【STL】string的常见接口使用
| 阿里云国内75折 回扣 微信号:monov8 |
| 阿里云国际,腾讯云国际,低至75折。AWS 93折 免费开户实名账号 代冲值 优惠多多 微信号:monov8 飞机:@monov6 |
目录
1、string类的基础概念
- 字符串是表示字符序列的类。
- 标准的字符串类提供了对此类对象的支持其接口类似于标准字符容器的接口但添加了专门用于操作单字节字符字符串的设计特性。
- string类是basic_string模板类的一个实例它使用char来实例化basic_string模板类并用char_traits和allocator作为basic_string的默认参数(根于更多的模板信息请参考basic_string)。
- 注意这个类独立于所使用的编码来处理字节:如果用来处理多字节或变长字符(如UTF-8)的序列这个类的所有成员(如长度或大小)以及它的迭代器将仍然按照字节(而不是实际编码的字符)来操作。
⭐总结
- string是表示字符串的字符串类
- 该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
- string包含的头文件是#include<string>
- string是属于std命名空间的using namespace std;
- string类是管理动态增长字符数组这个字符串以\0结尾
2、string类的常见接口说明及应用
2.1、string类的成员函数
- 以下内容参考网站https://m.cplusplus.com/
constructor构造函数
函数名称 功能说明 1、string()重点 无参构造空的string类对象即空字符串。 2、string(const string& str)重点 拷贝构造函数 3、string(const char* s)重点 带参的常量字符串初始化 4、string(const char*s,size_t n) 对一个字符串的前n个初始化 5、string(size_t n,char c) 用n个字符c进行初始化 6、string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos) 从pos位置处取len长度的字符进行拷贝构造
- 🚩1、string() 无参构造
string s1;//无参初始化等价于string s1("")
- 🚩2、string(const string&str) 拷贝构造
string s2("hello world"); //带参字符串初始化 string s3(s2); //拷贝构造 string s4 = s2; //拷贝构造
- 🚩3、string(const char* s) 带参构造
string s2("hello world"); //带参字符串初始化
- 🚩4、string (const char* s, size_t n) 对一个字符串的前n个初始化
string s5("https://cplusplus.com/reference/string", 5); //用字符串前5个字符对s5初始化 cout << s5 << endl; //https
- 🚩5、string (size_t n, char c) 用n个c初始化
string s6(5, 'k'); //用5个K字符进行初始化 cout << s6 << endl; //kkkkk
- 🚩6、string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos) 从pos位置处取len长度的字符进行拷贝构造
string s2("hello world!");//带参拷贝构造 string s7(s2, 6, 5);//从s2字符串的第6个位置往后取5个字符初始化 cout << s7 << endl;//world我想到这里大家会有点疑问那个缺省参数npos是什么
下面我们来看一下
- 我们可以看到npos就是一个string类的静态成员变量。其值等于-1转变为非负整型就是int整型最大值。
destructor析构函数
我们已经学过了类与对象我们知道string是管理动态增长字符数组的对于动态申请的内存空间我们需要用到析构函数将其释放掉。这里编译器会默认自动调用构造函数。
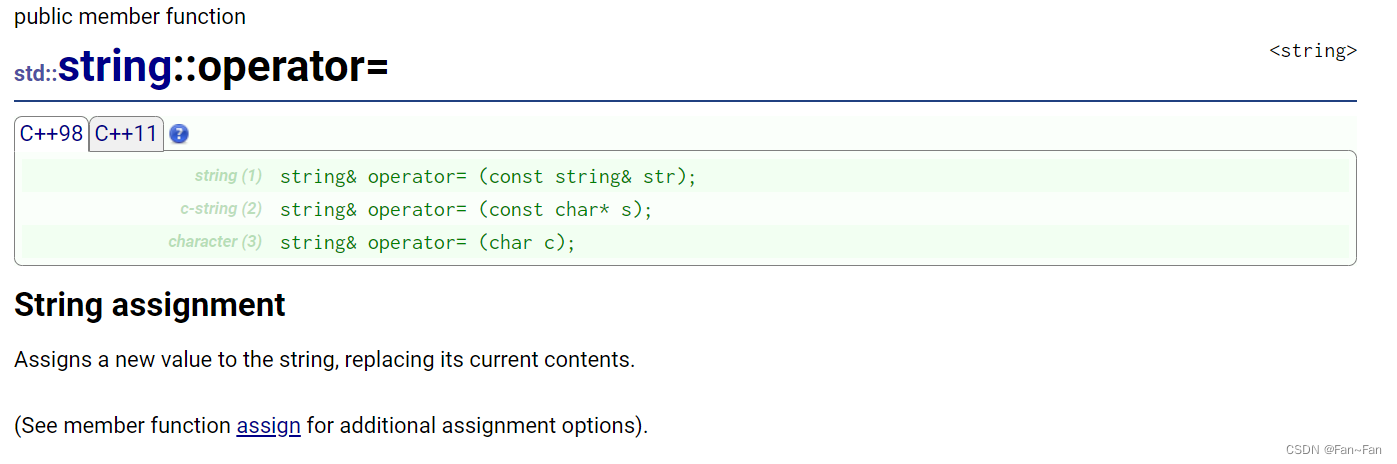
operator=赋值
我们看其应用情况
void test_string2() { string s1("hello"); string s2("world"); s1 = s2; cout << s1 << endl; //hello s1 = "kkk"; cout << s1 << endl; //kkk s1 = 'k'; cout << s1 << endl; //k }
string类对象的容量操作
函数名称 功能说明 1、size重点 返回字符串有效字符长度 2、length 返回字符串有效字符长度 3、max_size 返回字符串最大长度 4、capacity
返回空间总大小 5、reserve重点 为字符串预留空间 6、resize重点 将有效字符的个数拆成n个多出的空间用字符c填充 7、clear重点 清空有效字符 8、empty重点 检测字符串释放为空串是返回true否则返回false
- 🚩1、size
size_t size() const;string s1("hello"); cout << s1.size() << endl; //5
- 🚩2、length
size_t length() const;length和size没有什么本质的区别在功能上都是返回字符串的有效长度。但是收到历史背景影响平常用的还是size。
string s1("hello"); cout << s1.length() << endl; //5
- 🚩3、max_szie
size_t max_size() const;max_size返回的就是字符的最大长度也就是nops-1 转换成无符号整型的数值。
- 🚩4、capacity
size_t capacity() const;capacity返回的就是容量的大小
- 🚩5、reserve
void reserve (size_t n = 0);reserve函数特性
- 请求将字符串容量调整为最大长度为n个字符的计划大小。
- 如果n大于当前字符串容量则函数会使容器将其容量增加到n个字符或更大)。
- 在所有其他情况下它被视为收缩字符串容量的非约束性请求容器实现可以自由地进行优化并使字符串的容量大于n。
- 此函数对字符串长度没有影响并且无法更改其内容。
- 利用reserve进行提前预留空间可以减少扩容带来的损耗。
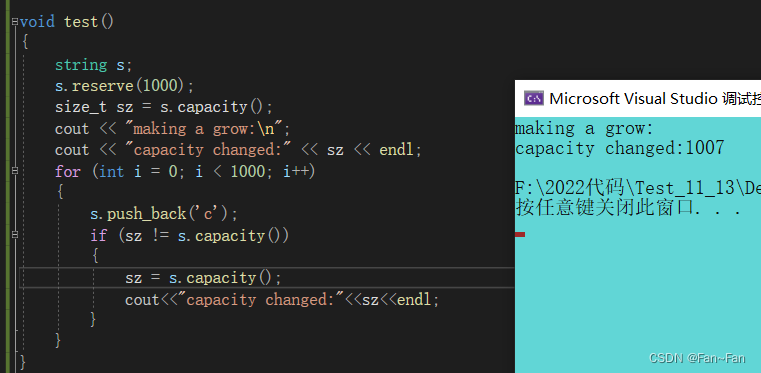
我们用如下代码进行测试
对于普通尾插我们需要进行多次扩容而频繁扩容会带来效率的损失在我们已知需要的空间大小下我们可以加上reserve预留空间进行优化
我们可以看到加上了reserve提前预留空间能够大大减少扩容带来的效率消耗。
下面我们再来看一组测试用例
void test() { string s("hello world"); cout << s << endl; //hello world cout << s.size() << endl; //11 cout << s.capacity() << endl; //15 //reverse(n)当n大于对象当前的capacity时将当前对象的capacity扩大为n或大于n s.reserve(20); cout << s << endl; //hello world cout << s.size() << endl; //11 cout << s.capacity() << endl; //31 //reverse(n)当n小于对象当前的capacity时什么也不做 s.reserve(5); cout << s << endl; //hello world cout << s.size() << endl; //11 cout << s.capacity() << endl; //31 }
- 🚩6、resize
resize函数特性
- 将字符串大小调整为 n 个字符的长度。
- 如果 n 小于当前字符串长度则当前值将缩短为其前 n 个字符并删除超出第 n 个字符的字符。
- 如果n大于当前字符串长度则通过在末尾插入所需数量的字符来扩展当前内容以达到n的大小。如果指定了c则将新元素初始化为c的副本否则它们是值初始化的字符空字符。
我们看如下测试代码
void test() { string s("hello world"); //resize(n) 当n小于对象当前的size时将size缩小到n s.resize(5); cout << s << endl; //hello cout << s.size() << endl; //5 cout << s.capacity() << endl; //15 string s1("hello world"); //resize(n) 当n大于对象当前的size时将size扩大到n扩大字符默认为'\0' s1.resize(20); cout << s1 << endl; //hello world cout << s1.size() << endl; //20 cout << s1.capacity() << endl; //31 string s2("hello world"); //resize(n, char)n大于对象当前的size时将size扩大到n扩大的字符为char s2.resize(20, 'x'); cout << s2 << endl; //hello worldxxxxxxxxx cout << s2.size() << endl; //20 cout << s2.capacity() << endl; //31 }
- 🚩7、clear
clear的功能是清除字符串内容将字符串变为空字符串。本质是清楚所有空间。
void test() { string s("hello world"); cout << s << endl;//hello world s.clear(); cout << s.size() << endl;//0 cout << s << endl;//空 }
- 🚩8、empty
empty的功能是判断string里的内容是否为空。
void test() { string s("hello world"); cout << s << endl;//hello world s.clear();//清空有效字符 if (s.empty()) cout << "empty" << endl;//empty }
迭代器
迭代器就是像指针一样的东西
函数名称 功能说明 1、begin 返回指向字符串第一个字符的迭代器 2、end 返回指向字符串最后一个字符的迭代器 3、rbegin 返回一个逆序迭代器它指向容器的最后一个元素 4、rend 返回一个逆序迭代器它指向容器的第一个元素前面的位置。
- 🚩1、begin
- 🚩2、end
示例如下
void test() { string s1("hello"); string::iterator it = s1.begin(); while (it != s1.end()) { cout << *it << " "; it++; } }
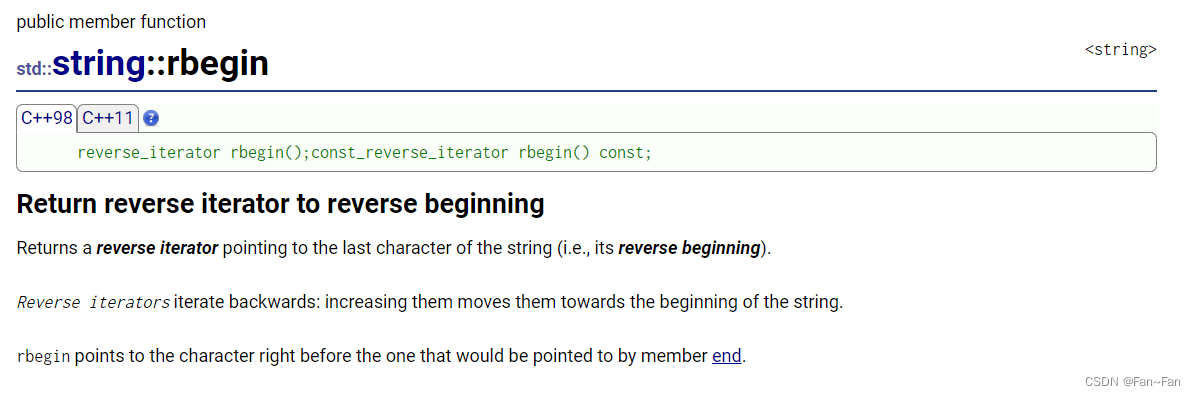
- 🚩3、rbegin
rbegin是一种逆向迭代器
rbegin的特性如下
- 返回一个反向迭代器指向字符串的最后一个字符即其反向开头。
- 反向迭代器向后迭代增加迭代器会将它们移向字符串的开头。
- rbegin 指向成员末尾将指向的字符之前的字符。
反向迭代器的++是往反方向走的区别于正向迭代器。
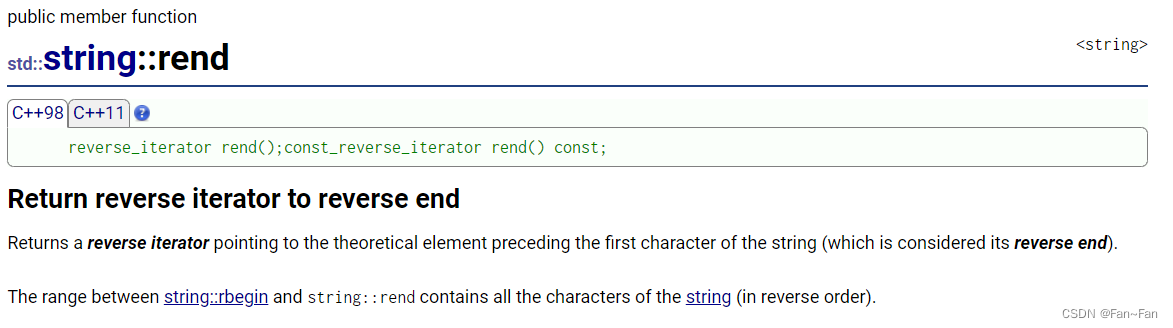
- 🚩4、rend
rend的特性如下
- 返回一个反向迭代器该迭代器指向字符串的第一个字符之前的理论元素被视为其反向结尾。
- string:rbegin 和 string:rend 之间的范围包含字符串的所有字符顺序相反。
- 🚩5、const正向迭代器
普通迭代器是可读可写的因此针对const修饰的特殊情况下我们不能如下操作
我们这里的Func里的s是cosnt修饰的而Func里的迭代器是可读可写的版本这里属于权限放大因此我们要对其进行修正
//const正向迭代器 void Func(const string& s) { //记得加上const_使其对于const的函数 string::const_iterator it = s.begin(); /* 或者使用auto自动推导类型 auto it = s.begin(); */ while (it != s.end()) { //*it += 1; 不能写 cout << *it << " "; it++; } }
- 🚩6、const反向迭代器
//const反向迭代器 void Func(const string& s) { string::const_reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin(); /* 或者使用auto自动推导类型 auto rit = s.rbegin(); */ while (rit != s.rend()) { //*rit += 1; 不能写 cout << *rit << " "; ++rit; } }
string类的元素访问
函数名称 功能说明 1、operator[ ] 获取字符串中的字符 2、at
获取字符串中的字符
- 🚩1、operator[ ]
⭐特性
- 返回对字符串中位置pos处字符的引用。
- 如果pos等于字符串长度并且字符串是常量限定的则函数返回对空字符“\0”的引用。
void test() { string s1("hello"); const string s2("world"); cout << s1[2] << endl; //打印字符'l' cout << s1[5] << endl; //下标5对应字符'\0',故打印出空字符 s1[0] = 'x'; s2[0] = 'y'; //err }s1没有被const修饰所以可读可写s2被const修饰只能读所以不能进行修改。
- 🚩2、at
⭐特性
- 返回对字符串中位置pos处字符的引用。
- 函数会自动检查pos是否是字符串中字符的有效位置即pos是否小于字符串长度如果不是则抛出out_of_range异常。
at和operator[ ]的功能一样,都是访问pos位置字符
- 🚩3、at和operator[ ]对比
虽然at和opertator[ ]的功能一样但是其在处理越界访问的情况是不一样的
operator[ ]:
这里[ ]越界是通过断言来报错
at
这里越界访问会导致抛异常。
这里我们可以演示一下捕获异常的场景
string类对象的遍历操作
函数名称 功能说明 1、operator[ ] 返回pos位置的字符const string类对象调用 2、begin+end 正向迭代器遍历 3、rbegin+rend 反向迭代器遍历 4、范围for C++11支持更简洁的范围for的新遍历方式
- 🚩法1:operator[ ]
有了[ ]的运算符重载我们就可以像C语言一样用下标方式进行元素的访问。
void test() { //下标+[] string s1("hello"); for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++) { //s1.operator[](i) cout << s1[i] << " "; //h e l l o } }
- 🚩法2:正向迭代器begin+end
void test() { //正向迭代器 string s1("hello"); string::iterator it = s1.begin(); while (it != s1.end()) { cout << *it << " "; //h e l l o it++; } }
- 🚩法3:反向迭代器rbegin+rend
void test() { //反向迭代器 string s1("hello"); string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin(); while (rit != s1.rend()) { cout << *rit << " "; //o l l e h ++rit; } }
- 🚩法4:范围for
void test() { //范围for string s1("hello"); for (auto ch : s1) //auto自动取s1里面的字符自动++ { cout << ch << " "; } cout << endl; }虽然范围for看起来特别简便但其实其内部原理还是利用迭代器进行实现。
⭐学完了string类对象的遍历操作后我们就要把它们运用起来下面我们看一道题
🙋🏻♂️双指针
🙋🏻♂️迭代器
string类对象的修改操作
函数名称 功能说明 1、push_back 在字符串后尾插字符 2、insert 指定位置插入 3、append 在字符串后追加一个字符串 4、operator+= 在字符串后追加字符串str 5、erase 删除字符或字符串 6、swap 交换 7、c_str 返回C格式字符串 8、find 从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符C返回该字符的位置 9、substr 在str中从pos位置开始截取n个字符然后返回 10、rfind 从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符C返回该字符的位置
- 🚩1、push_back 尾插字符
void push_back (char c);作用将字符c追加到字符串的末尾使其长度增加1。
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string str("word"); cout << str << endl; //world str.push_back('s'); cout << str << endl; //worlds }
- 🚩2、insert 指定位置插入
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string str("hello world"); //头部插入一个字符 str.insert(0, 1, 'x'); cout << str << endl; //xhello world //使用迭代器头插 str.insert(str.begin(), 1, 'y'); cout << str << endl; //yxhello world //在第n个位置插入字符 str.insert(3, 1, 'x'); cout << str << endl; //yxhxello world str.insert(str.begin() + 3, 1, 'k'); cout << str << endl; //yxhkxello world //头插一个字符串 str.insert(0, "!!!!"); cout << str << endl; //!!!!yxhkxello world }
- 🚩3、append 追加字符串
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string s1("hello"); string s2(" every"); //追加一个string对象 s1.append(s2); cout << s1 << endl; //hello every //追加一个常量字符串 s1.append("body"); cout << s1 << endl; //hello everybody //用n个字符拼接 s1.append(3, '!'); cout << s1 << endl; //hello everybody!!! }
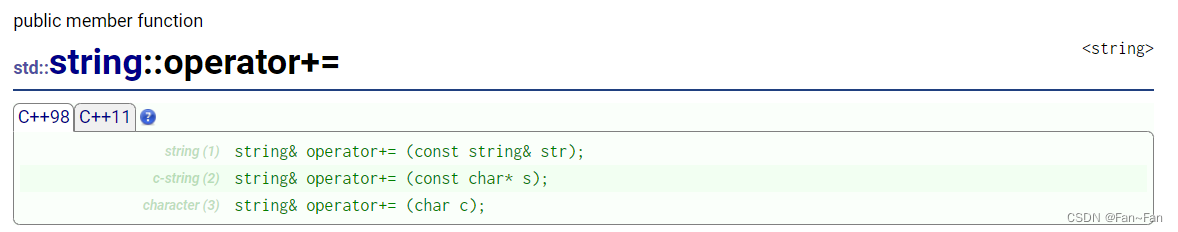
- 🚩4、operator+=
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string str("hello"); str += ' '; str += "world"; cout << str << endl; //hello world string ptr = "!!!!"; str += ptr; cout << str << endl; //hello world!!!! }
- 🚩5、erase 删除
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string str("hello world"); //头删 str.erase(str.begin()); cout << str << endl; //ello world //头删指定字符 str.erase(str.begin() + 3); cout << str << endl; //ell world //从pos处位置删除n个字符 str.erase(2, 3); cout << str << endl; //elorld //利用缺省值只给定删除的位置往后全删 str.erase(2); cout << str << endl; //el str.erase(0); cout << str << endl; //空 }
- 🚩6、swap 交换
注意
- 通过 str另一个字符串对象的内容交换容器的内容。长度可能不同。
- 在调用此成员函数之后此对象的值是str在调用之前的值str的值是此对象在调用之前具有的值。
- 请注意存在一个具有相同名称swap的非成员函数该函数使用与该成员函数类似的优化来重载该算法。
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string s1("hello world"); string s2("HELLO WORLD"); s1.swap(s2); //string类域里面的swap 效率高 本质交换指针 swap(s1, s2);//全局的swap 效率低 本质深拷贝 }
- 🚩7、c_str 返回C格式字符串
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string s1("hello"); cout << s1 << endl; //hello cout << s1.c_str() << endl;//hello }
- 🚩8、find
返回值第一个匹配项的第一个字符的位置。如果没有找到匹配项则该函数返回stringnpos。
- 🚩9、substr
返回值具有此对象的子字符串的字符串对象。
int main() { string file("string.cpp"); size_t pos = file.find('.'); if (pos != string::npos) { string suffix = file.substr(pos); cout << file << "后缀" << suffix << endl; } else { cout << "没有后缀" << endl; } }
- 🚩10、rfind
int main() { string file("string.cpp.tar.zip"); size_t pos = file.rfind('.'); if (pos != string::npos) { string suffix = file.substr(pos); cout << file << "后缀" << suffix << endl; } else { cout << "没有后缀" << endl; } }
int main() { //取出url的域名 string url1("https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/rfind/"); string url2("https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60718941?spm=1000.2115.3001.5343"); //协议 域名 uri(资源名) string& url = url1; //取协议 string protocol; size_t pos1 = url.find("://"); if (pos1 != string::npos) { protocol = url.substr(0, pos1); cout << "protocol:" << protocol << endl; //https } else { cout << "非法url" << endl; } //取域名 string domain; size_t pos2 = url.find('/', pos1 + 3); if (pos2 != string::npos) { domain = url.substr(pos1 + 3, pos2 - (pos1 + 3)); cout << "domain:" << domain << endl; //domain:cplusplus.com } //取uri string uri = url.substr(pos2 + 1); cout << "uri:" << uri << endl; //uri:reference/string/string/rfind/ }
2.2、string类非成员函数
函数 功能说明 1、operator+ 尽量少用因为传值返回导致深拷贝效率低 2、operator>> 输入运算符重载 3、operator<< 输出运算符重载 4、relational operators 大小比较 5、getline 获取一行字符串
- 🚩1、operator+
int main() { string s1("hello"); string s2("world"); //1、string类+string类 string s3 = s1 + s2; cout << s3 << endl; //helloworld //2、string类+字符 s3 = s1 + '!'; cout << s3 << endl; //hello! //3、字符+string类 s3 = '!' + s2; cout << s3 << endl; //! world //4、string类+字符串 s3 = s1 + "Fan~Fan"; cout << s3 << endl; //hello Fan~Fan //5、字符串+string类 s3 = "!!!!" + s2; cout << s3 << endl; //!!!!world }
- 🚩2、operator>> / operator<<
istream& operator>> (istream& is, string& str); ostream& operator<< (ostream& os, const string& str);int main() { string str; cin >> str; //hello world cout << str << endl; //hello }
- 🚩3、relational operators
string类对==、=、<、<=、>、>=这些运算符进行了重载并且支持string类和string类string类和字符串间的比较使用效果如下
int main() { string s1("abcd"); string s2("efgh"); cout << (s1 > s2) << endl; //0 cout << (s1 < s2) << endl; //1 cout << (s1 >= s2) << endl; //0 cout << (s1 <= s2) << endl; //1 }
- 🚩4、getline
⭐特性
- 从is中提取字符并将其存储到str中直到找到分隔字符delim或2的换行符“\n”。
- 如果在 is 中到达文件末尾或者在输入操作期间发生其他错误则提取也会停止。
- 如果找到分隔符则会提取并丢弃它即不存储它下一个输入操作将在它之后开始。
- str中在调用之前的任何内容都会被新提取的序列替换。
- 每个提取的字符都会附加到字符串就像调用了其成员push_back一样。
例题
原题链接字符串最后一个单词的长度_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { string str; //不能用cin>>str getline(cin,str); size_t pos=str.rfind(' '); if(pos!=string::npos) { cout<<str.size()-pos-1<<endl; } else { cout<<str.size()<<endl; } return 0; }原题链接387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符 - 力扣Leetcode
class Solution { public: int firstUniqChar(string s) { int count[26]={0}; //统计次数 for(auto ch:s) { count[ch-'a']++; } for(size_t i=0;i<s.size();i++) { if(count[s[i]-'a']==1) { return i; } } return -1; } };
class Solution { public: string addStrings(string num1, string num2) { int end1=num1.size()-1; int end2=num2.size()-1; int carry=0; string retStr; while(end1>=0||end2>=0) { int val1=end1>=0?num1[end1]-'0':0; int val2=end2>=0?num2[end2]-'0':0; int ret=val1+val2+carry; if(ret>9) { ret-=10; carry=1; } else { carry=0; } //retStr.insert(retStr.begin(),'0'+ret); retStr+=('0'+ret); end1--; end2--; } if(carry==1) retStr+='1'; //retStr.insert(retStr.begin(),'1'); reverse(retStr.begin(),retStr.end()); return retStr; } };