map和set
阿里云国际版折扣https://www.yundadi.com |
| 阿里云国际,腾讯云国际,低至75折。AWS 93折 免费开户实名账号 代冲值 优惠多多 微信号:monov8 飞机:@monov6 |
一、关联式容器
STL中的部分容器比如vector、list、deque、 forward_list(C++11)等这些容器统称为 序列式容器 因为其底层为线性序列的数据结构里面存储的是元素本身。关联式容器 也是用来存储数据的与序列式容器不同的是其里面存储的是<key, value>结构的 键值对在数据检索时比序列式容器效率更高。
二、树形结构的关联性容器
2.1 set
对于set
2.1.1 set的使用
| 函数声明 | 功能介绍 |
|
void erase ( iterator position )
|
删除set中position位置上的元素
|
|
size_type erase ( const key_type& x )
|
删除set中值为x的元素返回删除的元素的个数
|
|
void erase ( iterator first, iterator last )
|
删除set中[first, last)区间中的元素
|
|
iterator fifind ( const key_type& x ) const
|
返回set中值为x的元素的位置
|
|
size_type count ( const key_type& x ) const
| 返回set中值为x的元素的个数。set中key是唯一的因此该函数的返回值要么为0要么为1因此也可以用该函数来检测一个key是否在set中 |
int main()
{
set<int> s;
//set.insert 自己 排序+去重
s.insert(1);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(4);
s.insert(7);
s.insert(4);
//set.erase
//找到并删除则返回1未找到没删除则返回0
cout << s.erase(2) << endl;
cout << s.erase(20) << endl;
//遍历
set<int> ::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//s.find() 与 库里的find()
//s.find()
set<int> ::iterator pos = s.find(3);//时间复杂度O(logN)
if (pos != s.end())
{
cout << "set.find()找到了" << endl;
}
//库里的find() --- 从头到尾遍历一遍查找
pos = find(s.begin(), s.end(), 4);//时间复杂度O(N)
if (pos != s.end())
{
cout << "find()找到了" << endl;
}
//s.count()
if (s.count(3))
{
cout << "3在" << endl;
}
if (s.find(3) != s.end())
{
cout << "3在" << endl;
}
//s.lower_bound
//返回 >=val 的位置迭代器 3返回3的位置 6返回7的位置
set<int> ::iterator Lowit = s.lower_bound(3);
Lowit = s.lower_bound(6);
//删除 >=3 的所有值
set<int> ::iterator lowIt = s.lower_bound(3);
s.erase(lowIt, s.end());
//s.upper_bound
//返回 > val 的位置迭代器
//删除[3,6)
auto leftIt = s.lower_bound(3); // [
auto rightIt = s.upper_bound(6); // )
s.erase(leftIt, rightIt);
return 0;
}2.2 map
对于map
2.2.1 map的使用
int main()
{
map<string, string> dict;
//pair构造函数
//1.
dict.insert(pair<string, string>("sort", "排序"));
//2.
pair<string, string> kv("left", "左边");
dict.insert(kv);
//make_pair
auto ret1 = dict.insert(make_pair("insert", "插入"));
auto ret2 = dict.insert(make_pair("left", "剩余"));
dict["operator"] = "重载";//插入+修改
dict["left"] = "左边剩余";//修改
dict["erase"];//插入
cout << dict["left"] << endl;//查找打印出"左边剩余"
cout << dict["erase"] << endl;//查找 ,什么都打印不出来
//遍历
//map<string,string> :: iterator it = dict.begin()
auto it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
it++;
}
for (const auto& kv : dict)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
//计数模拟
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
//1.
map<string, int> countMap1;
for (auto& str : arr)
{
//pair<map<string, int> :: iterator, bool> ret = countMap.insert(make_pair(str, 1));
auto ret = countMap1.insert(make_pair(str, 1));
if (ret.second == false)
{
ret.first->second++;
}
}
//2.
map<string, int> countMap2;
for (auto& str : arr)
{
countMap2[str]++;
}
for (const auto& kv : countMap1)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}2.3 multiset和multimap
- multiset与set的区别是multiset中的元素可以重复set是中value是唯一的。其他用法一致
2.2.1 multiset的使用
int main()
{
multiset<int> s;
s.insert(1);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(4);
s.insert(7);
s.insert(4);
//区别
// 多个x的话find返回中序第一个x
auto pos = s.find(3);
while (pos != s.end())
{
cout << *pos << " ";
++pos;
}
return 0;
}三、底层结构
3.1 AVL树
一颗AVL树是具有以下性质的二叉搜索树
3.1.1 AVL树的旋转
1.新节点插入较高右子树的右侧---右右左单旋
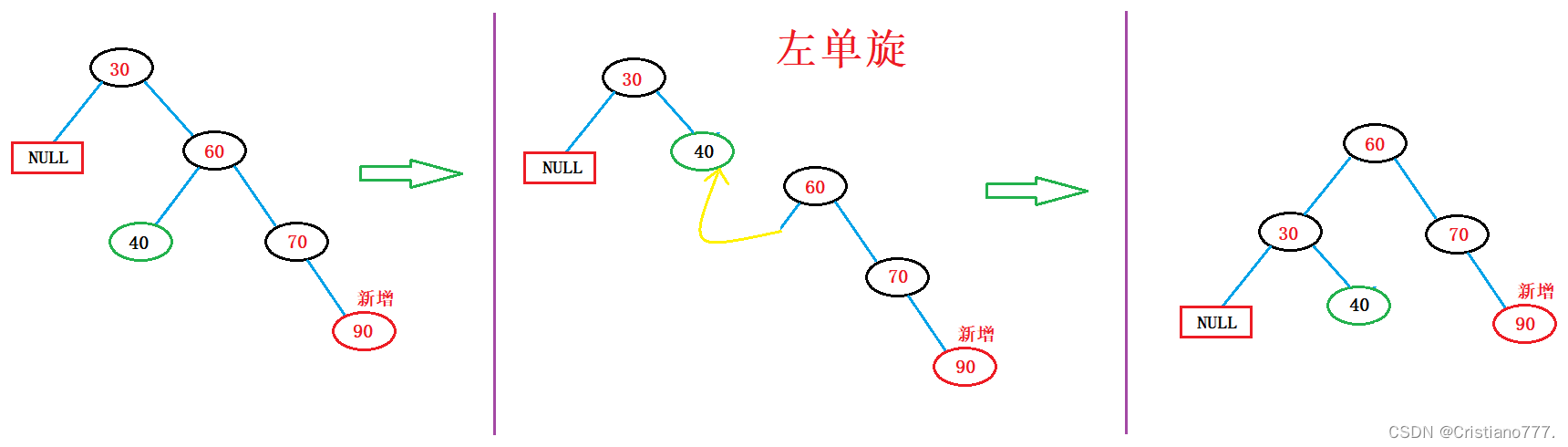
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subR;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent = ppNode->_left)
{
ppNode->_left = subR;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = ppNode;
}
//更新平衡因子
parent->_bf = subR->_bf = 0;
}2.新节点插入较高左子树的左侧---左左右单旋

void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subL;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppNode->_left == parent)
{
ppNode->_left = subL;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = ppNode;
}
//更新平衡因子
subL->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;
}3.新节点插入较高左子树的右侧---左右先左单旋再右单旋
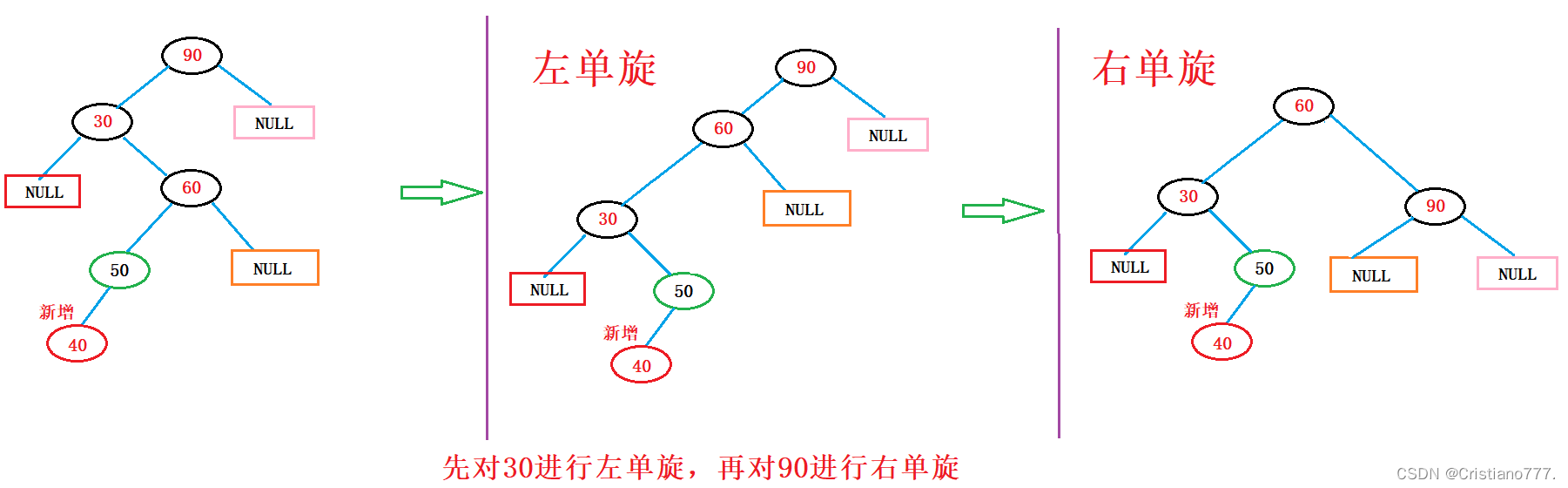
void RotateLR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = parent->_right;
int bf = subLR->_bf;
//先左旋再右旋
//旋转完成后再考虑平衡因子的更新
RotateL(parent->_left);
RotateR(parent);
//更新平衡因子
//画图即可知这些特定的平衡因子怎么来
if (bf == 0)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
subL->_bf = 0;
subLR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
subL->_bf = -1;
subLR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
parent->_bf = 1;
subL->_bf = 0;
subLR->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
//subLR->_bf旋转前就有问题
assert(false);
}
}4. 新节点插入较高右子树的左侧---右左先右单旋再左单旋

void RotateRL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
int bf = subRL->_bf;
RotateR(parent->_right);
RotateL(parent);
if (bf == 0)
{
subR->_bf = 0;
subRL->_bf = 0;
parent->_parent = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
subRL->_bf = 0;
parent->_bf = -1;
subR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
subRL->_bf = 0;
parent->_bf = 0;
subR->_bf = 1;
}
else
{
// subRL->_bf旋转前就有问题
assert(false);
}
}总结
假如以parent为根的子树不平衡即parent的平衡因子为2 or -2分以下情况考虑
- parent的平衡因子为2说明parent的右子树高设parent的右子树的根为subR
当subR的平衡因子为1时执行左单旋
当subR的平衡因子为-1时执行右左双旋
parent的平衡因子为-2说明parent的左子树高设parent的左子树的根为sub当当 当subL的平衡因子为-1时执行右单旋 当subL的平衡因子为1时执行左右双旋
3.1.2 AVL树的检验
检验其为AVL树的要点
- 如果中序遍历可得到一个有序的序列就说明为二叉搜索树
bool _IsBalanceTree(Node* root)
{
//空树也是AVL树
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
// 计算root节点的平衡因子,即root左右子树的高度差
int LHeight = _Height(root->_left);
int RHeight = _Height(root->_right);
int diff = RHeight - LHeight;//右-左
// 如果计算出的平衡因子与root的平衡因子不相等
// 或者root平衡因子的绝对值超过1则一定不是AVL树
if (abs(diff) >= 2)
{
cout << root->_kv.first << "节点平衡因子异常" << endl;
return false;
}
if (diff != root->_bf)
{
cout << root->_kv.first << "节点平衡因子不符合实际" << endl;
return false;
}
// root的左和右如果都是AVL树则该树一定是AVL树
return _IsBalanceTree(root->_left)
&& _IsBalanceTree(root->_right);
}
3.1.3 AVL树的模拟实现
template<class k, class v>
struct AVLTreeNode
{
pair<k, v> _kv;
AVLTreeNode<k, v>* _left;
AVLTreeNode<k, v>* _right;
AVLTreeNode<k, v>* _parent;
//balance fator 平衡因子
//右子树-左子树的高度差
int _bf;
AVLTreeNode(const pair<k, v>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _bf(0)
{}
//AVL树并没有规定必须要设计平衡因子只是一个实现的选择方便控制平衡
};
template<class k, class v>
class AVLTree
{
typedef AVLTreeNode<k, v> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<k, v>& kv)
{
//1.搜索树的规则插入
//2、看是否违反平衡规则如果违反就需要处理 -> 旋转
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_bf = 0;
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
//找位置
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
//插入,梳理关系
if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
//更新平衡因子
while (parent)
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
parent->_bf++;
}
else
{
parent->_bf--;
}
// 是否继续更新
if (parent->_bf == 0)
{
// 1 or -1 -> 0 插入的节点刚好填上矮的那边
break;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 1 || parent->_bf == -1)
{
// 0 -> 1 or -1 插入的节点导致一边变高了
//子树的高度变了继续更新祖先
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 || parent->_bf == -2)
{
// -1 or 1 -> 2 或 -2 插入的节点导致本来高一边又变高了
//子树不平衡需要旋转处理
if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
//左单旋
RotateL(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
//右单旋
RotateR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == -2 && cur->_bf == 1)
{
//左右单旋
RotateLR(parent);
}
else if (parent->_bf == 2 && cur->_bf == -1)
{
//右左单旋
RotateRL(parent);
}
}
else
{
// 插入之前AVL就存在不平衡子树|平衡因子| >= 2的节点
assert(false);
}
}
return true;
}
private:
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subR;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent = ppNode->_left)
{
ppNode->_left = subR;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = ppNode;
}
//更新平衡因子
parent->_bf = subR->_bf = 0;
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subL;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppNode->_left == parent)
{
ppNode->_left = subL;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = ppNode;
}
//更新平衡因子
subL->_bf = parent->_bf = 0;
}
void RotateLR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = parent->_right;
int bf = subLR->_bf;
//先左旋再右旋
//旋转完成后再考虑平衡因子的更新
RotateL(parent->_left);
RotateR(parent);
//更新平衡因子
//画图即可知这些特定的平衡因子怎么来
if (bf == 0)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
subL->_bf = 0;
subLR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
parent->_bf = 0;
subL->_bf = -1;
subLR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
parent->_bf = 1;
subL->_bf = 0;
subLR->_bf = 0;
}
else
{
//subLR->_bf旋转前就有问题
assert(false);
}
}
void RotateRL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
int bf = subRL->_bf;
RotateR(parent->_right);
RotateL(parent);
if (bf == 0)
{
subR->_bf = 0;
subRL->_bf = 0;
parent->_parent = 0;
}
else if (bf == 1)
{
subRL->_bf = 0;
parent->_bf = -1;
subR->_bf = 0;
}
else if (bf == -1)
{
subRL->_bf = 0;
parent->_bf = 0;
subR->_bf = 1;
}
else
{
// subRL->_bf旋转前就有问题
assert(false);
}
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
int _Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int lh = _Height(root->_left);
int rh = _Height(root->_right);
return lh > rh ? lh + 1 : rh + 1;
}
bool _IsBalanceTree(Node* root)
{
//空树也是AVL树
if (root == nullptr)
return true;
// 计算root节点的平衡因子,即root左右子树的高度差
int LHeight = _Height(root->_left);
int RHeight = _Height(root->_right);
int diff = RHeight - LHeight;//右-左
// 如果计算出的平衡因子与root的平衡因子不相等
// 或者root平衡因子的绝对值超过1则一定不是AVL树
if (abs(diff) >= 2)
{
cout << root->_kv.first << "节点平衡因子异常" << endl;
return false;
}
if (diff != root->_bf)
{
cout << root->_kv.first << "节点平衡因子不符合实际" << endl;
return false;
}
// root的左和右如果都是AVL树则该树一定是AVL树
return _IsBalanceTree(root->_left)
&& _IsBalanceTree(root->_right);
}
public:
//层序遍历
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder() {
vector<vector<int>> vv;
if (_root == nullptr)
return vv;
queue<Node*> q;
int levelSize = 1;
q.push(_root);
while (!q.empty())
{
// levelSize控制一层一层出
vector<int> levelV;
while (levelSize--)
{
Node* front = q.front();
q.pop();
levelV.push_back(front->_kv.first);
if (front->_left)
q.push(front->_left);
if (front->_right)
q.push(front->_right);
}
vv.push_back(levelV);
for (auto e : levelV)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 上一层出完下一层就都进队列
levelSize = q.size();
}
return vv;
}
bool IsBalanceTree()
{
return _IsBalanceTree(_root);
}
int Height()
{
return _Height(_root);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};4.2 红黑树
任何一条从根到叶子的路径上各个结点着色方式的限制红黑树确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出两倍
4.2.1 红黑树的性质
4.2.2 红黑树的插入
新节点的默认颜色是 红色 因此如果其双亲节点的颜色是黑色没有违反红黑树任何性质则不需要调整但当新插入节点的双亲节点颜色为 红色 时就违反了性质不能有连在一起的 红色 节点此时需要对红黑树分情况来讨论约定: cur为当前节点 p(parent)为父节点 g(grandfather)为祖父节点 u(uncle)为叔叔节点
情况一cur为红p为红g为黑u存在且为红
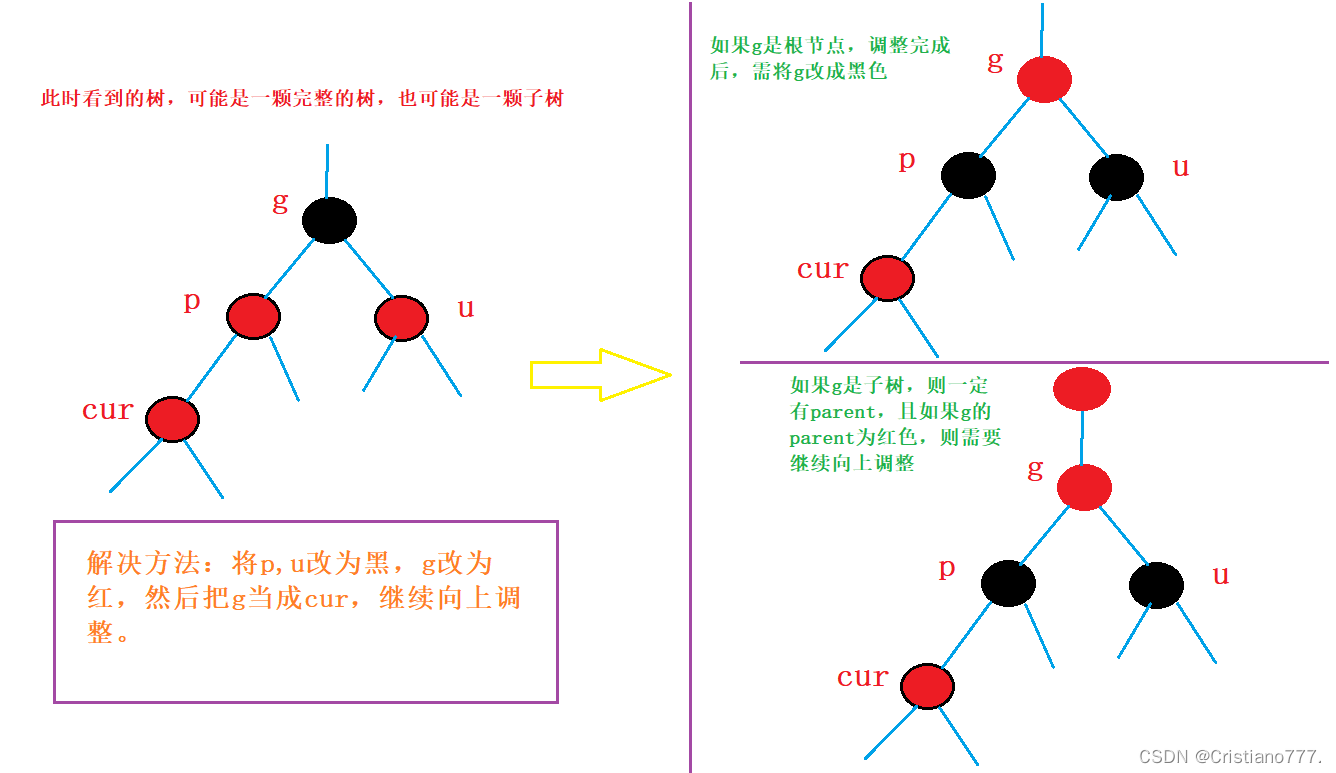
情况二: cur为红p为红g为黑u不存在/u存在且为黑
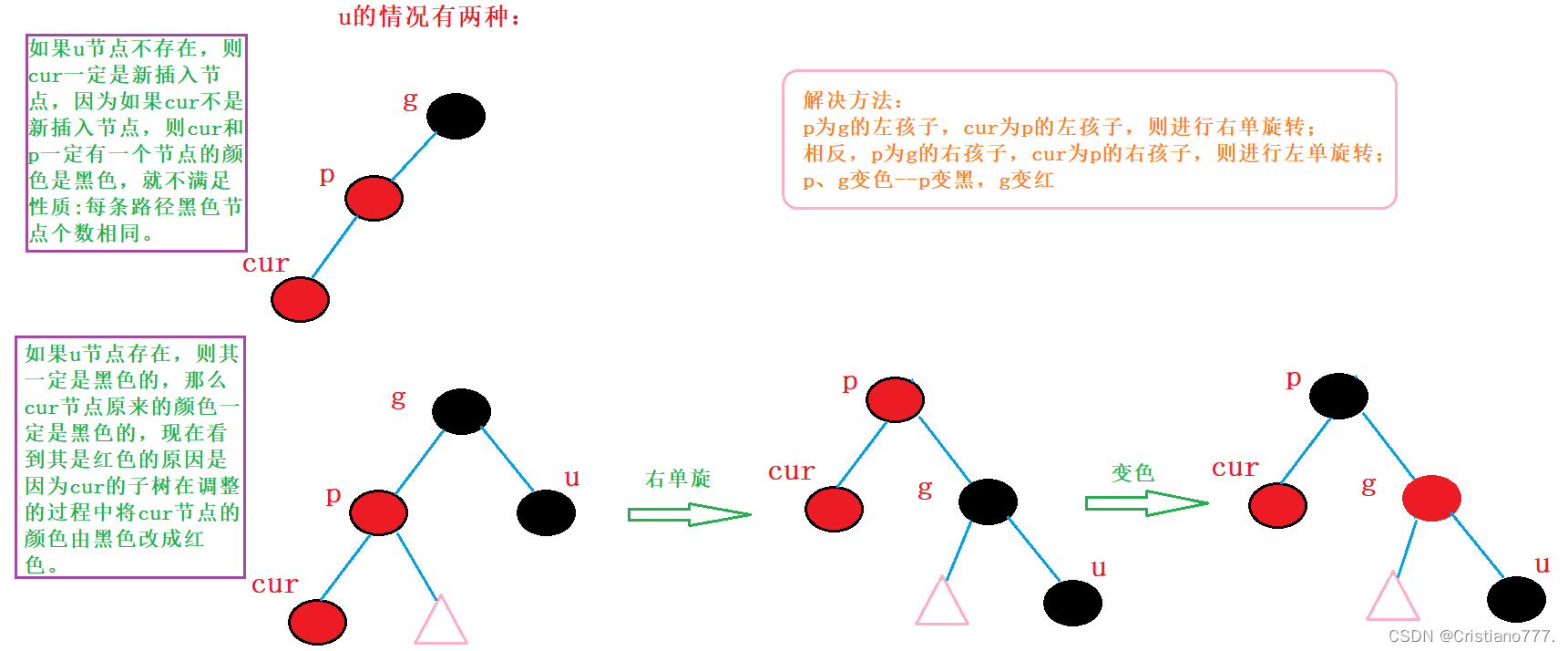
情况三: cur为红p为红g为黑u不存在/u存在且为黑
和情况二的区别为
- p、g、cur位置不同
- 情况二只对g进行旋转情况三对p进行旋转后就转变成情况二

bool Insert(const pair<k,v>& kv)
{
// 1、搜索树的规则插入
// 2、看是否违反平衡规则如果违反就需要处理旋转
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_col = RED;
if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//存在红色的连续节点
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
assert(grandfather);
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//情形一
//叔叔存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续向上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//叔叔不存在 or 叔叔存在且为黑色
{
if (cur == parent->_left)//单旋
{
// grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else//双旋
{
// grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else//grandfather->_right = parent
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//情形一
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续向上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)//单旋
{
//grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else//双旋
{
// grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}4.2.3 红黑树的验证
bool _IsValidRBTree(Node* pRoot, size_t k, const size_t blackCount)
{
//走到NULL之后判断k和blackCount是否相等
if (nullptr == pRoot)
{
if (k != blackCount)
{
cout << "违反性质每条路径中黑色节点的个数必须相同" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
//统计黑色节点个数
if (BLACK == pRoot->_col)
k++;
//检测当前节点与其双亲是否都为红色
if (RED == pRoot->_col && pRoot->_parent && pRoot->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << "违反性质存在连在一起的红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
return _IsValidRBTree(pRoot->_left, k, blackCount) &&
_IsValidRBTree(pRoot->_right, k, blackCount);
}4.2.4 红黑树的模拟实现
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK,
};
template<class k,class v>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<k, v>* _left;
RBTreeNode<k, v>* _right;
RBTreeNode<k, v>* _parent;
pair<k, v> _kv;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode(const pair<k,v>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_col(RED)
{}
};
template<class k, class v>
struct RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<k, v> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<k,v>& kv)
{
// 1、搜索树的规则插入
// 2、看是否违反平衡规则如果违反就需要处理旋转
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_col = RED;
if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//存在红色的连续节点
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
assert(grandfather);
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//情形一
//叔叔存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续向上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//叔叔不存在 or 叔叔存在且为黑色
{
if (cur == parent->_left)//单旋
{
// grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else//双旋
{
// grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else//grandfather->_right = parent
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//情形一
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续向上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)//单旋
{
//grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else//双旋
{
// grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
//层序遍历
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder()
{
vector<vector<int>> vv;
if (_root == nullptr)
return vv;
queue<Node*> q;
int levelSize = 1;
q.push(_root);
while (!q.empty())
{
// levelSize控制一层一层出
vector<int> levelV;
while (levelSize--)
{
Node* front = q.front();
q.pop();
levelV.push_back(front->_kv.first);
if (front->_left)
q.push(front->_left);
if (front->_right)
q.push(front->_right);
}
vv.push_back(levelV);
for (auto e : levelV)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 上一层出完下一层就都进队列
levelSize = q.size();
}
return vv;
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subR;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent == ppNode->_left)
{
ppNode->_left = subR;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = ppNode;
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subL;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppNode->_left == parent)
{
ppNode->_left = subL;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = ppNode;
}
}
int _maxHeight(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int lh = _maxHeight(root->_left);
int rh = _maxHeight(root->_right);
return lh > rh ? lh + 1 : rh + 1;
}
int _minHeight(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int lh = _minHeight(root->_left);
int rh = _minHeight(root->_right);
return lh < rh ? lh + 1 : rh + 1;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
bool _IsValidRBTree(Node* pRoot, size_t k, const size_t blackCount)
{
//走到NULL之后判断k和blackCount是否相等
if (nullptr == pRoot)
{
if (k != blackCount)
{
cout << "违反性质每条路径中黑色节点的个数必须相同" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
//统计黑色节点个数
if (BLACK == pRoot->_col)
k++;
//检测当前节点与其双亲是否都为红色
if (RED == pRoot->_col && pRoot->_parent && pRoot->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << "违反性质存在连在一起的红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
return _IsValidRBTree(pRoot->_left, k, blackCount) &&
_IsValidRBTree(pRoot->_right, k, blackCount);
}
public:
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
void Height()
{
cout << "最长路径:" << _maxHeight(_root) << endl;
cout << "最短路径:" << _minHeight(_root) << endl;
}
bool IsBalanceTree()
{
// 检查红黑树规则
Node* pRoot = _root;
// 空树也是红黑树
if (nullptr == pRoot)
return true;
// 检测根节点是否满足情况
if (BLACK != pRoot->_col)
{
cout << "违反性质根节点必须为黑色" << endl;
return false;
}
// 获取任意一条路径中黑色节点的个数 -- 比较基准值
size_t blackCount = 0;
Node* pCur = pRoot;
while (pCur)
{
if (BLACK == pCur->_col)
blackCount++;
pCur = pCur->_left;
}
// 检测是否满足红黑树的性质k用来记录路径中黑色节点的个数
size_t k = 0;
return _IsValidRBTree(pRoot, k, blackCount);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};4.2.5 红黑树与AVL树的比较
红黑树不追求绝对平衡其只需保证最长路径不超过最短路径的2倍。相对而言降低了插入和旋转的次数所以在经常进行增删的结构中性能比AVL树更优而且红黑树实现比较简单所以实际运用中红黑树更多。
4.3 红黑树模拟实现STL中map和set
4.3.1 红黑树的改造以及红黑树迭代器
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
T _data; // 数据
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _col(RED)
{}
};
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct _RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeNode<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
//找中序遍历中的下一个
Self& operator++()
{
//首先判断当前右子树位置是否为空
//空 ---> 找 孩子 是 祖先的左边 的 祖先
//非空 ---> 找右子树的最左节点
if (_node->_right == nullptr)
{
//找祖先里面孩子是父亲左的那个
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent
}
_node = parent;
}
else
{
//右子树的最左节点
Node* subLeft = _node->_right;
while (subLeft)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
_node = subLeft;
}
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
++(*this);
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node->_left == nullptr)
{
// 找祖先里面孩子是父亲右的那个
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
else
{
// 左子树的最右节点
Node* subRight = _node->_left;
while (subRight->_right)
{
subRight = subRight->_right;
}
_node = subRight;
}
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
--(*this);
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s->_node;
}
};
// T决定红黑树存什么数据
// set RBTree<K, K>
// map RBTree<K, pair<K, V>>
// KeyOfT -> 支持取出T对象中key的仿函数
template<class K,class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef _RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef _RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
public:
iterator Begin()
{
Node* subLeft = _root;
while (subLeft && subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
return iterator(subLeft);
}
iterator End()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator Begin() const
{
Node* subLeft = _root;
while (subLeft && subLeft->_left)
{
subLeft = subLeft->_left;
}
return const_iterator(subLeft);
}
const_iterator End() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
// 1、搜索树的规则插入
// 2、看是否违反平衡规则如果违反就需要处理旋转
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur), true);
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
cur->_col = RED;
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//存在红色的连续节点
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
assert(grandfather);
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//情形一
//叔叔存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续向上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//叔叔不存在 or 叔叔存在且为黑色
{
if (cur == parent->_left)//单旋
{
// grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else//双旋
{
// grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else//grandfather->_right = parent
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//情形一
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续向上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)//单旋
{
//grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else//双旋
{
// grandfather
// parent
// cur
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subR;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent == ppNode->_left)
{
ppNode->_left = subR;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = ppNode;
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* ppNode = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = subL;
_root->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (ppNode->_left == parent)
{
ppNode->_left = subL;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = ppNode;
}
}
iterator Find(const k& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
KeyOfT kot;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return iterator(cur);
}
}
return End();
}
};4.3.2 map和set的模拟实现
map.h
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace Cris
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}set.h
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace Cris
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
}
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator _iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
//pair<typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(key);
auto ret = _t.Insert(key);
return pair<iterator, bool>(iterator(ret.first._node), ret.second);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
