并不需要这个数据所以接收数据的实体类没有dishList这个属性也没有关系前端传过来的数据都是自动映射到接收数据的实体类的属性上的没有对应起来就不会映射。
涉及两张表的操作套餐表和菜品表
/**
* 新增套餐
* 涉及两张表的操作套餐表和菜品表
* @param setmealDto
* @return
*/
@PostMapping
public R<String> save(@RequestBody SetmealDto setmealDto){
setmealService.saveWithDish(setmealDto);
return R.success("新增套餐成功");
}SetmealService中添加自定义的方法
/**
* 新增套餐同时需要保存套餐和菜品的关联关系
* @param setmealDto
*/
void saveWithDish(SetmealDto setmealDto);@Autowired
SetmealDishService setmealDishService;
/**
* 新增套餐同时需要保存套餐和菜品的关联关系
* @param setmealDto
*/
@Transactional
@Override
public void saveWithDish(SetmealDto setmealDto) {
//保存套餐的基本信息操作setmeal,执行insert
this.save(setmealDto);
log.info(setmealDto.toString()); //查看一下这个套餐的基本信息是什么
//保存套餐和菜品的关联信息操作setmeal_dish ,执行insert操作
List<SetmealDish> setmealDishes = setmealDto.getSetmealDishes();
//注意上面拿到的setmealDishes是没有setmeanlId这个的值的通过debug可以发现
setmealDishes.stream().map((item)->{
item.setSetmealId(setmealDto.getId());
return item; //这里返回的就是集合的泛型
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
setmealDishService.saveBatch(setmealDishes); //批量保存
}功能测试自己测试
套餐信息分页查询
需求分析
代码开发
前端发起的请求以及携带的参数
查询分页

controller层代码编写
/**
* 套餐分页查询
* @param page
* @param pageSize
* @param name
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/page")
public R<Page> page(int page, int pageSize, String name){
//分页构造器对象
Page<Setmeal> pageInfo = new Page<>(page,pageSize);
//构造条件查询对象
LambdaQueryWrapper<Setmeal> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加查询条件根据name进行like模糊查询
queryWrapper.like(name != null,Setmeal::getName,name);
//添加排序条件根据更新时间降序排列
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Setmeal::getUpdateTime);
setmealService.page(pageInfo,queryWrapper);
/**
* 注意如果这里直接返回R.success(pageInfo)
* 虽然不会报错但是分页的数据的套餐分类的名字是显示不了的
* 因为这个分页的泛型是Setmeal,Setmeal只封装了f分类的Id categoryId没有分类的名称 name
* 所以又需要进行name的获取和设值
*/
return R.success(pageInfo);
}bug修复
/**
* 套餐分页查询
* @param page
* @param pageSize
* @param name
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/page")
public R<Page> page(int page, int pageSize, String name){
//分页构造器对象
Page<Setmeal> pageInfo = new Page<>(page,pageSize);
Page<SetmealDto> dtoPage = new Page<>(page,pageSize);
//构造条件查询对象
LambdaQueryWrapper<Setmeal> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加查询条件根据name进行like模糊查询
queryWrapper.like(name != null,Setmeal::getName,name);
//添加排序条件根据更新时间降序排列
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Setmeal::getUpdateTime);
setmealService.page(pageInfo,queryWrapper);
//对象的拷贝 注意这里要把分页数据的全集合records给忽略掉
BeanUtils.copyProperties(pageInfo,dtoPage,"records");
List<Setmeal> records = pageInfo.getRecords();
//对records对象进行处理然后封装好赋值给list
List<SetmealDto> list = records.stream().map((item)->{
SetmealDto setmealDto = new SetmealDto();
//对setmealDto进行除categoryName的属性进行拷贝(因为item里面没有categoryName)
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item,setmealDto);
//获取分类id 通过分类id获取分类对象 然后再通过分类对象获取分类名
Long categoryId = item.getCategoryId();
//根据分类id获取分类对象 判断是否为null
Category category = categoryService.getById(categoryId);
if (category != null){
String categoryName = category.getName();
setmealDto.setCategoryName(categoryName);
}
return setmealDto;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
dtoPage.setRecords(list);
return R.success(dtoPage);
}删除套餐
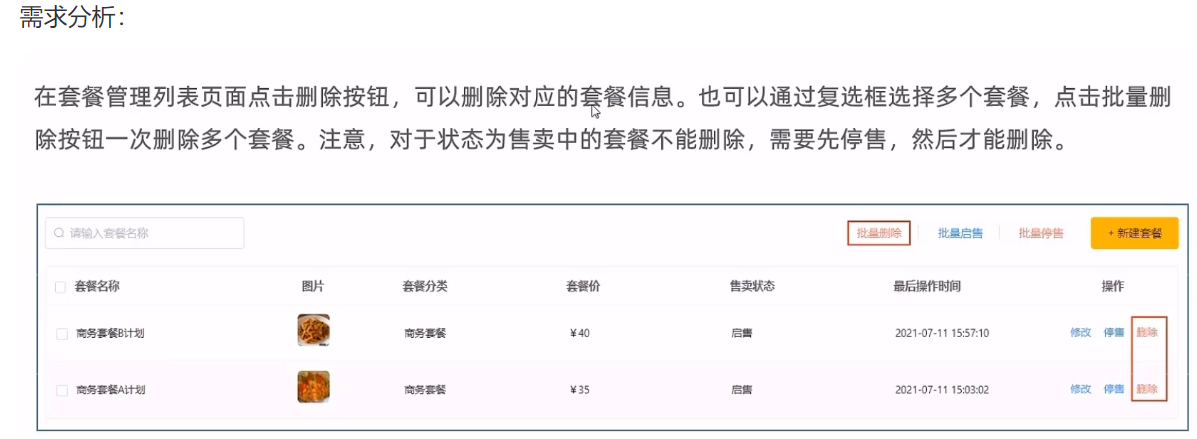
代码开发
单个套餐删除前端发的请求和携带的参数
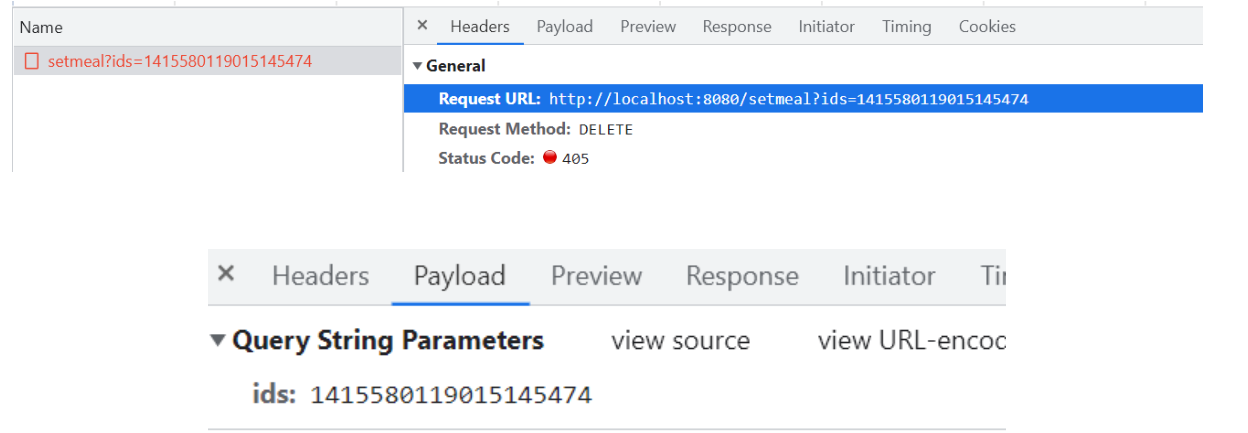
套餐批量删除前端发的请求和携带的参数
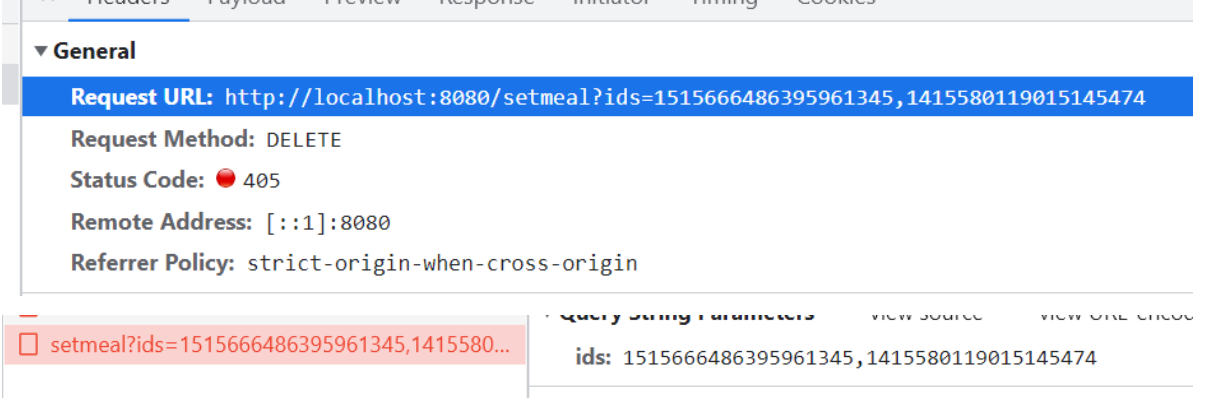
controller层开发
在SetmealService中添加自定义的方法
/**
* 删除套餐同时需要删除套餐和菜品的关联数据
* @param ids
*/
void removeWithDish(List<Long> ids);实现该方法
/**
* 删除套餐同时需要删除套餐和菜品的关联数据
* @param ids
*/
@Override
@Transactional
public void removeWithDish(List<Long> ids) {
//sql语句应该是这样的:select count(*) setmeal where id in () and status = 1;
//查询套餐的状态看是否可以删除
LambdaQueryWrapper<Setmeal> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper();
queryWrapper.in(Setmeal::getId,ids);
queryWrapper.eq(Setmeal::getStatus,1);
int count = this.count(queryWrapper);
//如果不能删除抛出一个业务异常
if (count > 0){
throw new CustomException("套餐正在售卖中,不能删除");
}
//如果可以删除先删除套餐表中的数据--setmeal
this.removeByIds(ids);
//删除关系表中的数据--setmeal_dish
//delete from setmeal_dish where setmeal_id in (1,2,3)
LambdaQueryWrapper<SetmealDish> lambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper();
lambdaQueryWrapper.in(SetmealDish::getSetmealId,ids);
setmealDishService.remove(lambdaQueryWrapper);
}功能测试
需要自己单独实现的功能
下面功能的具体代码在我的另一篇博客(8条消息) 瑞吉外卖项目剩余功能补充_未来很长别只看眼前的博客-CSDN博客
套餐管理的启售停售
套餐管理的修改
后台订单展示和查询
移动端开发
见另一篇博客瑞吉外卖移动端开发 笔记 基于springBoot+mybatis-plus_未来很长别只看眼前的博客-CSDN博客

