Android 中关于 FileObserver类监听文件状态的实践
| 阿里云国内75折 回扣 微信号:monov8 |
| 阿里云国际,腾讯云国际,低至75折。AWS 93折 免费开户实名账号 代冲值 优惠多多 微信号:monov8 飞机:@monov6 |
文章目录
需求背景
当某一个目录的文件发生变化创建、修改、删除、移动时需要给一个回调事件给其他端调用。
其他场景阅后即焚等等。
比如在 Android 的 VR 设备中有一个用于部署的文件在Android 系统中发生变化时需要给 Unity 端的一个回调Unity 端基于该回调做相应的操作。
涉及到的技术点
Unity 和 Android 端的数据交互Android系统中 接口的设计、以及 AIDL 跨进程的通信等等此处不在展开后期再更新。本文只介绍一下文件监听的使用及注意事项。
android.os下的FileObserver类是一个用于监听文件访问、创建、修改、删除、移动等操作的监听器基于linux的inotify。
FileObserver 是个抽象类必须继承它才能使用。每个FileObserver对象监听一个单独的文件或者文件夹如果监视的是一个文件夹那么文件夹下所有的文件和级联子目录的改变都会触发监听的事件。
所能监听的事件类型如下
- ACCESS即文件被访问
- MODIFY文件被 修改
- ATTRIB文件属性被修改如 chmod、chown、touch 等
- CLOSE_WRITE可写文件被 close
- CLOSE_NOWRITE不可写文件被 close
- OPEN文件被 open
- MOVED_FROM文件被移走,如 mv
- MOVED_TO文件被移来如 mv、cp
- CREATE创建新文件
- DELETE文件被删除如 rm
- DELETE_SELF自删除即一个可执行文件在执行时删除自己
- MOVE_SELF自移动即一个可执行文件在执行时移动自己
- CLOSE文件被关闭等同于(IN_CLOSE_WRITE | IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE)
- ALL_EVENTS包括上面的所有事件
走进源码
/**
FileObserver 类是一个用于监听文件访问、创建、修改、删除、移动等操作的监听器基于linux的inotify。
FileObserver 是个抽象类必须继承它才能使用。
每个FileObserver对象监听一个单独的文件或者文件夹如果监视的是一个文件夹那么文件夹下所有的文件和级联子目录的改变都会触发监听的事件。
**/
public abstract class FileObserver {
/** @hide */
@IntDef(flag = true, value = {
ACCESS,
MODIFY,
ATTRIB,
CLOSE_WRITE,
CLOSE_NOWRITE,
OPEN,
MOVED_FROM,
MOVED_TO,
CREATE,
DELETE,
DELETE_SELF,
MOVE_SELF
})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface NotifyEventType {}
/** Event type: Data was read from a file */
public static final int ACCESS = 0x00000001;
/** Event type: Data was written to a file */
public static final int MODIFY = 0x00000002;
/** Event type: Metadata (permissions, owner, timestamp) was changed explicitly */
public static final int ATTRIB = 0x00000004;
/** Event type: Someone had a file or directory open for writing, and closed it */
public static final int CLOSE_WRITE = 0x00000008;
/** Event type: Someone had a file or directory open read-only, and closed it */
public static final int CLOSE_NOWRITE = 0x00000010;
/** Event type: A file or directory was opened */
public static final int OPEN = 0x00000020;
/** Event type: A file or subdirectory was moved from the monitored directory */
public static final int MOVED_FROM = 0x00000040;
/** Event type: A file or subdirectory was moved to the monitored directory */
public static final int MOVED_TO = 0x00000080;
/** Event type: A new file or subdirectory was created under the monitored directory */
public static final int CREATE = 0x00000100;
/** Event type: A file was deleted from the monitored directory */
public static final int DELETE = 0x00000200;
/** Event type: The monitored file or directory was deleted; monitoring effectively stops */
public static final int DELETE_SELF = 0x00000400;
/** Event type: The monitored file or directory was moved; monitoring continues */
public static final int MOVE_SELF = 0x00000800;
/** Event mask: All valid event types, combined */
@NotifyEventType
public static final int ALL_EVENTS = ACCESS | MODIFY | ATTRIB | CLOSE_WRITE
| CLOSE_NOWRITE | OPEN | MOVED_FROM | MOVED_TO | DELETE | CREATE
| DELETE_SELF | MOVE_SELF;
private static final String LOG_TAG = "FileObserver";
private static class ObserverThread extends Thread {
private HashMap<Integer, WeakReference> m_observers = new HashMap<Integer, WeakReference>();
private int m_fd;
public ObserverThread() {
super("FileObserver");
m_fd = init();
}
public void run() {
observe(m_fd);
}
public int[] startWatching(List<File> files,
@NotifyEventType int mask, FileObserver observer) {
final int count = files.size();
final String[] paths = new String[count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
paths[i] = files.get(i).getAbsolutePath();
}
final int[] wfds = new int[count];
Arrays.fill(wfds, -1);
startWatching(m_fd, paths, mask, wfds);
final WeakReference<FileObserver> fileObserverWeakReference =
new WeakReference<>(observer);
synchronized (m_observers) {
for (int wfd : wfds) {
if (wfd >= 0) {
m_observers.put(wfd, fileObserverWeakReference);
}
}
}
return wfds;
}
public void stopWatching(int[] descriptors) {
stopWatching(m_fd, descriptors);
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public void onEvent(int wfd, @NotifyEventType int mask, String path) {
// look up our observer, fixing up the map if necessary...
FileObserver observer = null;
synchronized (m_observers) {
WeakReference weak = m_observers.get(wfd);
if (weak != null) { // can happen with lots of events from a dead wfd
observer = (FileObserver) weak.get();
if (observer == null) {
m_observers.remove(wfd);
}
}
}
// ...then call out to the observer without the sync lock held
if (observer != null) {
try {
observer.onEvent(mask, path);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
Log.wtf(LOG_TAG, "Unhandled exception in FileObserver " + observer, throwable);
}
}
}
private native int init();
private native void observe(int fd);
private native void startWatching(int fd, String[] paths,
@NotifyEventType int mask, int[] wfds);
private native void stopWatching(int fd, int[] wfds);
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private static ObserverThread s_observerThread;
static {
s_observerThread = new ObserverThread();
s_observerThread.start();
}
// instance
private final List<File> mFiles;
private int[] mDescriptors;
private final int mMask;
/**
* Equivalent to FileObserver(path, FileObserver.ALL_EVENTS).
*
* @deprecated use {@link #FileObserver(File)} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public FileObserver(String path) {
this(new File(path));
}
/**
* Equivalent to FileObserver(file, FileObserver.ALL_EVENTS).
*/
public FileObserver(@NonNull File file) {
this(Arrays.asList(file));
}
/**
* Equivalent to FileObserver(paths, FileObserver.ALL_EVENTS).
*
* @param files The files or directories to monitor
*/
public FileObserver(@NonNull List<File> files) {
this(files, ALL_EVENTS);
}
/**
* Create a new file observer for a certain file or directory.
* Monitoring does not start on creation! You must call
* {@link #startWatching()} before you will receive events.
*
* @param path The file or directory to monitor
* @param mask The event or events (added together) to watch for
*
* @deprecated use {@link #FileObserver(File, int)} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public FileObserver(String path, @NotifyEventType int mask) {
this(new File(path), mask);
}
/**
* Create a new file observer for a certain file or directory.
* Monitoring does not start on creation! You must call
* {@link #startWatching()} before you will receive events.
*
* @param file The file or directory to monitor
* @param mask The event or events (added together) to watch for
*/
public FileObserver(@NonNull File file, @NotifyEventType int mask) {
this(Arrays.asList(file), mask);
}
/**
* Version of {@link #FileObserver(File, int)} that allows callers to monitor
* multiple files or directories.
*
* @param files The files or directories to monitor
* @param mask The event or events (added together) to watch for
*/
public FileObserver(@NonNull List<File> files, @NotifyEventType int mask) {
mFiles = files;
mMask = mask;
}
protected void finalize() {
stopWatching();
}
/**
* Start watching for events. The monitored file or directory must exist at
* this time, or else no events will be reported (even if it appears later).
* If monitoring is already started, this call has no effect.
*/
public void startWatching() {
if (mDescriptors == null) {
mDescriptors = s_observerThread.startWatching(mFiles, mMask, this);
}
}
/**
* Stop watching for events. Some events may be in process, so events
* may continue to be reported even after this method completes. If
* monitoring is already stopped, this call has no effect.
*/
public void stopWatching() {
if (mDescriptors != null) {
s_observerThread.stopWatching(mDescriptors);
mDescriptors = null;
}
}
/**
* The event handler, which must be implemented by subclasses.
*
* <p class="note">This method is invoked on a special FileObserver thread.
* It runs independently of any threads, so take care to use appropriate
* synchronization! Consider using {@link Handler#post(Runnable)} to shift
* event handling work to the main thread to avoid concurrency problems.</p>
*
* <p>Event handlers must not throw exceptions.</p>
*
* @param event The type of event which happened
* @param path The path, relative to the main monitored file or directory,
* of the file or directory which triggered the event. This value can
* be {@code null} for certain events, such as {@link #MOVE_SELF}.
*/
public abstract void onEvent(int event, @Nullable String path);
}
源码解读及注意事项
相关实现类并不复杂代码也不多这里可以完整看一下学习一下实现原理。
-
ALL_EVENTS 这个事件由 “|”位运算实现位运算相关知识回顾。这里用或运算后面在监听时的回调
onEvent会用到。符号 描述 运算规则 & 与 两个位都为1时结果才为1 | 或 两个位都为0时结果才为0 ^ 异或 两个位相同为0相异为1 ~ 取反 0变11变0 << 左移 各二进位全部左移若干位高位丢弃低位补0 >> 右移 各二进位全部右移若干位对无符号数高位补0有符号数各编译器处理方法不一样有的补符号位算术右移有的补0逻辑右移 -
在
onEvent的回调事件处理中我们得注意 用 "&"来监听否则会出现返回未确定定义的 event type.这里其实不是bug.是我们用错的方式。在
@Override public void onEvent(int event, String path) { Log.d(TAG, "event: " + event); /* event的值是与 0x40000000 进行或运算后的值所以在 case 之前需要先和 FileObserver.ALL_EVENTS进行与运算*/ int e = event & FileObserver.ALL_EVENTS; switch (e) { case FileObserver.CREATE: break; case FileObserver.DELETE: break; } }如果不做 与
&运算,你会得到以下的测试数字以为是 bug. 其实不是。我们了解一下位运算就知道了。
| 类型值 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 1073742080 | “文件夹”的创建(Create)操作 |
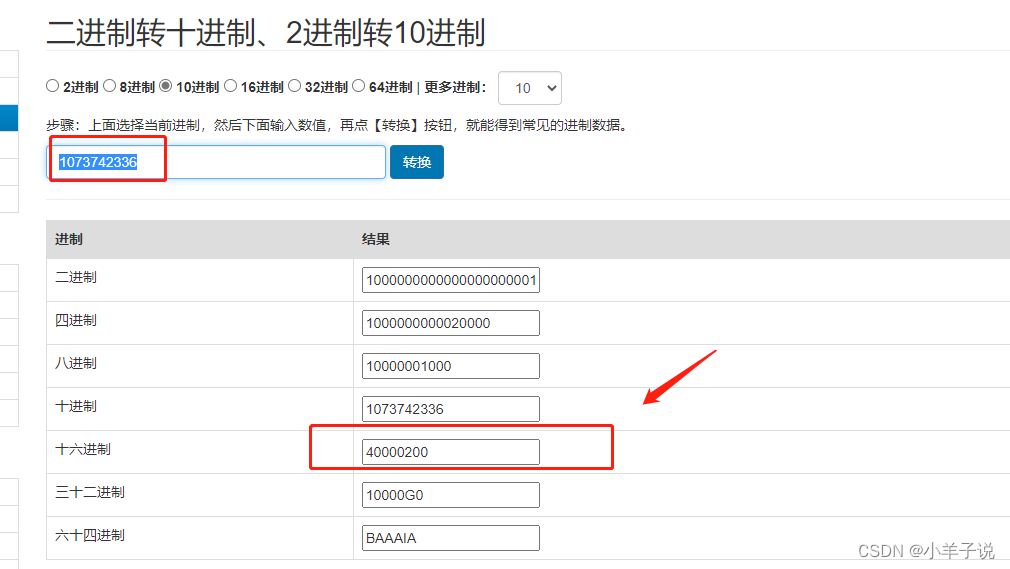
| 1073742336 | “文件夹”的删除(Delete)操作 |
| 1073741888 | “文件夹”的移出MOVE_FROM 操作 |
| 1073741952 | “文件夹”的移入MOVE_TO 操作 |
| 32768 | “文件夹” 的打开操作 OPEN 操作 |
 |
实现示例
FileObserver是一个抽象类使用的时候我们需要自己实现一个类来继承FileObserver。
/**
* <pre>
* @author : JuneYang
* time : 2023/01/20
* desc :
* version: 1.0
* </pre>
*/
public class SDCardFileObServer extends FileObserver {
public static final String TAG = SDCardFileObServer.class.getSimpleName();
public SDCardFileObServer(String path) {
/*
* 这种构造方法是默认监听所有事件的,如果使用 super(String,int)这种构造方法
* 则int参数是要监听的事件类型.
*/
super(path);
}
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.Q)
public SDCardFileObServer(@NonNull File file, int mask) {
super(file, mask);
}
@Override public void onEvent(int event, @Nullable String path) {
//注意点
int e = event & FileObserver.ALL_EVENTS;
switch (e) {
case FileObserver.CREATE:
break;
case FileObserver.DELETE:
break;
case FileObserver.MODIFY:
break;
default:
break;
}
}
// 调用
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "xx/xx/xx";
// 初始化操作
SDCardFileObServer sdCardFileObServer = new SDCardFileObServer(path);
sdCardFileObServer.startWatching();
// 服务结束后关闭监听
sdCardFileObServer.stopWatching();
}
测试用例
以监听某个目录为例,当目录下发生文件的状态变化时测试情况如下
- 拷贝文件时如果文件过大
modify方法会每 50ms 左右回调一次接口因为文件在一直变化直到不再变化为止。 - 替换文件时,会回调
delete和create和modify方法。 - 该路径下的两个文件如果执行拷贝、删除、替换有几个文件就会执行几个文件的几种状态的回调。
- 文件夹删除时也会执行删除
delete回调文件夹新建时会有create回调. - 文件夹合并时不会有回调
Tips: 在项目中由于 FileObserver对象必须保持一个引用确保不被垃圾收集器回收掉否则就不会触发事件。我们可以考虑使用 Service 服务。
也就是说在 Service 中的 Oncreate中初始化startWatching在OnDestory中(stopWatching)。

