SpringBoot框架_springboot
| 阿里云国内75折 回扣 微信号:monov8 |
| 阿里云国际,腾讯云国际,低至75折。AWS 93折 免费开户实名账号 代冲值 优惠多多 微信号:monov8 飞机:@monov6 |
目录
2.2 创建一个 Spring MVC 的 Spring BootController
3.4 Spring Boot 下的 Spring MVC注解
1.1 简介
springboot是spring家族中的一个全新框架用来简化spring程序的创建和开发过程。在以往我们通过SpringMVC+Spring+Mybatis框架进行开发的时候我们需要配置web.xmlspring配置mybatis配置然后整合在一起而springboot抛弃了繁琐的xml配置过程采用大量默认的配置来简化我们的spring开发过程。
SpringBoot化繁为简使开发变得更加的简单迅速。
1.2 特性
- 能够快速创建基于spring的程序
- 能够直接使用Java main方法启动内嵌的Tomcat服务器运行springboot程序不需要部署war包
- 提供约定的starter POM来简化Maven配置让Maven的配置变得简单
- 自动化配置根据项目的Maven依赖配置springboot自动配置spring、springmvc等
- 提供了程序的健康检查功能
- 基本可以完全不使用xml配合文件采用注解配置
1.3 四大核心
自动配置、起步依赖、Actuator、命令行界面
2 springboot入门案例
2.1 SpringBoot 项目开发步骤
1创建一个 Module选择类型为Spring Initializr 快速构建
2设置 GAV 坐标及 pom 配置信息

3选择 Spring Boot 版本及依赖
4设置模块名称、Content Root 路径及模块文件的目录然后点击finish即可

5项目结构如下

static存放静态资源。如图片、CSS、JavaScript 等
templates存放 Web 页面的模板文件
application.properties/application.yml 用于存放程序的各种依赖模块的配置信息比如 服务端口数据库连接配置等
.gitignore使用版本控制工具 git 的时候设置一些忽略提交的内容
Application.javaSpringBoot 程序执行的入口执行该程序中的 main 方法启动当前SpringBoot项目。
6对pom.xml文件进行解释
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<!--继承 SpringBoot 框架的一个父项目所有自己开发的 Spring Boot 都必须的继承-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<!--当前项目的 GAV 坐标-->
<groupId>com.bjpowernode.springboot</groupId>
<artifactId>002-springboot-springmvc</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<!--maven 项目名称可以删除-->
<name>002-springboot-springmvc</name>
<!--maven 项目描述可以删除-->
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<!--maven 属性配置可以在其它地方通过${}方式进行引用-->
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--SpringBoot 框架 web 项目起步依赖通过该依赖自动关联其它依赖不需要我们一个一个去添加
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringBoot 框架的测试起步依赖例如junit 测试如果不需要的话可以删除-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!--SpringBoot提供的打包编译等插件-->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project> 2.2 创建一个 Spring MVC 的 Spring BootController
1创建SpringBootController 类
注意新创建的类一定要位于 Application 同级目录或者下级目录否则 SpringBoot 加
载不到。
package com.bjpowernode.springboot.web;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class SpringBootController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/springBoot/say")
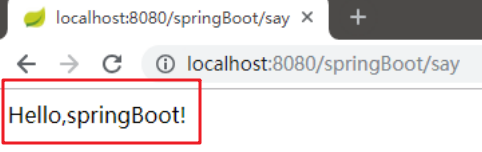
public @ResponseBody String say() {
return "Hello,springBoot!";
}
} 2启动Application类中的main方法
通过在控制台的输出可以看到启动 SpringBoot 框架会启动一个内嵌的 tomcat端
口号为 8080上下文根为空 。
![]()
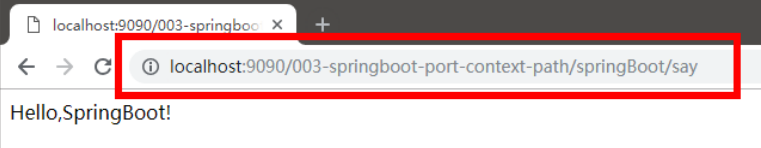
3在浏览器中输入 http://localhost:8080/springBoot/say进行访问
2.3 分析
1spring-boot-starter-parent 是一个 Springboot 的父级依赖开发 SpringBoot 程序都需
要继承该父级项目它用来提供相关的 Maven 默认依赖使用它之后常用的 jar
包依赖可以省去 version 配置
2Spring Boot 提供了一些默认的jar 包的依赖可查看该父级依赖的 pom 文件
3如果不想使用某个默认的依赖版本可以通过 pom.xml 文件的属性配置覆盖各个
依赖项比如覆盖 Spring 版本
<properties>
<spring-framework.version>5.0.0.RELEASE</ spring-framework.version >
</properties> 4 @SpringBootApplication 注解是 Spring Boot 项目的核心注解主要作用是开启
Spring 自动配置如果在 Application 类上去掉该注解那么不会启动 SpringBoot程序
5main 方法是一个标准的 Java 程序的 main 方法是boot项目启动运行的入口
6@Controller 及 @ResponseBody 依然是我们之前的 Spring MVC因为 Spring Boot
的里面依然是使用我们的 Spring MVC + Spring + MyBatis 等框架
2.4 核心配置文件格式
1.properties 文件默认采用该文件
通过修改 application.properties 配置文件修改默认 tomcat 端口号及项目上下文件根
#设置内嵌 Tomcat 端口号
server.port=9090
#配置项目上下文根
server.servlet.context-path=/003-springboot-port-context-path
页面显示结果
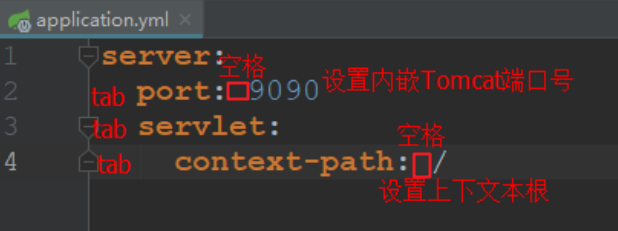
2 .yml 文件
项目名称004-springboot-yml
yml 是一种 yaml 格式的配置文件主要采用一定的空格、换行等格式排版进行配置。它能够直观的被计算机识别数据序列化格式容易被人类阅读yaml 类似于 xml但是语法比 xml 简洁很多值与前面的冒号配置项必须要有一个空格 yml 后缀也可以使用 yaml 后缀 。
注意当两种格式配置文件同时存在时使用的是.properties 配置文件。
3多环境配置.properties方式
在实际开发的过程中我们的项目会经历很多的阶段开发->测试->上线每个阶段
的配置也会不同例如端口、上下文根、数据库等那么这个时候为了方便在不同的环境
之间切换SpringBoot 提供了多环境配置具体步骤如下
项目名称005-springboot-multi-environment
为每个环境创建一个配置文件命名必须为 application-环境标识.properties|yml
application-dev.properties
#开发环境
#设置内嵌 Tomcat 默认端口号
server.port=8080
#设置项目的上下文根
server.servlet.context-path=/005-springboot-multi-environment-dev
application-product.properties
#生产环境
#配置内嵌 Tomcat 默认端口号
server.port=80
#配置项目上下文根
server.servlet.context-path=/005-springboot-multi-environment-product
application-test.properties
#测试环境
#配置内嵌 Tomcat 端口号
server.port=8081
#配置项目的上下文根
server.servlet.context-path=/005-springboot-multi-environment-test
在总配置文件 application.properties 进行环境的激活
#SpringBoot 的总配置文件
#激活开发环境
#spring.profiles.active=dev
#激活测试环境
#spring.profiles.active=test
#激活生产环境
spring.profiles.active=product
4多环境配置.yml方式
application-dev.yml
#设置开发环境配置
server:
port: 8080 #设置 Tomcat 内嵌端口号
servlet:
context-path: /dev #设置上下文根 application-product.yml
#设置生产环境配置
server:
port: 80
servlet:
context-path: /product
application-test.yml
#设置测试环境配置
server:
port: 9090
servlet:
context-path: /test在总配置文件 application.yml进行环境的激活
#springboot 总配置文件
#激活开发环境
#spring:
# profiles:
# active: dev
#激活测试环境
#spring:
# profiles:
# active: test
#激活生产环境
spring:
profiles:
active: product
5Spring Boot 自定义配置
在 SpringBoot 的核心配置文件中除了使用内置的配置项之外我们还可以在自定义配
置然后采用如下注解去读取配置的属性值
A@Value注解 用于逐个读取application.properties中的配置
案例演示
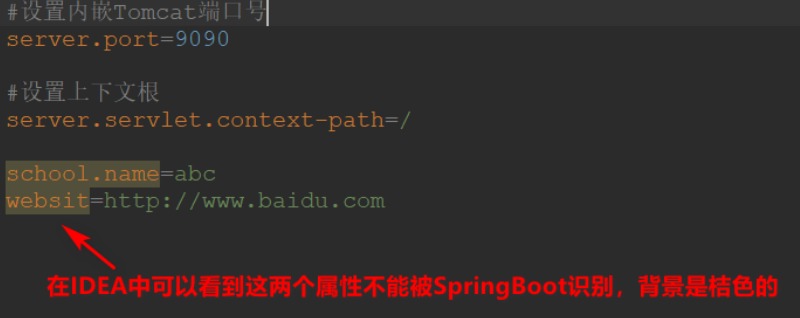
1 在核心配置文件 applicatin.properties 中添加两个自定义配置项 school.name 和
website。在 IDEA 中可以看到这两个属性不能被 SpringBoot 识别背景是桔色的
.properties方式
.yml方式
#设置端口号及上下文根
server:
port: 9090
servlet:
context-path: /
school:
name: ssm
websit: http://www.baidu.com 2在 SpringBootController 中定义属性并使用@Value 注解或者自定义配置值并对其方法进行测试
@Controller
public class SpringBootController {
@Value("${school.name}")
private String schoolName;
@Value("${websit}")
private String websit;
@RequestMapping(value = "/springBoot/config")
public @ResponseBody String say() {
return schoolName + "------" + websit;
}
} 3重新运行 Application在浏览器中进行测试

B@ConfigurationProperties
作用将整个文件映射成一个对象用于自定义配置项比较多的情况 。
案例演示
1在 com.abc.springboot.config 包下创建 ConfigInfo 类并为该类加上 Component 和
ConfigurationProperties 注解并在 ConfigurationProperties 注解中添加属性 prefix可以区分同名配置 。
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "school")
public class ConfigInfo {
private String name;
private String websit;
} 2application.properties 配置文件
#设置内嵌 Tomcat 端口号
server.port=9090
#设置上下文根
server.servlet.context-path=/config
school.name=ssm
school.websit=http://www.baidu.com
3在 SpringBootController 中注入 ConfigInfo 配置类
@Autowired
private ConfigInfo configInfo;
4修改 SpringBootController 类中的测试方法
@RequestMapping(value = "/springBoot/config")
public @ResponseBody String say() {
return configInfo.getName() + "=======" + configInfo.getWebsit();
} 5重新运行 Application在浏览器中进行测试 
C警告解决
在 ConfigInfo 类中使用了 ConfigurationProperties 注解后IDEA 会出现一个警告不影响程序的执行。
点击 open documentnation 跳转到网页在网页中提示需要加一个依赖我们将这
个依赖拷贝粘贴到 pom.xml 文件中 即可。
<!--解决使用@ConfigurationProperties 注解出现警告问题-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency> D中文乱码
如果在 SpringBoot 核心配置文件中有中文信息会出现乱码
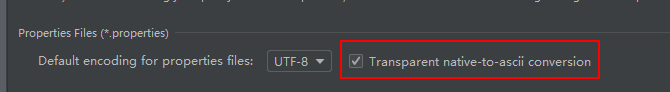
- 一般在配置文件中不建议出现中文注释除外
- 如果出现中文可以先转化为 ASCII 码
2.5 Spring Boot 前端使用 JSP
1在 pom.xml 文件中配置以下依赖项
<!--引入 Spring Boot 内嵌的 Tomcat 对 JSP 的解析包不加解析不了 jsp 页面-->
<!--如果只是使用 JSP 页面可以只添加该依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--如果要使用 servlet 必须添加该以下两个依赖-->
<!-- servlet 依赖的 jar 包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--如果使用 JSTL 必须添加该依赖-->
<!--jstl 标签依赖的 jar 包 start-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency> 2在 pom.xml 的 build 标签中要配置以下信息
SpringBoot 要求 jsp 文件必须编译到指定的 META-INF/resources 目录下才能访问否则
访问不到。其实官方已经更建议使用模板技术。
<!--
SpringBoot 要求 jsp 文件必须编译到指定的 META-INF/resources 目录下才能访问否则访问
不到。
其它官方已经建议使用模版技术
-->
<resources>
<resource>
<!--源文件位置-->
<directory>src/main/webapp</directory>
<!--指定编译到 META-INF/resources该目录不能随便写-->
<targetPath>META-INF/resources</targetPath>
<!--指定要把哪些文件编译进去**表示 webapp 目录及子目录*.*表示所有文件-->
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources> 3在 application.properties 文件配置 Spring MVC 的视图展示为jsp这里相当于 Spring MVC 的配置。
#SpringBoot 核心配置文件
#指定内嵌 Tomcat 端口号
server.port=8090
#配置 SpringMVC 视图解析器
#其中/ 表示目录为 src/main/webapp
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
4在 com.abc.springboot.controller 包下创建 JspController 类
@Controller
public class SpringBootController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/springBoot/jsp")
public String jsp(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("data","SpringBoot 前端使用 JSP 页面");
return "index";
}
}
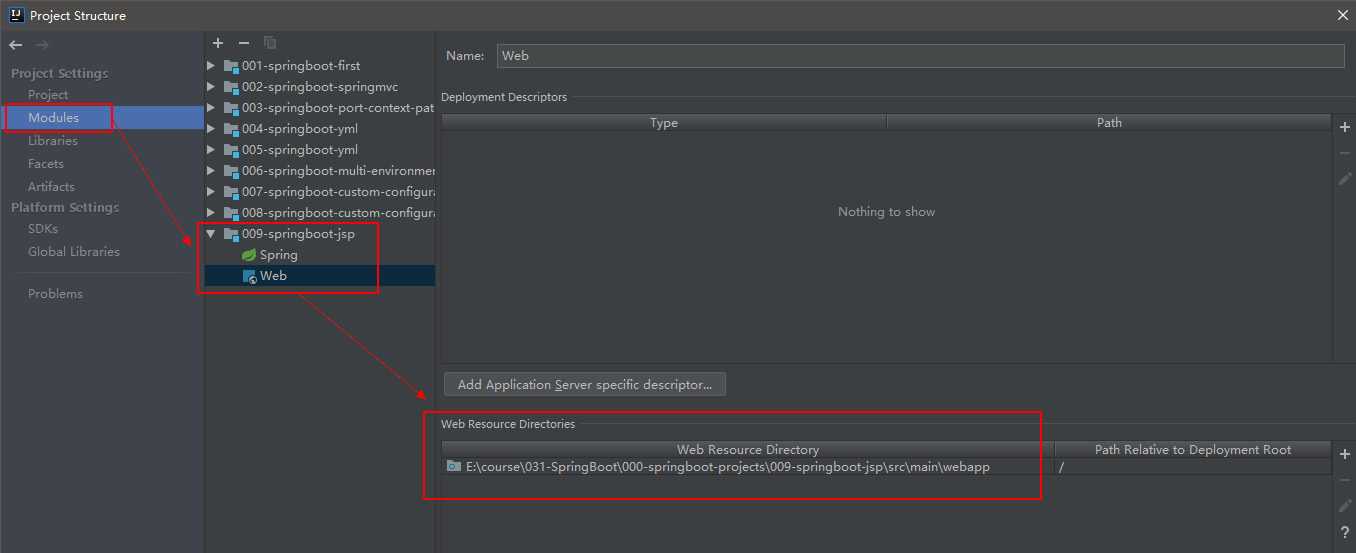
5在 src/main 下创建一个 webapp 目录然后在该目录下新建index.jsp 页面
注意 如果在webapp目录下右键没有创建jsp的选项可以在Project Structure中指定webapp为 Web Resource Directory 。
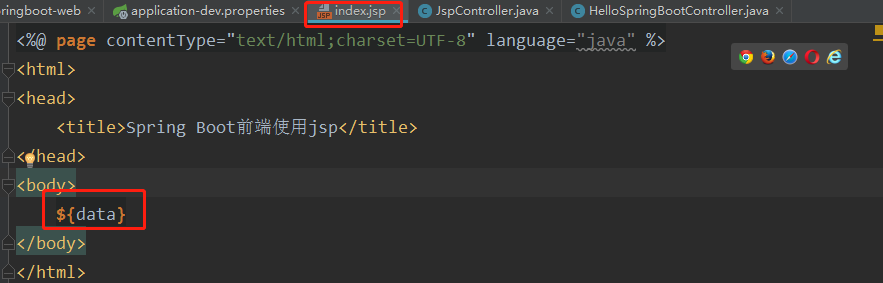
6在 index.jsp 中获取 Controller 传递过来的数据
7重新运行 Application通过浏览器访问测试

3 SpringBoot框架Web开发
通过实际代码案例进行梳理
3.1 Spring Boot 集成 MyBatis
通过 SpringBoot +MyBatis 实现对数据库学生表的查询操作的实现步骤
1创建新的数据库springboot并向表中插入数据
2创建一个新的 SpringBoot 的 Module
创建项目的过程省略
3在 pom.xml 中添加相关 jar 依赖
<!--MyBatis 整合 SpringBoot 的起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--MySQL 的驱动依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency> 4在 Springboot 的核心配置文件 application.properties 中配置数据源
#配置内嵌 Tomcat 端口号
server.port=9090
#配置项目上下文根
server.servlet.context-path=/010-springboot-web-mybatis
#配置数据库的连接信息
#注意这里的驱动类有变化
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
5开发代码代码生成器
使用 Mybatis 反向工程生成接口、映射文件以及实体 bean具体步骤参见附录 1
A在 web 包下创建 StudentController 并编写代码
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/springBoot/student")
public @ResponseBody Object student() {
Student student = studentService.queryStudentById(1);
return student;
}
}
B在 service 包下创建 service 接口并编写代码
public interface StudentService {
/**
* 根据学生标识获取学生详情
* @param id
* @return
*/
Student queryStudentById(Integer id);
}C在 service.impl 包下创建 service 接口并编写代码
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Override
public Student queryStudentById(Integer id) {
return studentMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
} D如果在 web 中导入 service 存在报错可以尝试进行如下配置解决 
E 在 Mybatis 反向工程生成的 StudentMapper 接口上加一个 Mapper 注解
@Mapper 作用mybatis 自动扫描数据持久层的映射文件及 DAO 接口的关系
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
} F默认情况下Mybatis 的 xml 映射文件不会编译到 target 的 class 目录下所
以我们需要在 pom.xml 文件中配置 resource 。
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
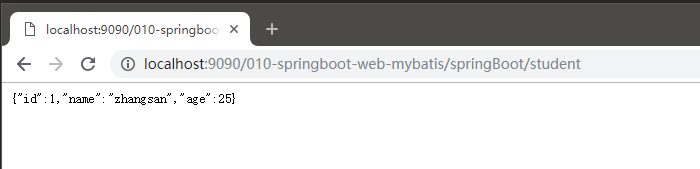
</resources>G启动 Application 应用浏览器访问测试运行
3.2 DAO 的其它开发方式
方式一
A注释掉 StudentMapper 接口上的@Mapper 注解

B在运行的主类上添加注解包扫描MapperScan("com.abc.springboot.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.abc.springboot.mapper")
public class Application {
或
@SpringBootApplication
//Mybatis 提供的注解扫描数据持久层的 mapper 映谢配置文件,DAO 接口上就不用加@Mapper
//basePackages 通常指定到数据持久层包即可
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.abc.springboot.mapper")
public class Application { 方式二
因为 SpringBoot 不能自动编译接口映射的 xml 文件还需要手动在 pom 文件中指定
所以有的公司直接将映射文件直接放到 resources 目录下 在 resources 目录下新建目录 mapper 存放映射文件将 StudentMapper.xml 文件移到resources/mapper 目录下
在 application.properties 配置文件中指定映射文件的位置这个配置只有接口和映
射文件不在同一个包的情况下才需要指定
# 指定 Mybatis 映射文件的路径
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
3.3 Spring Boot 事务支持
springboot事务底层依然采用的是 Spring 本身提供的事务管理。
- 在入口类中使用注解@EnableTransactionManagement开启事务支持
- 在访问数据库的service方法上添加注解@Transactional即可
在上述案例的基础上通过 SpringBoot +MyBatis 实现对数据库学生表的更新操作在 service 层的方法中构建异常查看事务是否生效
1在 StudentController 中添加更新学生的方法
@RequestMapping(value = "/springboot/modify")
public @ResponseBody Object modifyStudent() {
int count = 0;
try {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1);
student.setName("Jack");
student.setAge(33);
count = studentService.modifyStudentById(student);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "fail";
}
return count;
} 2在 StudentService 接口中添加更新学生方法
int modifyStudentById(Student student);
3在 StudentServiceImpl 接口实现类中对更新学生方法进行实现并构建一个异常同时在该方法上加@Transactional 注解。
@Override
@Transactional //添加此注解说明该方法添加的事务管理
public int update(Student student) {
int updateCount = studentMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(student);
System.out.println("更新结果" + updateCount);
//在此构造一个除数为 0 的异常测试事务是否起作用
int a = 10/0;
return updateCount;
}
4在Application类上加@EnableTransactionManagement开启事务支持。
@EnableTransactionManagement 可选但是业务方法上必须添加@Transactional 事务才生效
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.abc.springboot.mapper")
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务支持(可选项但@Transactional 必须添加)
public class Application {
3.4 Spring Boot 下的 Spring MVC注解
springboot下的springMVC主要有以下注解
1@ControllerSpring MVC 的注解处理 http 请求
2@RestController @Controller 与@ResponseBody 的组合注解
如果一个 Controller 类添加了@RestController那么该 Controller 类下的所有方法都相当
于添加了@ResponseBody 注解 用于返回字符串或json数据。
创建 MyRestController 类演示@RestController 替代@Controller + @ResponseBody
@RestController
public class MyRestController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping("/boot/stu")
public Object stu(){
return studentService.getStudentById(1);
}
} 3@RequestMapping支持 Get 请求也支持 Post 请求 。
4@GetMapping 只支持 Get 请求主要用于查询操作。
5@PostMapping只支持Post请求主要用于新增数据。
6@PutMapping只支持put请求主要用于修改数据
7@DeleteMapping只支持delete请求通常用与删除数据
8综合案例
A创建一个 MVCController里面使用上面介绍的各种注解接收不同的请求
//RestController 注解相当于加了给方法加了@ResponseBody 注解所以是不能跳转页面的只能返回字符串或者 json 数据
@RestController
public class MVCController {
@GetMapping(value = "/query")
public String get() {
return "@GetMapping 注解,通常查询时使用";
}
@PostMapping(value = "/add")
public String add() {
return "@PostMapping 注解通常新增时使用";
}
@PutMapping(value = "/modify")
public String modify() {
return "@PutMapping 注解通常更新数据时使用";
}
@DeleteMapping(value = "/remove")
public String remove() {
return "@DeleteMapping 注解通常删除数据时使用";
}
} B启动应用在浏览器中输入不同的请求进行测试

C结合POSTMan工具测试其他请求类型

3.5 SpringBoot实现RESTFUL
1简介
它是一种互联网软件设计的风格它只是提出了一组客户端和服务器交互时的架构理念和设计原则基于这种理念和原则设计的接口可以更简洁更有层次。
比如我们要访问一个 http 接口http://localhost:8080/boot/order?id=1021&status=1
采用 RESTFul 风格则 http 地址为http://localhost:8080/boot/order/1021/1
2开发RESTFUL主要用到以下注解
- @PathVariable 获取 url 中的数据该注解是实现 RESTFul 最主要的一个注解
- @PostMapping 接收和处理post方式的请求
- @DeleteMapping接收delete方式的请求可以用GetMapping代替
- @PutMapping 接收put方式的请求可以用 PostMapping 代替
- @GetMapping 接收get方式请求
3案例使用 RESTful 风格模拟实现对学生的增删改查操作
该项目集成了 MyBatis、spring、SpringMVC通过模拟实现对学生的增删改查操作
pom.xml文件
<dependencies>
<!--SpringBoot 框架 web 项目起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--MyBatis 集成 SpringBoot 框架起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--MySQL 驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<!--指定配置资源的位置-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
<plugins>
<!--mybatis 代码自动生成插件-->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.3.6</version>
<configuration>
<!--配置文件的位置-->
<configurationFile>GeneratorMapper.xml</configurationFile>
<verbose>true</verbose>
<overwrite>true</overwrite>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build> application. properties核心配置文件
#配置内嵌 Tomcat 端口号
server.port=8090
#配置项目上下文根
server.servlet.context-path=/
#配置数据库的连接信息
#注意这里的驱动类有变化
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
通过逆向工程生成 DAO
创建 RESTfulController
@RestController
public class RESTfulController {
/**
* 添加学生
* 请求地址
http://localhost:9090/014-springboot-restful/springBoot/student/wangpeng/23
* 请求方式POST
* @param name
* @param age
* @return
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/springBoot/student/{name}/{age}")
public Object addStudent(@PathVariable("name") String name, @PathVariable("age") Integer age) {
Map<String,Object> retMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
retMap.put("name",name);
retMap.put("age",age);
return retMap;
}
/**
* 删除学生
* 请求地址
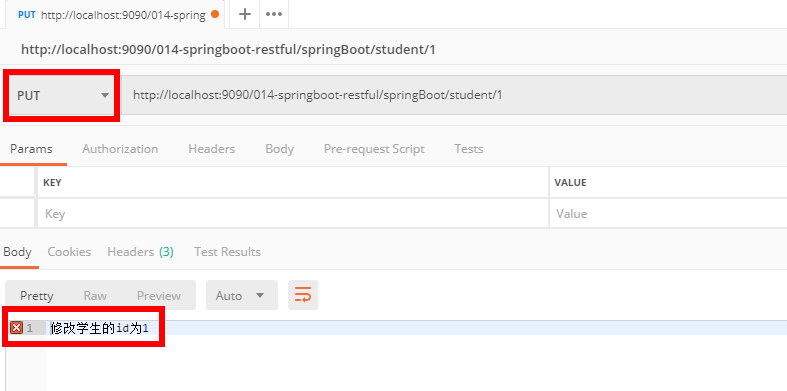
http://localhost:9090/014-springboot-restful/springBoot/student/1
* 请求方式Delete
* @param id
* @return
*/
@DeleteMapping(value = "/springBoot/student/{id}")
public Object removeStudent(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return "删除的学生 id 为" + id;
}
/**
* 修改学生信息
* 请求地址
http://localhost:9090/014-springboot-restful/springBoot/student/2
* 请求方式Put
* @param id
* @return
*/
@PutMapping(value = "/springBoot/student/{id}")
public Object modifyStudent(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return "修改学生的 id 为" + id;
}
@GetMapping(value = "/springBoot/student/{id}")
public Object queryStudent(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return "查询学生的 id 为" + id;
}
}
使用 Postman 模拟发送请求进行测试 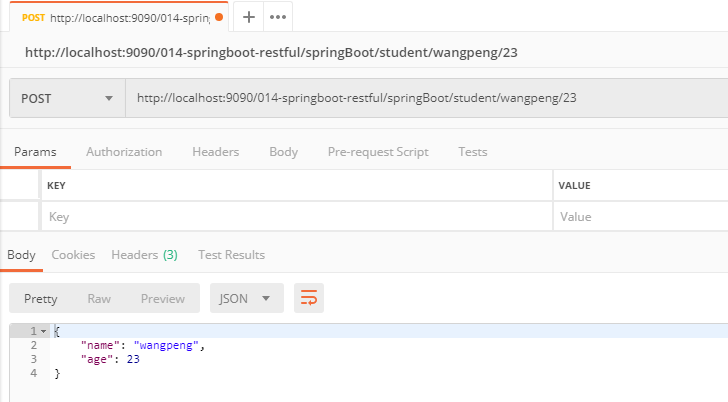


4请求冲突的问题
解决方案<1>修改路径 <2>修改请求方式
创建 RESTfulController 类结合 Postman 进行测试说明
@RestController
public class RESTfulController {
/**
* id:订单标识
* status订单状态
* 请求路径
http://localhost:9090/015-springboot-restful-url-conflict/springBoot/orde
r/1/1001
* @param id
* @param status
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/springBoot/order/{id}/{status}")
public Object queryOrder(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("status") Integer status) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("id",id);
map.put("status",status);
return map;
}
/**
* id:订单标识
* status订单状态
* 请求路径
http://localhost:9090/015-springboot-restful-url-conflict/springBoot/1/or
der/1001
* @param id
* @param status
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/springBoot/{id}/order/{status}")
public Object queryOrder1(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("status") Integer status) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("id",id);
map.put("status",status);
return map;
}
/**
* id:订单标识
* status订单状态
* 请求路径
http://localhost:9090/015-springboot-restful-url-conflict/springBoot/1001
/order/1
* @param id
* @param status
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/springBoot/{status}/order/{id}")
public Object queryOrder2(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("status") Integer status) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("id",id);
map.put("status",status);
return map;
}
/**
* id:订单标识
* status订单状态
* 请求路径
http://localhost:9090/015-springboot-restful-url-conflict/springBoot/1001
/order/1
* @param id
* @param status
* @return
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/springBoot/{status}/order/{id}")
public Object queryOrder3(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("status") Integer status) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("id",id);
map.put("status",status);
return map;
}
/**
* query1 和 query2 两个请求路径会发生请求路径冲突问题
* query3 与 query1 和 query2 发生请求冲突
* 注意虽然两个路径写法改变了但是由于传递的两个参数都是 int 值所以不知道该交给
哪个请求进行处理
* 就会出现匹配模糊不清的异常所以要想解决冲突有两种方式
* 1.修改请求路径
* 2.修改请求方式
*/
}
5RESTful 原则
- 增 post 请求、删 delete 请求、改 put 请求、查 get 请求
- 请求路径不要出现动词

- 分页、排序等操作不需要使用斜杠传参数

3.6 Spring Boot 集成 Redis
完善根据学生 id 查询学生的功能先从 redis 缓存中查找如果找不到再从数据库中
查找然后放到 redis 缓存中。
具体实现步骤
A首先通过 MyBatis 逆向工程生成实体 bean 和数据持久层
B在 pom.xml 文件中添加 redis 依赖
<!-- 加载 spring boot redis 包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
CSpring Boot 核心配置文件application.properties 如下
#配置内嵌 Tomcat 端口号
server.port=9090
#配置项目上下文根
server.servlet.context-path=/016-springboot-redis
#配置连接 MySQL 数据库信息
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/springbootuseUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDa
tetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#配置 redis 连接信息
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
spring.redis.port=6379
#spring.redis.password=root
D启动redis服务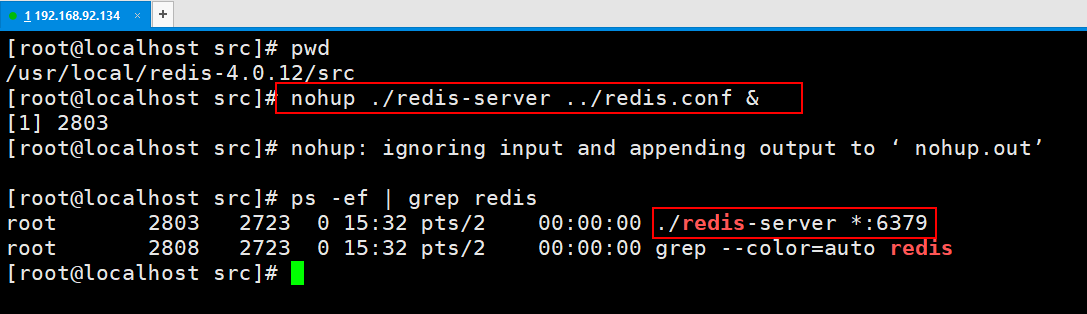
ERedisController类
@RestController
public class RedisController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
/**
* 请求地址
http://localhost:9090/016-springboot-redis//springboot/allStudentCount
* @param request
* @return
*/
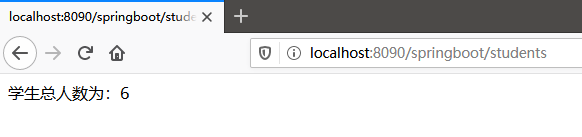
@GetMapping(value = "/springboot/allStudentCount")
public Object allStudentCount(HttpServletRequest request) {
Long allStudentCount = studentService.queryAllStudentCount();
return "学生总人数" + allStudentCount;
}
} FStudentService 接口
public interface StudentService {
/**
* 获取学生总人数
* @return
*/
Long queryAllStudentCount();
} G在 StudentServiceImpl 中注入 RedisTemplate并编写根据 id获取学生的方法
配置了上面的步骤Spring Boot 将自动配置 RedisTemplate在需要操作 redis 的类中注入 redisTemplate 即可。
注意Spring Boot 帮我们注入 RedisTemplate 类泛型里面只能写 <String, String>、<Object, Object>或者什么都不写。
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate;
@Override
public Long queryAllStudentCount() {
//设置 redisTemplate 对象 key 的序列化方式
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
//从 redis 缓存中获取总人数
Long allStudentCount = (Long) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("allStudentCount");
//判断是否为空
if ( allStudentCount==null) {
//去数据库查询并存放到 redis 缓存中
allStudentCount = studentMapper.selectAllStudentCount();
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("allStudentCount",allStudentCount,15,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
return allStudentCount;
}
}
HStudentMapper 接口
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
/**
* 获取学生总人数
* @return
*/
Long selectAllStudentCount();
}
IStudentMapper 映射文件
<!--获取学生总人数-->
<select id="selectAllStudentCount" resultType="java.lang.Long">
select count(*) from t_student
</select>
J启动类 Application
在 SpringBoot 启动类上添加扫描数据持久层的注解并指定扫描包
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.abc.springboot.mapper")//扫描数据持久层
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
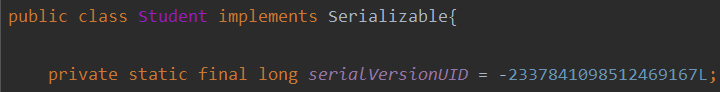
} K让 Student 类实现序列化接口可选
在类名上 Alt + 回车如果没有提示生成序列化 id那么需要做如下的配置

L启动 SpringBoot 应用访问测试