JavaScript(07): 实例3---Google Eye
| 阿里云国内75折 回扣 微信号:monov8 |
| 阿里云国际,腾讯云国际,低至75折。AWS 93折 免费开户实名账号 代冲值 优惠多多 微信号:monov8 飞机:@monov6 |
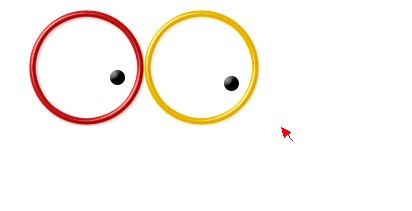
下面的例子源于Google Eye(如下图所示的效果),通过这个例子可以好好体会一下JavaScript的面向对象编程。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Google Eye</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<style>
#l_pupil, #r_pupil {
position: relative; /* the position of pupil is relative to its container eye*/
width: 15px;
height: 15px;
left: 52px;
top: 52px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" border="0" align="center" style="margin-top:20px;" >
<tr>
<td background="eye-r.gif">
<div style="width:117px;height:117px;">
<img src="pupil.gif" id="l_pupil" />
</div>
</td>
<td background="eye-y.gif">
<div style="width:117px;height:117px;">
<img src="pupil.gif" id="r_pupil" />
</div>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<script type="text/javascript">
var myEyes = {
EyeRadius: 55, /* radius of eye */
PupilRadius: 7, /* radius of pupil */
MAX_DISTANCE: 38, /* to control the pupil not out of eye */
body: document.documentElement || document.body /* browser compatible */
};
myEyes.STATCK = []; // array to store two pupils
myEyes.$ = function(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
};
myEyes.getMousePosition = function(e) {
return {
left: e.clientX + myEyes.body.scrollLeft,
top: e.clientY + myEyes.body.scrollTop
};
};
myEyes.getObjectPosition = function(elem) {
var rect = elem.getBoundingClientRect();
return {
left: rect.left + myEyes.body.scrollLeft, top: rect.top + myEyes.body.scrollTop
};
}
myEyes.init = function() {
myEyes.STATCK = [
myEyes.$('l_pupil'),
myEyes.$('r_pupil')
];
document.onmousemove = function(e) {
myEyes.mouseMove(e || window.event);
}
};
myEyes.mouseMove = function(e) {
for(var i = 0, len = myEyes.STATCK.length; i < len; i++) {
var pupil = myEyes.STATCK[i];
var dx = myEyes.getMousePosition(e).left - myEyes.getObjectPosition(pupil.parentNode).left - myEyes.PupilRadius;
var dy = myEyes.getMousePosition(e).top - myEyes.getObjectPosition(pupil.parentNode).top - myEyes.PupilRadius;
var distance = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(dx, 2) + Math.pow(dy, 2));
/*
if the distance between mouse pointer and eye is greater than constant
MAX_DISTANCE, it's a good idea to zoom out the distance by proportion
*/
if(distance > myEyes.MAX_DISTANCE) {
var scale = myEyes.MAX_DISTANCE / distance;
dx *= scale;
dy *= scale;
}
pupil.style.left = parseInt(dx + myEyes.EyeRadius - myEyes.PupilRadius) + 'px';
pupil.style.top = parseInt(dy + myEyes.EyeRadius - myEyes.PupilRadius) + 'px';
}
};
myEyes.init();
</script>
</body>
</html> 如果你看懂了,那么你的JavaScript应该很不错的:)代码中对对象表达式的使用、方法的动态绑定以及37行短路运算都是亮点……
| 阿里云国内75折 回扣 微信号:monov8 |
| 阿里云国际,腾讯云国际,低至75折。AWS 93折 免费开户实名账号 代冲值 优惠多多 微信号:monov8 飞机:@monov6 |

