Java注解详解
| 阿里云国内75折 回扣 微信号:monov8 |
| 阿里云国际,腾讯云国际,低至75折。AWS 93折 免费开户实名账号 代冲值 优惠多多 微信号:monov8 飞机:@monov6 |
什么是注解
用一个词就可以描述注解那就是元数据即一种描述数据的数据。所以可以说注解就是源代码的元数据
元注解
JDK1.5之后内部提供的注解
@Deprecated意思是“废弃的过时的”@Override意思是“重写、覆盖”@SuppressWarnings意思是“压缩警告”@Documented–注解是否将包含在JavaDoc中@Target–注解用于什么地方@Inherited– 是否允许子类继承该注解@Retention–什么时候使用该注解@Repeatablesince jdk1.8-多次赋值@SafeVarargssince jdk1.7@FunctionalInterfacesince jdk1.8-函数式接口
@Retention
定义注解的生命周期
-
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE在编译阶段丢弃。这些注解在编译结束之后就不再有任何意义所以它们不会写入字节码。@Override,
@SuppressWarnings都属于这类注解。 -
RetentionPolicy.CLASS在类加载的时候丢弃。在字节码文件的处理中有用。注解默认使用这种方式。
-
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME始终不会丢弃运行期也保留该注解因此可以使用反射机制读取该注解的信息。我们自定义的注解通常使用这种方式。
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Retention {
/**
* Returns the retention policy.
* @return the retention policy
*/
RetentionPolicy value();
}
@Target
表示该注解用于什么地方。如果不明确指出该注解可以放在任何地方。以下是一些可用的参数。需要说明的是属性的注解是兼容的如果你想给7个属性都添加注解仅仅排除一个属性那么你需要在定义target包含所有的属性。
-
ElementType.TYPE: 用于描述类、接口或enum声明 -
ElementType.FIELD: 用于描述字段 -
ElementType.METHOD用于描述方法 -
ElementType.PARAMETER用于描述参数 -
ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR用于描述构造函数 -
ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE用于描述本地变量 -
ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE用于描述注解 -
ElementType.PACKAGE用于记录java文件的package信息 包注解不能修饰常规Java文件中包声明或包引入语句而只能用于修饰
package-info.java文件中的包声明语句(也不能修饰package-info.java文件中的包引入语句)。
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Target {
ElementType[] value();
}
JDK1.8新增ElementType
-
ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER表示该注解能写在类型变量的声明语句中(如:泛型声明)class C<@AAA T> { T get() { return null; } } @Target(ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER) @interface AAA { }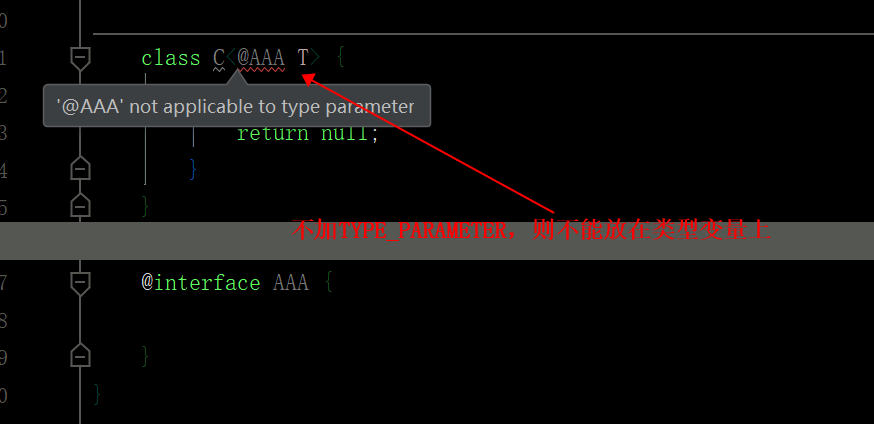
-
ElementType.TYPE_USE表示该注解能写在使用类型的任何语句中
@Inherited
Inherited 是继承的意思但是它并不是说注解本身可以继承而是说如果一个超类被 @Inherited 注解过的注解进行注解的话那么如果它的子类没有被任何注解应用的话那么这个子类就继承了超类的注解。
说的比较抽象。代码来解释
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Test {}
@Test
public class A {}
public class B extends A {}
//被其他注解 应用了
@Other
public class C extends A
{}
注解 Test 被 @Inherited 修饰之后类 A 被 Test 注解类 B 继承 A,类 B 也拥有 Test 这个注解。
但是C不拥有@Test注解因为被@Other注解应用了
@Repeatable
在JDK1.8之前注解同时只能被应用一次应用2次会编译错误。
什么样的注解会多次应用呢通常是注解的值可以同时取多个。
举个例子一个人他既是程序员又是产品经理,同时他还是个画家。
@interface Persons {
Person[] value();
}
@Repeatable(Persons.class)
@interface Person{
String role default "";
}
@Person(role="artist")
@Person(role="coder")
@Person(role="PM")
public class SuperMan{
}
注意上面的代码@Repeatable 注解了 Person。而 @Repeatable 后面括号中的类相当于一个容器注解。
什么是容器注解呢就是用来存放其它注解的地方。它本身也是一个注解。
我们再看看代码中的相关容器注解。
@interface Persons {
Person[] value();
}
按照规定它里面必须要有一个 value 的属性属性类型是一个被 @Repeatable 注解过的注解数组注意它是数组。
如果不好理解的话可以这样理解。Persons 是一张总的标签上面贴满了 Person 这种同类型但内容不一样的标签。把 Persons 给一个 SuperMan 贴上相当于同时给他贴了程序员、产品经理、画家的标签。
我们可能对于 @Person(role=”PM”) 括号里面的内容感兴趣它其实就是给 Person 这个注解的 role 属性赋值为 PM .
当一个可重复的注解应用于某个元素时获取不到这个注解的实例而是 注解容器的实例例如是获取不到Person的实例的获取到的是Persons的实例。
@SafeVarargs
参数安全类型注解。它的目的是提醒开发者不要用参数做一些不安全的操作,它的存在会阻止编译器产生 unchecked 这样的警告。它是在 Java 1.7 的版本中加入的。
@SafeVarargs // Not actually safe!
static void m(List<String>... stringLists) {
Object[] array = stringLists;
List<Integer> tmpList = Arrays.asList(42);
array[0] = tmpList; // Semantically invalid, but compiles without warnings
String s = stringLists[0].get(0); // Oh no, ClassCastException at runtime!
}
上面的代码中编译阶段不会报错但是运行时会抛出 ClassCastException 这个异常所以它虽然告诉开发者要妥善处理但是开发者自己还是搞砸了。
@FunctionalInterface
函数式接口注解这个是 Java 1.8 版本引入的新特性。函数式编程很火所以 Java 8 也及时添加了这个特性。
函数式接口 (Functional Interface) 就是一个具有一个方法的普通接口。
注解定义
定义
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME )
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Controller {
String name() default "";
}
注解不支持继承
注解是不支持继承的因此不能使用关键字extends来继承某个@interface但注解在编译后编译器会自动继承java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口
属性
注解内部可以定义一些属性。
语法
类型 属性名() [ default 默认值 ];
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME )
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Controller {
String name() default "";
}
其实从代码的写法上来看注解更像是一种特殊的接口注解的属性定义方式就和接口中定义方法的方式一样而应用了注解的类可以认为是实现了这个特殊的接口。
注解属性支持以下类型
- 所有基本类型int,float,boolean,byte,double,char,long,short
- String
- Class
- enum
- Annotation
- 上述类型的数组
注解的属性必须有明确的值要么使用默认值要么在应用注解时指定值。
注解合并
每个开发人员都应该有过这样的经历在编写某个类或接口的时候需要声明Spring本身的注解@Controller、@Service@Dao又需要声明自己公司编写的注解来完成公司的独特业务然后就悲剧了一个类上边声明了五六个注解茫茫然不知所云。注解本身是好的它可以替我们完成一些事情。但和XML一样过度使用就编程了一种灾难。
于是一种新的替代方案出现了那就是组合注解。比较经典的组合注解就是SpringBoot的@SpringBootApplication注解。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Configuration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
String[] excludeName() default {};
//spring 在解析此处时做特殊处理
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages")
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
//spring 在解析此处时做特殊处理
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses")
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
}
注解应用
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
enum EnumType
{
First ,
Second
}
@interface Reference
{
}
@interface Test
{
String value();
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME )
@Target(value={ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface RequestMapping {
//基本类型
int size() default 0;
//String
String name() default "";
//枚举
EnumType Order() default EnumType.First;
//Class类
Class<?> ClassType() default Void.class;
//注解
Reference Reference() default @Reference;
//数组
int[] Ids() default {1,3,4};
}
@RequestMapping(
size = 5
,name="jack"
,Order=EnumType.Second
,ClassType=Integer.class
,Reference=@Reference
,Ids={4,5,7}
)
@Test("mytest") //当注解仅有一个名称为value的属性时可以省略属性名称
class AAA
{
}
注解提取
通过反射可以获取注解的信息。
Java反射的各个类型都实现了AnnotatedElement接口。AnnotatedElement接口标识一个可以被Java Annotation注解的Java语言元素。在java.lang.reflect包下像ClassMethodFieldConstructorGenericDeclaration泛型声明等Java语法元素对应的实现都需要实现这个接口。
AnnotatedElement接口有个子接口 AnnotatedType其有4个子接口分别对应反射中Type的4个泛型相关的类。
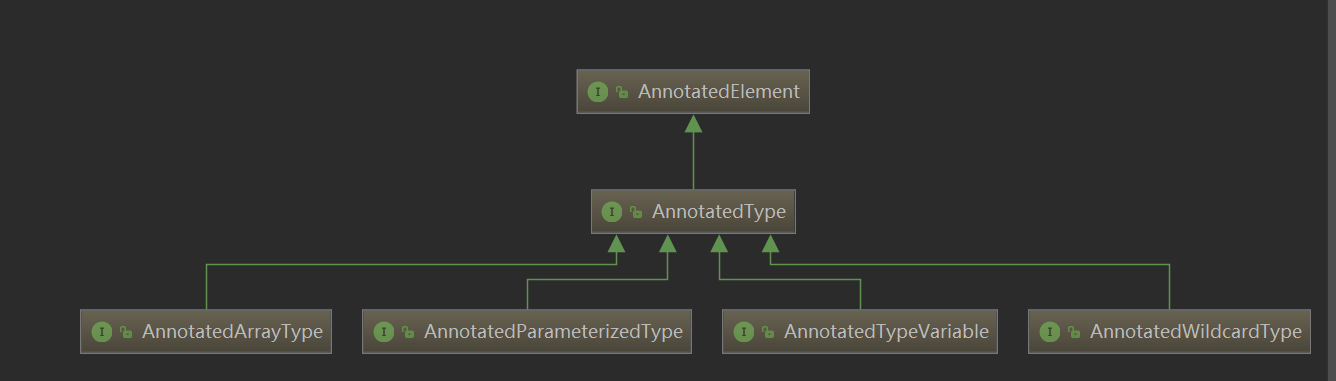
public interface AnnotatedElement {
/** 如果一个注解 present 在这个元素上则返回true。
等价于{@code getAnnotation(annotationClass) != null}
*/
default boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) {
return getAnnotation(annotationClass) != null;
}
/** 返回应用于此元素的指定注解类型的注解实例。
* 没有应用指定的注解类型则返回null。
*/
<T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass);
/**
* 返回所有应用于此元素的注解(实例)
*/
Annotation[] getAnnotations();
/**
考虑父类 @Inherited。
*/
default <T extends Annotation> T[] getAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
T[] result = getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(annotationClass);
if (result.length == 0 && // Neither directly nor indirectly present
this instanceof Class && // the element is a class
AnnotationType.getInstance(annotationClass).isInherited()) { // Inheritable
Class<?> superClass = ((Class<?>) this).getSuperclass();
if (superClass != null) {
// Determine if the annotation is associated with the
// superclass
result = superClass.getAnnotationsByType(annotationClass);
}
}
return result;
}
/** 返回 直接present 于 此元素的指定注解类型的注解实例。
* 没有应用指定的注解类型则返回null。
*/
default <T extends Annotation> T getDeclaredAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
// Loop over all directly-present annotations looking for a matching one
for (Annotation annotation : getDeclaredAnnotations()) {
if (annotationClass.equals(annotation.annotationType())) {
// More robust to do a dynamic cast at runtime instead
// of compile-time only.
return annotationClass.cast(annotation);
}
}
return null;
}
/**
返回 直接 present 和 间接 present 的注解忽略 @Inherited
与 getDeclaredAnnotation 的区别是此方法识别是否是可重复注解。
如果是则即可查找容器注解(返回一个array只有一个元素)也可以查找元素注解(返回一个array可能多个元素)
注意 TYPE_USE 类型的 获取不到。
*/
default <T extends Annotation> T[] getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return AnnotationSupport.
getDirectlyAndIndirectlyPresent(Arrays.stream(getDeclaredAnnotations()).
collect(Collectors.toMap(Annotation::annotationType,
Function.identity(),
((first,second) -> first),
LinkedHashMap::new)),
annotationClass);
}
/**
返回直接应用在元素上的注解而不是派生的。
* @since 1.5
*/
Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations();
}
getDeclaredAnnotationsByTypegetAnnotationsByType获取不到仅使用了TYPE_USE的注解。
Present(存在)
present 指示一个注解使用应用于某个元素。
present是指满足以下任一条件则代表元素上present某个注解
- 元素上**直接 应用(apply to)**某个注解
- 某个被
@Inherited标注的注解能够继承的注解应用于该元素的父类上(此元素没有标记任何其他注解)
直接present元素上**直接 应用(apply to)**某个注解
间接present通过@Repeatable标记一个注解这个注解应用于某个元素时。
关联的(associated)是指满足以下任一条件则代表元素上关联某个注解
- 元素上直接present或者间接present某个注解
- 某个被
@Inherited标注的注解能够继承的注解与该元素的父类是关联的
AnnotatedElement中的方法都是基于注解以何种形式存在于对象上获取元素上的注解的 下表总结了此接口中各方法获取元素注解的范围
| 注解存在的形式 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方法 | 方法 | 直接present | 间接present | present | 关联的 |
| T | getAnnotation(Class annotationClass) | √ | |||
| Annotation[] | getAnnotations() | √ | |||
| T[] | getAnnotationsByType(Class annotationClass) | √ | |||
| T | getDeclaredAnnotation(Class annotationClass) | √ | |||
| Annotation[] | getDeclaredAnnotations() | √ | |||
| T[] | getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class annotationClass) | √ | √ |
public interface AnnotatedType extends AnnotatedElement {
//返回被注解的Type
public Type getType();
}
public interface AnnotatedArrayType extends AnnotatedType {
/** 返回泛型的元素type
*/
AnnotatedType getAnnotatedGenericComponentType();
}
public interface AnnotatedParameterizedType extends AnnotatedType {
/**
烦恼会泛型Type的被注解的实际类型参数
*/
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedActualTypeArguments();
}
public interface AnnotatedTypeVariable extends AnnotatedType {
/**
* 返回类型变量的边界
*/
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedBounds();
}
public interface AnnotatedWildcardType extends AnnotatedType {
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedLowerBounds();
AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedUpperBounds();
}
首先可以通过 Class 对象的 isAnnotationPresent() 方法判断它是否应用了某个注解
public boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) {}
然后通过 getAnnotation() 方法来获取 Annotation 对象。
public <A extends Annotation> A getAnnotation(Class<A> annotationClass) {}
//AA:class
//P3:@Merge的属性
AA.class.getAnnotation(Merge.class).P3();
Class 注解提取相关的方法
//获取super 类型
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedSuperclass() ;
//获取接口类型
public AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedInterfaces();
Method
//返回被注解的参数的 AnnotatedType 。即使被多个注解应用于一个参数也只返回一个AnnotatedType里面的annotations属性包含多个注解实例。
//每个参数返回一个AnnotatedType即使参数没有应用注解。
public AnnotatedType[] getAnnotatedParameterTypes();
//返回参数上应用的Annotation每个参数对应一个 Annotation[]即使参数没有应用注解也返回一个0元素的Annotation[]
public Annotation[][] getParameterAnnotations();
//获取返回值的AnnotatedType
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedReturnType();
getParameterAnnotations获取不到仅使用了TYPE_USE的注解。
Field
//获取字段类型上的注解
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedType();
Constructor
public Annotation[][] getParameterAnnotations();
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedReturnType();
public AnnotatedType getAnnotatedReceiverType();
示例
package demon.research.anno;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*;
public class AnnoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test1();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void test1() throws NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException {
C<Integer> c = new C();
Integer x = c.m(5);
Annotation[] annotations = C.class.getAnnotations();
System.out.println("类上的注解 = " + annotations);
annotations = C.class.getDeclaredAnnotations();
System.out.println("类上的直接定义的注解 = " + annotations);
Method method = C.class.getMethod("m", Integer.class, Integer.class, Integer.class);
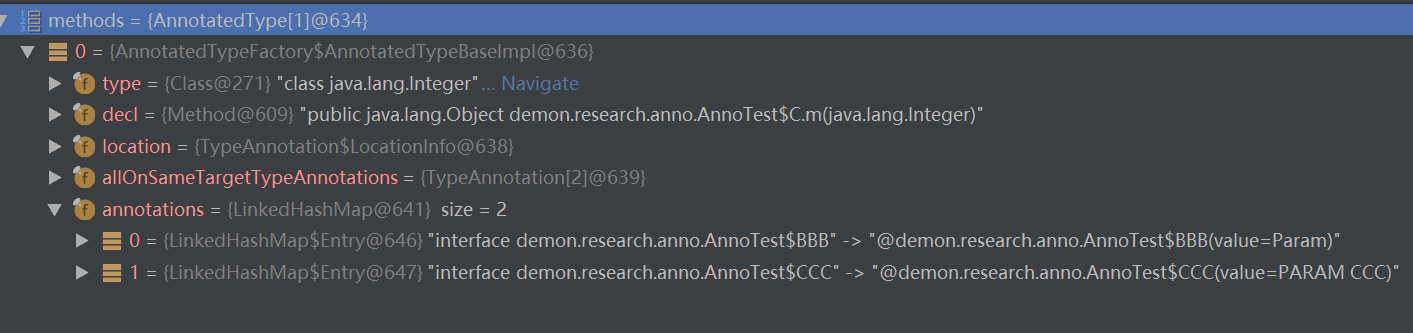
AnnotatedType[] methods = method.getAnnotatedParameterTypes();
Annotation[] annotations1 = methods[0].getAnnotations();
System.out.println("形参上的注解 = " + annotations1[0]);
AnnotatedType methods2 = method.getAnnotatedReturnType();
//CCC 可以获取到
System.out.println("方法返回值的注解 ->CCC = " + methods2.getAnnotation(CCC.class));
//BBB 获取不到
System.out.println("方法返回值的注解 ->BBB = " + methods2.getAnnotation(BBB.class));
/// BBBS 可以获取到
System.out.println("方法返回值的注解 ->BBBS = " + methods2.getAnnotation(BBBS.class));
// 获取不到DDD因为他仅使用了 TYPE_USE
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
System.out.println("方法返回值的注解 = " + parameterAnnotations);
AnnotatedType a = C.class.getDeclaredField("a").getAnnotatedType();
BBBS bbb = a.getAnnotation(BBBS.class);
System.out.println("成员变量上的注解 = " + bbb);
}
@BBB("Class")
@CCC("Class CCC")
@DDD("Class DDD")
static class C<@BBB("Type Param") T> {
@BBB("Field")
@CCC("Field CCC")
@DDD("Field DDD")
private @BBB("Field 222") String a;
// 注解放在此处与放在返回类型前 是一样的效果通过 getAnnotatedReturnType 获取。
@BBB("Method")
@CCC("Method CCC")
@DDD("Method DDD")
public @BBB("Method 222") T m(@BBB("Param") @CCC("PARAM CCC") Integer i) {
@BBB("Local Variable")
Integer xx = 5;
return null;
}
@BBB("Method")
@CCC("Method CCC")
@DDD("Method DDD")
public @BBB("Method 222") T m(
@BBB("Param") @CCC("PARAM CCC") Integer i
, Integer j
, @BBB("Param K") @CCC("PARAM CCC K") @DDD("PARAM DDD K ") Integer k) {
@BBB("Local Variable")
Integer xx = 5;
return null;
}
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = {TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE, ANNOTATION_TYPE, PACKAGE, TYPE_PARAMETER,
TYPE_USE})
@Repeatable(BBBS.class)
@interface BBB {
String value() default "";
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = {TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE, ANNOTATION_TYPE, PACKAGE, TYPE_PARAMETER,
TYPE_USE})
@interface BBBS {
BBB[] value();
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = {TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE, ANNOTATION_TYPE, PACKAGE, TYPE_PARAMETER,
TYPE_USE})
@interface CCC {
String value() default "";
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = {TYPE_USE})
@interface DDD {
String value() default "";
}
}
输出
类上的注解 = [Ljava.lang.annotation.Annotation;@180bc464
类上的直接定义的注解 = [Ljava.lang.annotation.Annotation;@1324409e
形参上的注解 = @demon.research.anno.AnnoTest$BBB(value=Param)
方法返回值的注解 ->CCC = @demon.research.anno.AnnoTest$CCC(value=Method CCC)
方法返回值的注解 ->BBB = null
方法返回值的注解 ->BBBS = @demon.research.anno.AnnoTest$BBBS(value=[@demon.research.anno.AnnoTest$BBB(value=Method), @demon.research.anno.AnnoTest$BBB(value=Method 222)])
方法返回值的注解 = [[Ljava.lang.annotation.Annotation;@34b7bfc0
成员变量上的注解 = @demon.research.anno.AnnoTest$BBBS(value=[@demon.research.anno.AnnoTest$BBB(value=Field), @demon.research.anno.AnnoTest$BBB(value=Field 222)])
附录
package-info.java文件
package-info.java文件是一个特殊的Java文件它里面主要包含3类语句包注释、包注解和包声明它可以被放在任意Java包对应的路径下。
package-info.java文件的作用
其中 package-info.java文件主要有下述的作用
提供包级别的注释(Comment)
我们都知道可以为类、变量、方法等元素编写注释但是如果我们想给某个Java包编写注释怎么办在Java5之前需要在Java包对应的路径下创建一个package.html文件并在其body标签中编写Javadoc注释。而在Java5及之后的版本中我们在Java包对应的路径下创建一个package-info.java文件来存放包的包声明、包注释和包注解。
提供包级别的注解(Annotation)
在Java5及之后的版本中我们可以在某个Java包对应路径下的package-info.java文件中用包注解来修饰包声明语句。
@Repeatable 是个语法糖
应用多个可重复的注解时会自动转化为@Repeatable注解value 属性为 多个此注解。
但是仅应用一次的时候则不会自动转换。
前面的示例中的代码 Class C 编译之后变为
@AnnoTest.BBB("Class") //注意此处没有自动转换。
@AnnoTest.CCC("Class CCC")
@AnnoTest.DDD("Class DDD")
static class C<T> {
@AnnoTest.BBBS({@AnnoTest.BBB("Field"), @AnnoTest.BBB("Field 222")})
@AnnoTest.CCC("Field CCC")
@AnnoTest.DDD("Field DDD")
private String a;
C() {
}
//注意 此处自动转换为 注解容器BBBS。
//可以看到把返回值类型 前面的注解 放到 方法上了。
@AnnoTest.BBBS({@AnnoTest.BBB("Method"), @AnnoTest.BBB("Method 222")})
@AnnoTest.CCC("Method CCC")
public T m(@AnnoTest.BBB("Param") @AnnoTest.CCC("PARAM CCC") Integer i) {
Integer xx = 5;
return null;
}
@AnnoTest.BBBS({@AnnoTest.BBB("Method"), @AnnoTest.BBB("Method 222")})
@AnnoTest.CCC("Method CCC")
public T m(@AnnoTest.BBB("Param") @AnnoTest.CCC("PARAM CCC") Integer i, Integer j, @AnnoTest.BBB("Param K") @AnnoTest.CCC("PARAM CCC K") Integer k) {
Integer xx = 5;
return null;
}
}

